Grey market shipping involves the distribution of genuine products through unauthorized channels, often bypassing official retailers and warranty providers, which can lead to varying product quality and uncertain after-sales service. White market shipping refers to the authorized supply chain where products are sold through official distributors, ensuring compliance with regional regulations, validated warranties, and predictable logistics standards. Explore further to understand the implications of each shipping method on supply chain management and customer assurance.
Why it is important
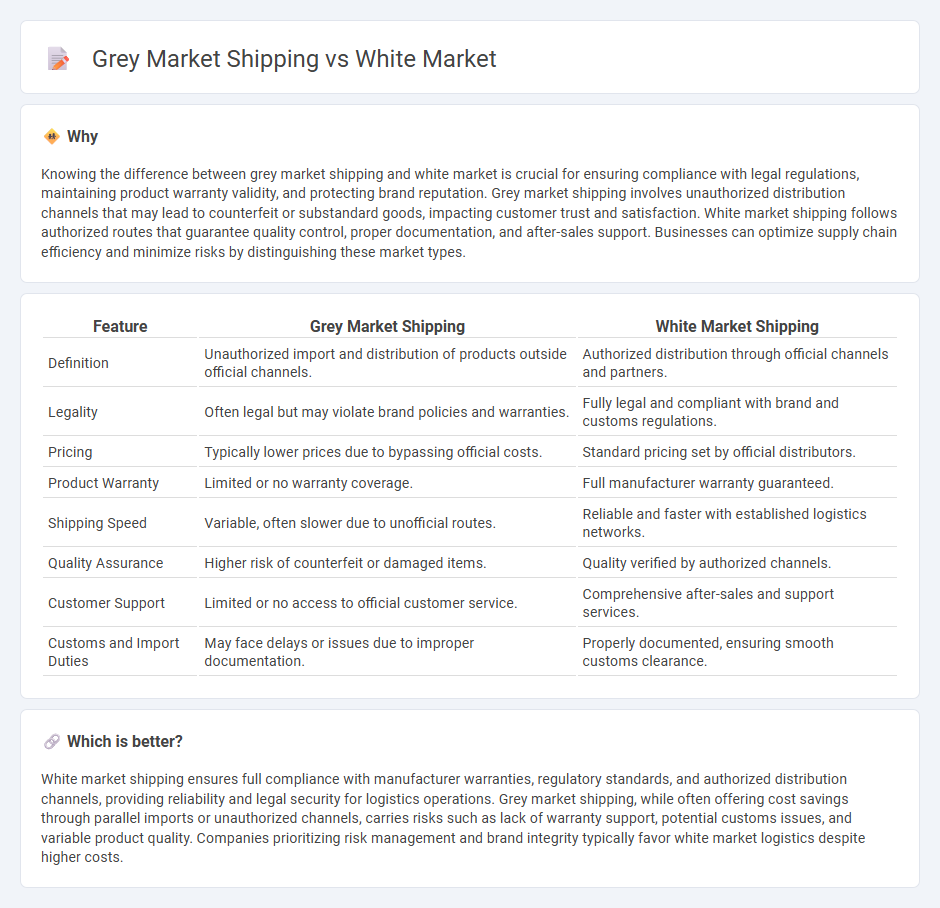
Knowing the difference between grey market shipping and white market is crucial for ensuring compliance with legal regulations, maintaining product warranty validity, and protecting brand reputation. Grey market shipping involves unauthorized distribution channels that may lead to counterfeit or substandard goods, impacting customer trust and satisfaction. White market shipping follows authorized routes that guarantee quality control, proper documentation, and after-sales support. Businesses can optimize supply chain efficiency and minimize risks by distinguishing these market types.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Grey Market Shipping | White Market Shipping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unauthorized import and distribution of products outside official channels. | Authorized distribution through official channels and partners. |
| Legality | Often legal but may violate brand policies and warranties. | Fully legal and compliant with brand and customs regulations. |
| Pricing | Typically lower prices due to bypassing official costs. | Standard pricing set by official distributors. |
| Product Warranty | Limited or no warranty coverage. | Full manufacturer warranty guaranteed. |
| Shipping Speed | Variable, often slower due to unofficial routes. | Reliable and faster with established logistics networks. |
| Quality Assurance | Higher risk of counterfeit or damaged items. | Quality verified by authorized channels. |
| Customer Support | Limited or no access to official customer service. | Comprehensive after-sales and support services. |
| Customs and Import Duties | May face delays or issues due to improper documentation. | Properly documented, ensuring smooth customs clearance. |
Which is better?
White market shipping ensures full compliance with manufacturer warranties, regulatory standards, and authorized distribution channels, providing reliability and legal security for logistics operations. Grey market shipping, while often offering cost savings through parallel imports or unauthorized channels, carries risks such as lack of warranty support, potential customs issues, and variable product quality. Companies prioritizing risk management and brand integrity typically favor white market logistics despite higher costs.
Connection
Grey market shipping involves the unauthorized distribution of goods outside official supply chains, often bypassing manufacturer controls, while white market logistics adhere strictly to authorized channels and regulatory compliance. Both markets intersect in global supply chains where discrepancies between authorized and unauthorized shipments affect inventory accuracy, pricing strategies, and brand integrity. Understanding their connection helps optimize risk management and fraud detection in logistics operations.
Key Terms
Authorized Distribution Channels
Authorized distribution channels ensure that products shipped through the white market are genuine, meet manufacturer standards, and come with valid warranties. Grey market shipping involves selling genuine products outside authorized channels, risking lack of manufacturer support and potential legal issues. Explore key differences and benefits of authorized distribution channels to safeguard your purchases.
Parallel Importation
Parallel importation involves the legal import of genuine products through unauthorized channels, which distinguishes it from the white market where products are distributed directly by the manufacturer or authorized dealers. Grey market shipping offers competitive pricing by bypassing official distribution networks but may lack manufacturer warranties and after-sales service associated with white market goods. Explore further to understand the implications of parallel importation on product authenticity and consumer rights.
Regulatory Compliance
White market shipping adheres strictly to regulatory compliance, ensuring all products meet legal standards, import regulations, and safety certifications required by authorities. Grey market shipping operates outside authorized distribution channels, often bypassing key regulatory requirements, which can lead to legal risks, product authenticity issues, and warranty voids. Explore more to understand how regulatory frameworks impact white and grey market shipping practices.
Source and External Links
white market - Wiktionary - The white market is defined as the legal, official, or intended market for goods and services, distinguished from the black market and grey market.
WHITE MARKET Definition & Meaning - Dictionary.com - The white market refers to the buying and selling of goods or coupons within a legal and regulated system, often contrasted with a black market.
white.market - white.market is a P2P platform specialized in trading CS2 skins with options for withdrawing funds in national currencies and cryptocurrencies, emphasizing quick verification and lack of trading bots.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com