Urban warehouses are strategically located within city limits to enable faster delivery and reduced transportation costs for last-mile logistics, focusing primarily on storage and immediate order fulfillment. Distribution centers operate on a larger scale, serving as hubs for receiving, sorting, and shipping goods to various locations, emphasizing inventory management and bulk distribution. Discover key differences and optimize your supply chain by exploring the roles of urban warehouses versus distribution centers.
Why it is important
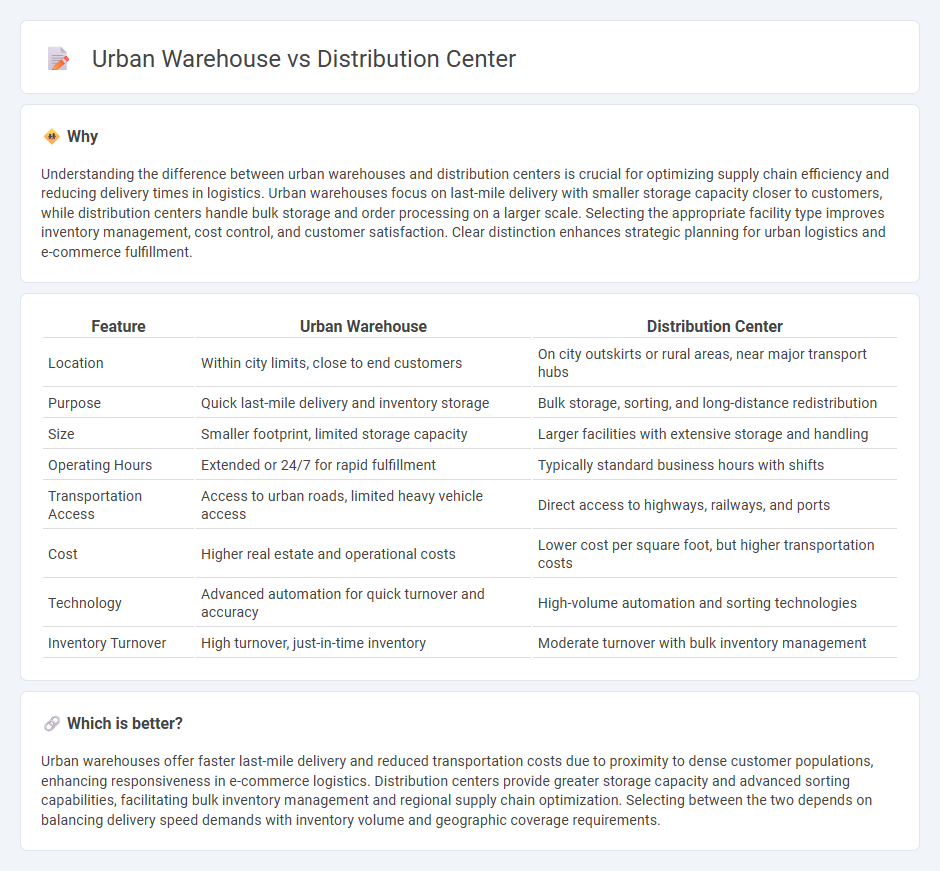
Understanding the difference between urban warehouses and distribution centers is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing delivery times in logistics. Urban warehouses focus on last-mile delivery with smaller storage capacity closer to customers, while distribution centers handle bulk storage and order processing on a larger scale. Selecting the appropriate facility type improves inventory management, cost control, and customer satisfaction. Clear distinction enhances strategic planning for urban logistics and e-commerce fulfillment.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Urban Warehouse | Distribution Center |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Within city limits, close to end customers | On city outskirts or rural areas, near major transport hubs |
| Purpose | Quick last-mile delivery and inventory storage | Bulk storage, sorting, and long-distance redistribution |
| Size | Smaller footprint, limited storage capacity | Larger facilities with extensive storage and handling |
| Operating Hours | Extended or 24/7 for rapid fulfillment | Typically standard business hours with shifts |
| Transportation Access | Access to urban roads, limited heavy vehicle access | Direct access to highways, railways, and ports |
| Cost | Higher real estate and operational costs | Lower cost per square foot, but higher transportation costs |
| Technology | Advanced automation for quick turnover and accuracy | High-volume automation and sorting technologies |
| Inventory Turnover | High turnover, just-in-time inventory | Moderate turnover with bulk inventory management |
Which is better?
Urban warehouses offer faster last-mile delivery and reduced transportation costs due to proximity to dense customer populations, enhancing responsiveness in e-commerce logistics. Distribution centers provide greater storage capacity and advanced sorting capabilities, facilitating bulk inventory management and regional supply chain optimization. Selecting between the two depends on balancing delivery speed demands with inventory volume and geographic coverage requirements.
Connection
Urban warehouses and distribution centers are integral components of modern logistics networks, facilitating efficient last-mile delivery in densely populated areas. Positioned strategically near urban demand hubs, these facilities minimize transit times and reduce transportation costs by enabling quick sorting, storage, and dispatch of goods. Advanced technologies like real-time inventory tracking and automated distribution systems enhance operational connectivity and responsiveness between warehouses and distribution centers.
Key Terms
Location Strategy
Distribution centers are typically located on the outskirts of cities to optimize large-scale logistics and reduce transportation costs, while urban warehouses are situated within city centers to ensure rapid last-mile delivery and better customer accessibility. The strategic placement of a distribution center prioritizes bulk storage capacity and efficient inbound and outbound freight handling, whereas urban warehouses emphasize proximity to end-consumers and flexible inventory management. Explore how location strategy impacts supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction in your logistics planning.
Inventory Management
Distribution centers prioritize bulk inventory storage with advanced automated systems to optimize order fulfillment and reduce lead times. Urban warehouses focus on smaller, strategically located stock for rapid replenishment and last-mile delivery efficiency, supporting just-in-time inventory practices. Explore how integrating both can enhance your supply chain agility and inventory control.
Last-Mile Delivery
Distribution centers are large-scale facilities designed for bulk storage and efficient processing of goods, typically located on city outskirts to support long-haul transportation. Urban warehouses, by contrast, are smaller facilities situated within or near city centers to facilitate rapid last-mile delivery, reducing transit time and enhancing customer satisfaction. Explore how these strategic differences impact delivery speed, costs, and logistics optimization in last-mile fulfillment.
Source and External Links
What Is a Distribution Center and How Do They Work? - A distribution center is a facility that receives goods, stores them temporarily, manages inventory, processes orders, and ships products to resellers or end users in a timely manner.
Distribution Centers Explained - NetSuite - Distribution centers store, pick, pack, and ship finished goods closer to delivery locations to quickly fulfill customer orders, combining warehouse and fulfillment practices supported by technology.
Logistics Distribution Center (DC): What is it and its functions? - A distribution center is a logistics facility designed to receive, store, and ship goods, serving as an intermediary in the supply chain by redistributing products to wholesalers, retailers, or warehouses.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com