Urban consolidation centres reduce city logistics costs and environmental impact by centralizing deliveries from multiple suppliers, streamlining last-mile distribution to retailers. Dark stores function as localized fulfillment hubs focused on rapid online order processing and delivery, enhancing e-commerce efficiency in densely populated urban areas. Explore the distinct roles of urban consolidation centres and dark stores in transforming urban logistics.
Why it is important
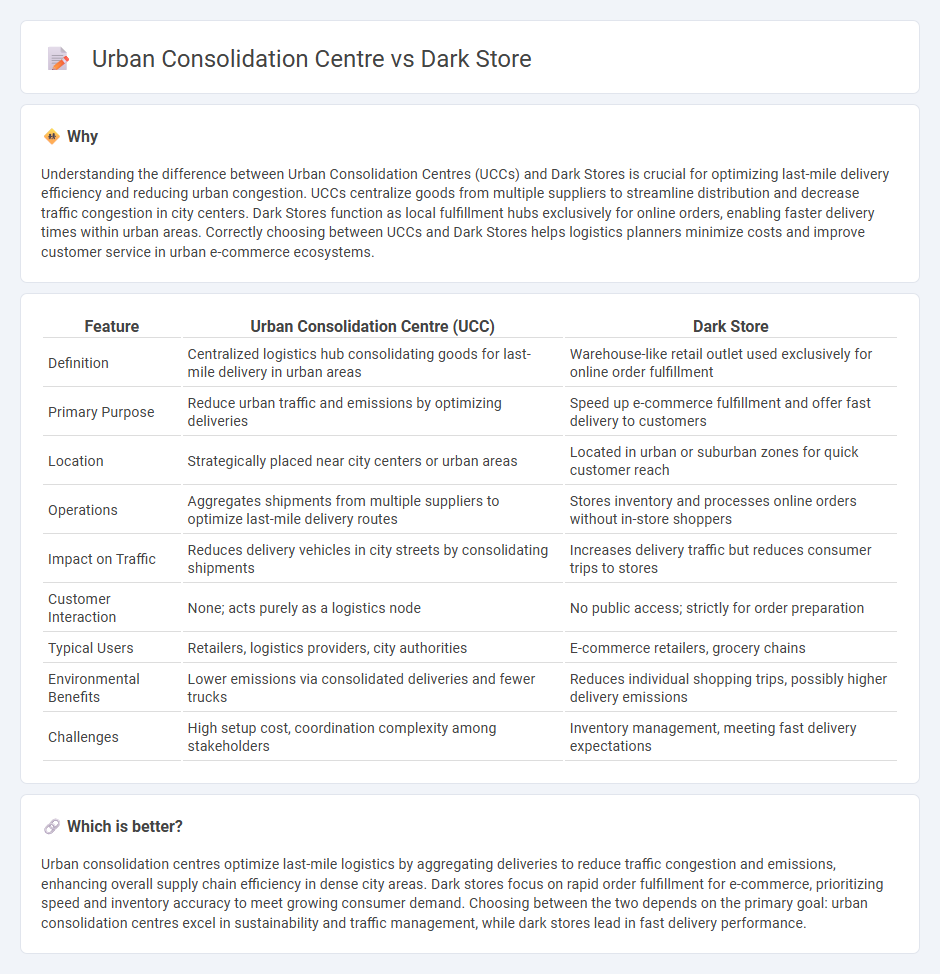
Understanding the difference between Urban Consolidation Centres (UCCs) and Dark Stores is crucial for optimizing last-mile delivery efficiency and reducing urban congestion. UCCs centralize goods from multiple suppliers to streamline distribution and decrease traffic congestion in city centers. Dark Stores function as local fulfillment hubs exclusively for online orders, enabling faster delivery times within urban areas. Correctly choosing between UCCs and Dark Stores helps logistics planners minimize costs and improve customer service in urban e-commerce ecosystems.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Urban Consolidation Centre (UCC) | Dark Store |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Centralized logistics hub consolidating goods for last-mile delivery in urban areas | Warehouse-like retail outlet used exclusively for online order fulfillment |
| Primary Purpose | Reduce urban traffic and emissions by optimizing deliveries | Speed up e-commerce fulfillment and offer fast delivery to customers |
| Location | Strategically placed near city centers or urban areas | Located in urban or suburban zones for quick customer reach |
| Operations | Aggregates shipments from multiple suppliers to optimize last-mile delivery routes | Stores inventory and processes online orders without in-store shoppers |
| Impact on Traffic | Reduces delivery vehicles in city streets by consolidating shipments | Increases delivery traffic but reduces consumer trips to stores |
| Customer Interaction | None; acts purely as a logistics node | No public access; strictly for order preparation |
| Typical Users | Retailers, logistics providers, city authorities | E-commerce retailers, grocery chains |
| Environmental Benefits | Lower emissions via consolidated deliveries and fewer trucks | Reduces individual shopping trips, possibly higher delivery emissions |
| Challenges | High setup cost, coordination complexity among stakeholders | Inventory management, meeting fast delivery expectations |
Which is better?
Urban consolidation centres optimize last-mile logistics by aggregating deliveries to reduce traffic congestion and emissions, enhancing overall supply chain efficiency in dense city areas. Dark stores focus on rapid order fulfillment for e-commerce, prioritizing speed and inventory accuracy to meet growing consumer demand. Choosing between the two depends on the primary goal: urban consolidation centres excel in sustainability and traffic management, while dark stores lead in fast delivery performance.
Connection
Urban consolidation centres optimize last-mile logistics by aggregating shipments from multiple suppliers near city centers, reducing traffic congestion and emissions. Dark stores, as localized fulfillment hubs, leverage these centres to streamline rapid order processing and delivery within urban areas. The integration of dark stores with urban consolidation centres enhances efficiency in e-commerce logistics by minimizing delivery times and operational costs.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Dark stores optimize inventory management by acting as localized fulfillment hubs exclusively for online orders, enabling real-time stock tracking and faster replenishment cycles. Urban consolidation centres streamline inventory flow by aggregating shipments from multiple suppliers, reducing stock redundancy and improving delivery efficiency within dense city areas. Explore more to understand how each model transforms urban logistics and inventory control.
Last-Mile Delivery
Dark stores streamline last-mile delivery by serving as localized warehouses optimized for e-commerce order fulfillment, accelerating delivery times and reducing logistics costs in urban areas. Urban consolidation centres aggregate shipments from multiple suppliers, minimizing last-mile delivery trips and cutting emissions while enhancing delivery efficiency. Explore the distinctions and benefits of both models for optimizing your last-mile delivery strategy.
Order Fulfillment
Dark stores function as localized warehouses designed solely for order fulfillment, enabling rapid processing and delivery of e-commerce orders, often equipped with tailored inventory and streamlined picking systems. Urban consolidation centres centralize goods from multiple suppliers to optimize last-mile deliveries, reducing urban traffic congestion and emissions while improving delivery efficiency in densely populated areas. Explore how these innovative logistics models revolutionize urban order fulfillment and transform supply chain dynamics.
Source and External Links
What is a Dark Store? How to Make it Work for You - A dark store is a brick-and-mortar location converted into a fulfillment center not open to customers, enabling online order fulfillment and faster delivery or pickup options.
Dark store - A dark store is a retail outlet or distribution center exclusively for online shopping, typically serving as a click-and-collect point or an order fulfillment platform, with origins in the UK and growing popularity worldwide.
What Is a Dark Store? - Dark stores are repurposed physical stores operating as fulfillment depots for online purchases, enhancing delivery and pickup convenience and using automation to handle complex logistics efficiently.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com