Empty miles reduction focuses on minimizing the distance trucks travel without cargo, thereby reducing fuel consumption and operational costs. Backhauling involves transporting goods on the return trip of a delivery route to maximize load efficiency and decrease empty miles. Explore more strategies to optimize logistics and enhance supply chain sustainability.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between empty miles reduction and backhauling is crucial in logistics because empty miles refer to non-revenue generating travel with unloaded trucks, significantly increasing operational costs and environmental impact. Backhauling involves using trucks returning from delivery with freight, maximizing asset utilization and reducing empty miles. Efficiently distinguishing and implementing both strategies enhances route optimization, reduces fuel consumption, and lowers carbon emissions, contributing to sustainable supply chain management. Logistics companies that master these concepts can improve profitability and competitive advantage by minimizing wasted resources and maximizing load efficiency.
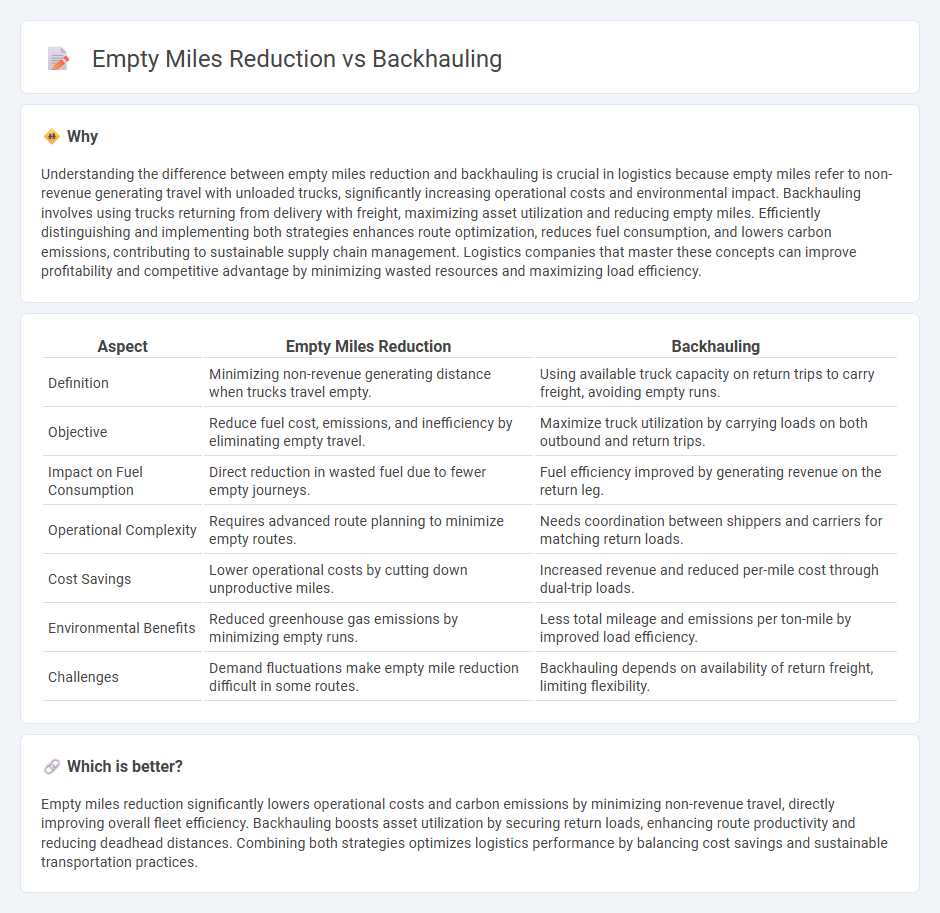
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Empty Miles Reduction | Backhauling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Minimizing non-revenue generating distance when trucks travel empty. | Using available truck capacity on return trips to carry freight, avoiding empty runs. |
| Objective | Reduce fuel cost, emissions, and inefficiency by eliminating empty travel. | Maximize truck utilization by carrying loads on both outbound and return trips. |
| Impact on Fuel Consumption | Direct reduction in wasted fuel due to fewer empty journeys. | Fuel efficiency improved by generating revenue on the return leg. |
| Operational Complexity | Requires advanced route planning to minimize empty routes. | Needs coordination between shippers and carriers for matching return loads. |
| Cost Savings | Lower operational costs by cutting down unproductive miles. | Increased revenue and reduced per-mile cost through dual-trip loads. |
| Environmental Benefits | Reduced greenhouse gas emissions by minimizing empty runs. | Less total mileage and emissions per ton-mile by improved load efficiency. |
| Challenges | Demand fluctuations make empty mile reduction difficult in some routes. | Backhauling depends on availability of return freight, limiting flexibility. |
Which is better?
Empty miles reduction significantly lowers operational costs and carbon emissions by minimizing non-revenue travel, directly improving overall fleet efficiency. Backhauling boosts asset utilization by securing return loads, enhancing route productivity and reducing deadhead distances. Combining both strategies optimizes logistics performance by balancing cost savings and sustainable transportation practices.
Connection
Empty miles reduction directly improves logistics efficiency by minimizing non-revenue travel, while backhauling optimizes freight movement by utilizing return trips to carry goods. Implementing backhauling strategies significantly cuts empty miles, reduces fuel consumption, and lowers transportation costs. Together, these methods enhance supply chain sustainability and increase asset utilization in transportation management.
Key Terms
Route Optimization
Backhauling enhances route optimization by utilizing return trips to carry freight, reducing empty miles and operational costs. Empty miles reduction specifically targets minimizing unladen vehicle travel, improving fuel efficiency and lowering carbon emissions. Explore advanced route optimization strategies to maximize backhauling benefits and drive sustainable logistics performance.
Load Matching
Backhauling improves logistics efficiency by transporting goods on return trips, minimizing empty miles and reducing fuel costs. Load matching platforms connect shippers and carriers, optimizing truck capacity utilization and further decreasing unproductive travel distances. Explore innovative load matching solutions to enhance your backhaul strategy and cut down on empty miles effectively.
Fleet Utilization
Backhauling improves fleet utilization by transporting goods on return trips, reducing empty miles and maximizing asset efficiency. Empty miles reduction directly addresses inefficiencies in fleet logistics, lowering fuel costs and environmental impact through optimized routing. Explore advanced strategies to enhance fleet productivity and minimize operational waste.
Source and External Links
What is backhauling? - In trucking, backhauling means planning roundtrip hauls so trucks carry goods both ways, improving vehicle utilization, reducing empty trips, saving fuel and cutting costs while boosting operational efficiency.
What Is Backhaul Trucking: Everything You Need To Know - Backhaul trucking is a reverse logistics strategy that hauls loads during a truck's return to its origin to reduce unprofitable empty miles, improving revenue for shippers and carriers and promoting an eco-friendly supply chain through internal or external backhaul operations.
What is Backhaul? Logistics Glossary - Backhaul involves transporting freight from point B back to its origin A to eliminate empty truck miles, helping carriers avoid losses from overhead costs on unloaded return trips while improving overall supply chain efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com