Urban logistics hubs streamline last-mile delivery by centralizing inventory and distribution within city limits, reducing transport times and emissions. Dark stores operate as localized fulfillment centers without customer access, enhancing speed and efficiency for e-commerce orders in dense urban areas. Explore how these models transform urban supply chains and elevate delivery performance.
Why it is important
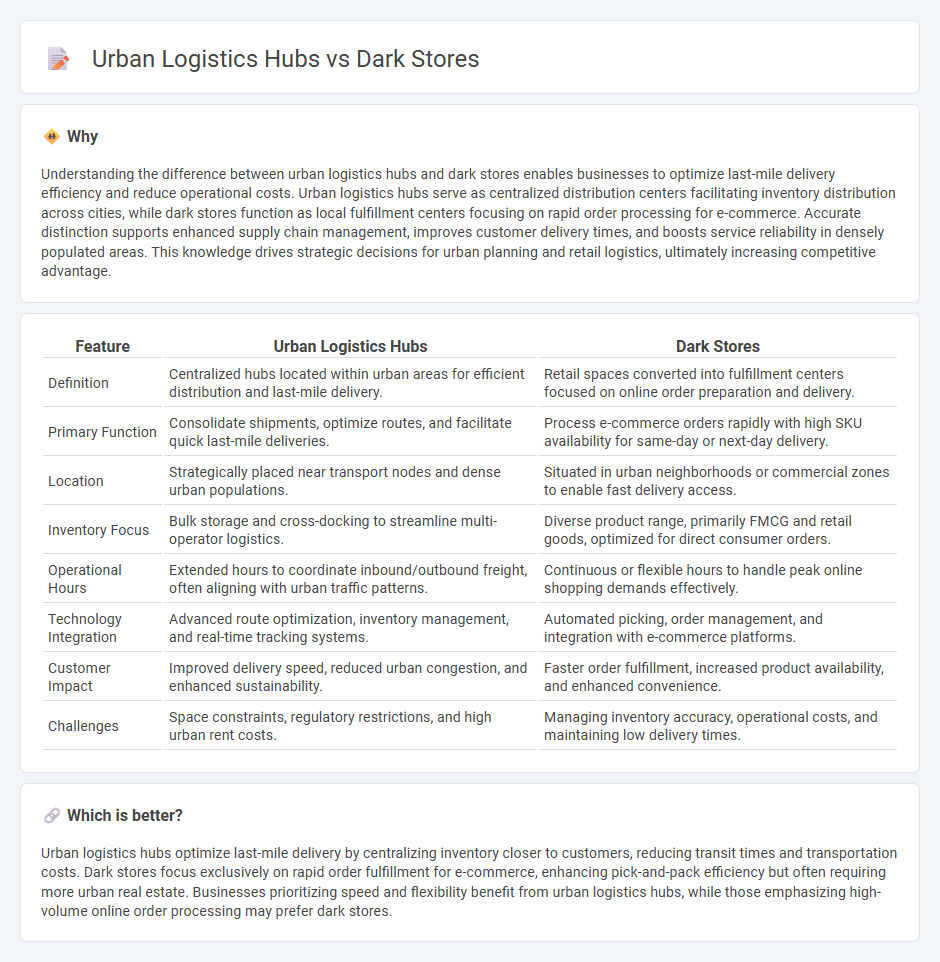
Understanding the difference between urban logistics hubs and dark stores enables businesses to optimize last-mile delivery efficiency and reduce operational costs. Urban logistics hubs serve as centralized distribution centers facilitating inventory distribution across cities, while dark stores function as local fulfillment centers focusing on rapid order processing for e-commerce. Accurate distinction supports enhanced supply chain management, improves customer delivery times, and boosts service reliability in densely populated areas. This knowledge drives strategic decisions for urban planning and retail logistics, ultimately increasing competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Urban Logistics Hubs | Dark Stores |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Centralized hubs located within urban areas for efficient distribution and last-mile delivery. | Retail spaces converted into fulfillment centers focused on online order preparation and delivery. |
| Primary Function | Consolidate shipments, optimize routes, and facilitate quick last-mile deliveries. | Process e-commerce orders rapidly with high SKU availability for same-day or next-day delivery. |
| Location | Strategically placed near transport nodes and dense urban populations. | Situated in urban neighborhoods or commercial zones to enable fast delivery access. |
| Inventory Focus | Bulk storage and cross-docking to streamline multi-operator logistics. | Diverse product range, primarily FMCG and retail goods, optimized for direct consumer orders. |
| Operational Hours | Extended hours to coordinate inbound/outbound freight, often aligning with urban traffic patterns. | Continuous or flexible hours to handle peak online shopping demands effectively. |
| Technology Integration | Advanced route optimization, inventory management, and real-time tracking systems. | Automated picking, order management, and integration with e-commerce platforms. |
| Customer Impact | Improved delivery speed, reduced urban congestion, and enhanced sustainability. | Faster order fulfillment, increased product availability, and enhanced convenience. |
| Challenges | Space constraints, regulatory restrictions, and high urban rent costs. | Managing inventory accuracy, operational costs, and maintaining low delivery times. |
Which is better?
Urban logistics hubs optimize last-mile delivery by centralizing inventory closer to customers, reducing transit times and transportation costs. Dark stores focus exclusively on rapid order fulfillment for e-commerce, enhancing pick-and-pack efficiency but often requiring more urban real estate. Businesses prioritizing speed and flexibility benefit from urban logistics hubs, while those emphasizing high-volume online order processing may prefer dark stores.
Connection
Urban logistics hubs and dark stores are interconnected through their strategic roles in last-mile delivery, optimizing the speed and efficiency of e-commerce order fulfillment within dense city environments. Urban logistics hubs serve as consolidation points where goods are received, sorted, and dispatched, while dark stores function as inventory nodes designed specifically for rapid online order processing without traditional retail customers. The synergy between these facilities reduces delivery times, lowers transportation costs, and enhances supply chain responsiveness in congested urban areas.
Key Terms
Fulfillment Center
Dark stores streamline last-mile delivery by serving as localized fulfillment centers, optimizing inventory access close to urban demand hotspots. Urban logistics hubs enhance efficiency by centralizing operations and leveraging proximity to transport infrastructure, reducing delivery times and costs. Explore how these fulfillment center models transform urban e-commerce logistics for faster, more reliable order fulfillment.
Last-Mile Delivery
Dark stores strategically located in dense urban areas optimize last-mile delivery by serving as mini-warehouses that enable rapid order fulfillment and reduce delivery times. Urban logistics hubs act as centralized distribution points integrating multiple transport modes to enhance efficiency and manage urban freight flow effectively. Explore the differences and benefits of these solutions to master urban last-mile delivery strategies.
Micro-fulfillment
Dark stores function as specialized retail outlets optimized for e-commerce order fulfillment in dense urban areas, leveraging micro-fulfillment technologies such as automated storage and robotic picking to accelerate delivery speeds. Urban logistics hubs serve as central nodes facilitating last-mile distribution, integrating micro-fulfillment systems to enhance inventory management and reduce delivery times within metropolitan regions. Explore the evolving trends and operational efficiencies driving the adoption of micro-fulfillment in both dark stores and urban logistics hubs.
Source and External Links
What Is a Dark Store? - NetSuite - Dark stores are brick-and-mortar locations converted to fulfill online orders, often located in suburbs or city outskirts, designed to simplify online shopping fulfillment through warehouse-like setups with pickers or automation.
Dark stores in retail: Concept, benefits, challenges, strategies 2025 - Dark stores function like warehouses optimized for picking and packing orders exclusively for online shopping, growing in popularity due to eCommerce expansion and offered benefits like cost-efficiency and rapid delivery.
Dark store - Wikipedia - A dark store is a retail outlet or distribution center that exists solely for online order fulfillment, originated in the UK and now widely used globally, enabling click-and-collect or rapid home deliveries.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com