Last mile delivery focuses on transporting goods directly from distribution centers to the final customer, emphasizing speed and efficiency. Crowdsourced delivery leverages a network of independent drivers or local couriers to complete deliveries, often reducing costs and increasing flexibility. Discover more about how these delivery models transform logistics and meet evolving consumer demands.
Why it is important
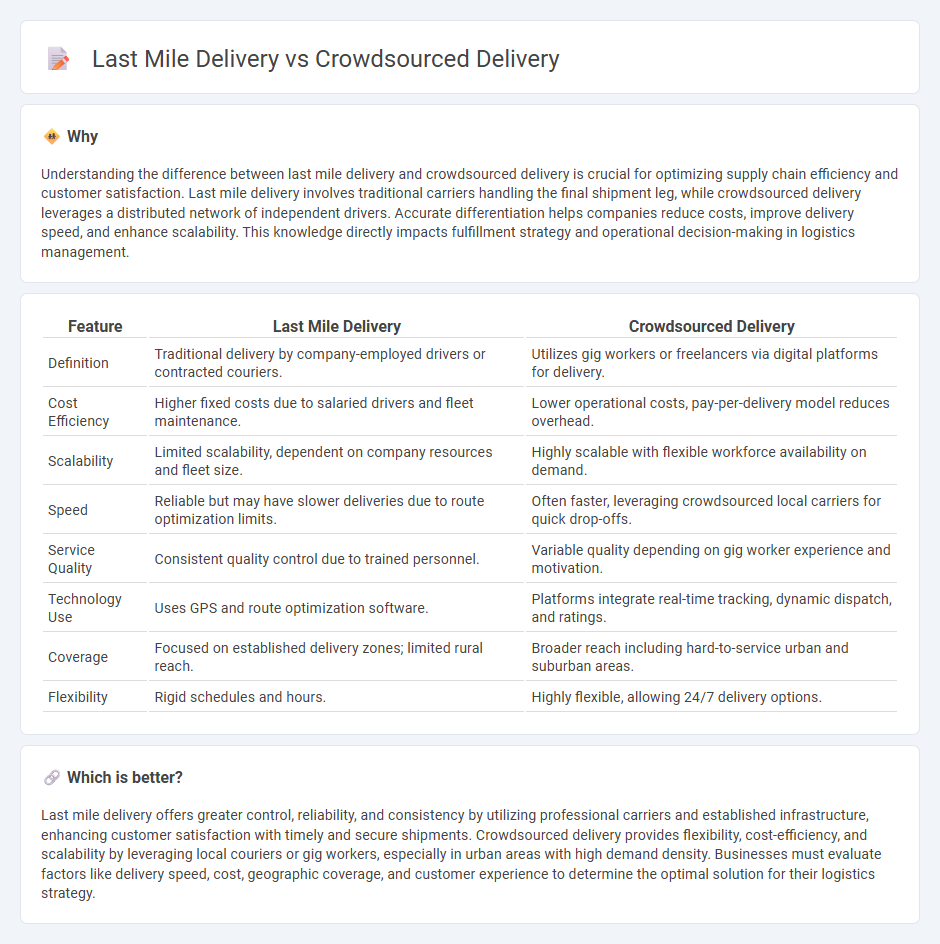
Understanding the difference between last mile delivery and crowdsourced delivery is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction. Last mile delivery involves traditional carriers handling the final shipment leg, while crowdsourced delivery leverages a distributed network of independent drivers. Accurate differentiation helps companies reduce costs, improve delivery speed, and enhance scalability. This knowledge directly impacts fulfillment strategy and operational decision-making in logistics management.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Last Mile Delivery | Crowdsourced Delivery |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional delivery by company-employed drivers or contracted couriers. | Utilizes gig workers or freelancers via digital platforms for delivery. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher fixed costs due to salaried drivers and fleet maintenance. | Lower operational costs, pay-per-delivery model reduces overhead. |
| Scalability | Limited scalability, dependent on company resources and fleet size. | Highly scalable with flexible workforce availability on demand. |
| Speed | Reliable but may have slower deliveries due to route optimization limits. | Often faster, leveraging crowdsourced local carriers for quick drop-offs. |
| Service Quality | Consistent quality control due to trained personnel. | Variable quality depending on gig worker experience and motivation. |
| Technology Use | Uses GPS and route optimization software. | Platforms integrate real-time tracking, dynamic dispatch, and ratings. |
| Coverage | Focused on established delivery zones; limited rural reach. | Broader reach including hard-to-service urban and suburban areas. |
| Flexibility | Rigid schedules and hours. | Highly flexible, allowing 24/7 delivery options. |
Which is better?
Last mile delivery offers greater control, reliability, and consistency by utilizing professional carriers and established infrastructure, enhancing customer satisfaction with timely and secure shipments. Crowdsourced delivery provides flexibility, cost-efficiency, and scalability by leveraging local couriers or gig workers, especially in urban areas with high demand density. Businesses must evaluate factors like delivery speed, cost, geographic coverage, and customer experience to determine the optimal solution for their logistics strategy.
Connection
Last mile delivery focuses on the final step of transporting goods from a warehouse to the customer's doorstep, often representing the most complex and costly part of the logistics process. Crowdsourced delivery leverages a network of independent drivers or couriers to efficiently fulfill these last mile deliveries, increasing flexibility and reducing delivery times. This connection enhances scalability for logistics companies while meeting growing consumer demands for fast and reliable service.
Key Terms
**Crowdsourced Delivery:**
Crowdsourced delivery leverages a network of independent drivers or gig workers who use their own vehicles to complete local deliveries, offering flexibility and scalability compared to traditional last mile delivery. This model reduces operational costs and allows for faster dispatch times by tapping into the existing community, enhancing delivery efficiency in urban and suburban areas. Explore how crowdsourced delivery transforms logistics with innovative tech and community-driven solutions.
Gig Workforce
Crowdsourced delivery leverages a flexible gig workforce, enabling businesses to scale operations rapidly by using independent contractors, whereas traditional last mile delivery relies heavily on dedicated drivers and structured logistics networks. The gig economy's emphasis on app-based task allocation offers efficiency and cost savings but raises concerns about labor rights and service consistency. Explore the evolving dynamics of gig workforce integration in last mile delivery to understand its impact on the future of urban logistics.
Real-time Matching
Crowdsourced delivery leverages real-time matching algorithms to connect nearby couriers with customer orders instantly, maximizing efficiency and reducing wait times. Last mile delivery traditionally relies on pre-assigned routes and fixed schedules, often lacking the dynamic allocation benefits of real-time data integration. Explore how real-time matching revolutionizes delivery logistics by bridging the gap between demand and supply efficiently.
Source and External Links
Crowdsourced Delivery: Logistics Guide | Fulfill.com Glossary - Crowdsourced delivery, or crowdshipping, is a fulfillment method using independent drivers who pick up and deliver packages via a digital platform, offering flexibility for drivers and real-time tracking for customers.
What Is Crowdsourced Delivery? Benefits, Trends, and Examples - This method employs the general public as couriers through technology platforms, helping businesses handle surges in e-commerce orders, with well-known examples including UberEats, DoorDash, and Amazon Flex.
What Is Crowdsourced Delivery? Benefits & Key Use Cases - Curri - Crowdsourced delivery connects businesses with freelance drivers using their own vehicles to reduce delivery costs and accommodate a variety of package types, emphasizing efficiency and sustainability through flexible vehicle matching.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com