Shadow fleets operate covertly outside official channels, often evading regulations and posing risks to supply chain transparency and security. Official fleets adhere to established standards and legal frameworks, ensuring compliance, accountability, and reliable delivery performance. Explore the critical differences and implications of shadow fleets versus official fleets in modern logistics.
Why it is important
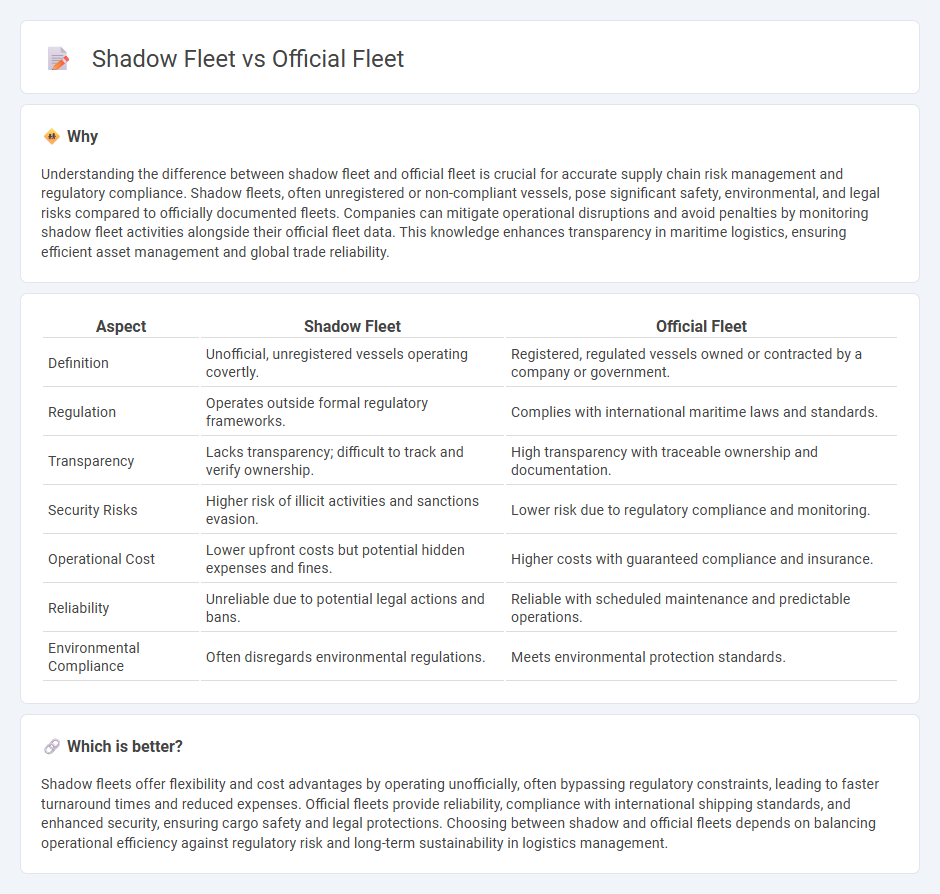
Understanding the difference between shadow fleet and official fleet is crucial for accurate supply chain risk management and regulatory compliance. Shadow fleets, often unregistered or non-compliant vessels, pose significant safety, environmental, and legal risks compared to officially documented fleets. Companies can mitigate operational disruptions and avoid penalties by monitoring shadow fleet activities alongside their official fleet data. This knowledge enhances transparency in maritime logistics, ensuring efficient asset management and global trade reliability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Shadow Fleet | Official Fleet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unofficial, unregistered vessels operating covertly. | Registered, regulated vessels owned or contracted by a company or government. |
| Regulation | Operates outside formal regulatory frameworks. | Complies with international maritime laws and standards. |
| Transparency | Lacks transparency; difficult to track and verify ownership. | High transparency with traceable ownership and documentation. |
| Security Risks | Higher risk of illicit activities and sanctions evasion. | Lower risk due to regulatory compliance and monitoring. |
| Operational Cost | Lower upfront costs but potential hidden expenses and fines. | Higher costs with guaranteed compliance and insurance. |
| Reliability | Unreliable due to potential legal actions and bans. | Reliable with scheduled maintenance and predictable operations. |
| Environmental Compliance | Often disregards environmental regulations. | Meets environmental protection standards. |
Which is better?
Shadow fleets offer flexibility and cost advantages by operating unofficially, often bypassing regulatory constraints, leading to faster turnaround times and reduced expenses. Official fleets provide reliability, compliance with international shipping standards, and enhanced security, ensuring cargo safety and legal protections. Choosing between shadow and official fleets depends on balancing operational efficiency against regulatory risk and long-term sustainability in logistics management.
Connection
The shadow fleet operates alongside the official fleet by utilizing aging or unregistered vessels that bypass regulatory frameworks, enabling companies to meet demand spikes and reduce operational costs. This parallel operation affects global supply chain efficiency and maritime security, as shadow fleet activities often escape standard monitoring and compliance checks. Integrating data from both fleets through advanced tracking technologies enhances logistics transparency and risk management in international shipping.
Key Terms
Ownership
Official fleets are directly owned and operated by governments or corporations, ensuring full control over assets and compliance with regulations. Shadow fleets consist of vessels that are nominally owned by third parties, often obscuring true ownership to bypass sanctions or regulatory scrutiny. Explore how ownership dynamics impact maritime security and global trade flows.
Regulation
Official fleets operate under strict regulatory frameworks established by governments and maritime organizations, ensuring compliance with safety, environmental, and labor standards. Shadow fleets, often unregulated or operating in legal gray zones, evade these standards, raising concerns about maritime security, human rights, and environmental protection. Explore the crucial differences in regulation and their global impact to understand the challenges posed by shadow fleets.
Transparency
Official fleets consist of vessels registered with transparent ownership and regulatory compliance, ensuring traceability and accountability in maritime operations. Shadow fleets operate with obscured ownership and minimal regulatory oversight, posing risks to safety, security, and environmental standards due to their hidden nature. Explore in-depth insights on how transparency impacts maritime governance and security.
Source and External Links
Fleet Management | Department of Energy - The DOE fleet management program covers agency owned, GSA leased, and commercially leased vehicles including cars, trucks, and buses, overseeing vehicle lifecycle management and database tracking systems.
GSAFleet.gov: Home - GSA Fleet offers federal agencies a comprehensive service for leasing, buying, and renting vehicles, acting as a centralized fleet management platform.
Fleet management | GSA - GSA Fleet provides federal agencies with safe, reliable, and cost-effective vehicle solutions tailored to federal transportation needs and regulations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com