Cold chain management ensures temperature-sensitive products maintain optimal conditions during storage and transportation, preserving quality and safety. Cross-docking streamlines supply chain operations by transferring goods directly from inbound to outbound transportation, minimizing storage time and reducing handling costs. Explore the key differences and benefits of cold chain management versus cross-docking to optimize your logistics strategy.
Why it is important
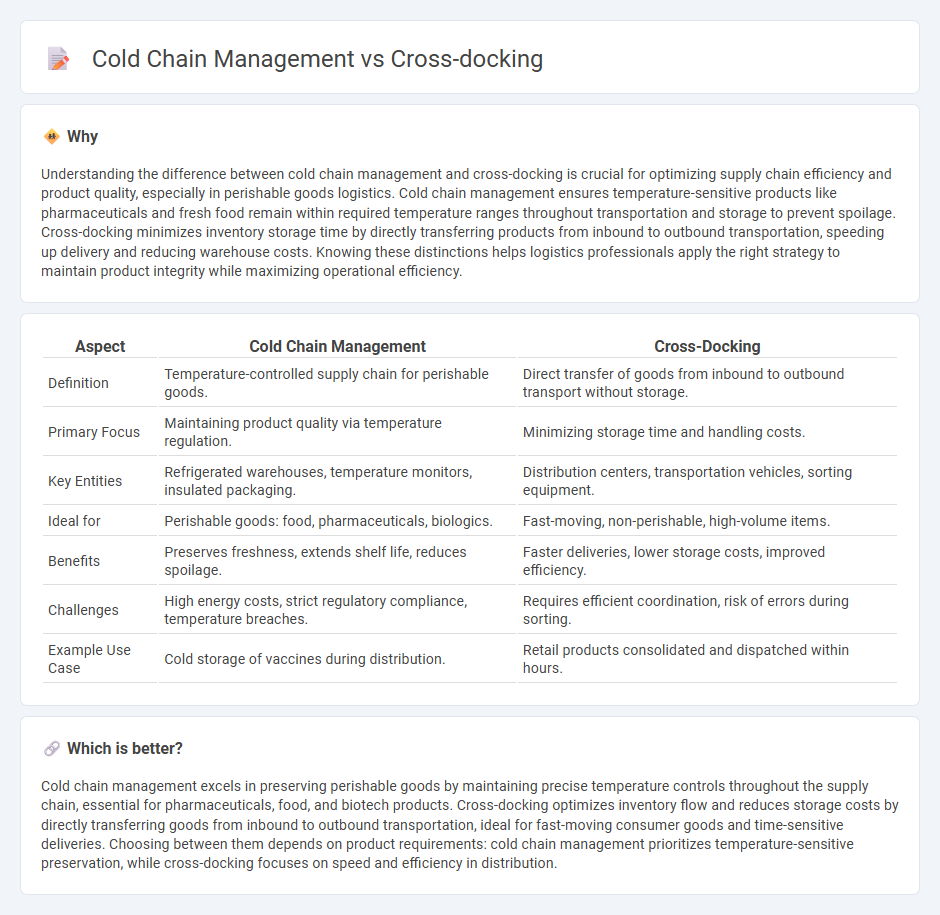
Understanding the difference between cold chain management and cross-docking is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and product quality, especially in perishable goods logistics. Cold chain management ensures temperature-sensitive products like pharmaceuticals and fresh food remain within required temperature ranges throughout transportation and storage to prevent spoilage. Cross-docking minimizes inventory storage time by directly transferring products from inbound to outbound transportation, speeding up delivery and reducing warehouse costs. Knowing these distinctions helps logistics professionals apply the right strategy to maintain product integrity while maximizing operational efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cold Chain Management | Cross-Docking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temperature-controlled supply chain for perishable goods. | Direct transfer of goods from inbound to outbound transport without storage. |
| Primary Focus | Maintaining product quality via temperature regulation. | Minimizing storage time and handling costs. |
| Key Entities | Refrigerated warehouses, temperature monitors, insulated packaging. | Distribution centers, transportation vehicles, sorting equipment. |
| Ideal for | Perishable goods: food, pharmaceuticals, biologics. | Fast-moving, non-perishable, high-volume items. |
| Benefits | Preserves freshness, extends shelf life, reduces spoilage. | Faster deliveries, lower storage costs, improved efficiency. |
| Challenges | High energy costs, strict regulatory compliance, temperature breaches. | Requires efficient coordination, risk of errors during sorting. |
| Example Use Case | Cold storage of vaccines during distribution. | Retail products consolidated and dispatched within hours. |
Which is better?
Cold chain management excels in preserving perishable goods by maintaining precise temperature controls throughout the supply chain, essential for pharmaceuticals, food, and biotech products. Cross-docking optimizes inventory flow and reduces storage costs by directly transferring goods from inbound to outbound transportation, ideal for fast-moving consumer goods and time-sensitive deliveries. Choosing between them depends on product requirements: cold chain management prioritizes temperature-sensitive preservation, while cross-docking focuses on speed and efficiency in distribution.
Connection
Cold chain management ensures the preservation of temperature-sensitive goods through controlled environments, while cross-docking facilitates rapid transfer of these products without storage delays. Integrating cross-docking within cold chain logistics minimizes handling time, reducing temperature fluctuation risks and maintaining product integrity. Efficient synchronization of cold chain protocols and cross-docking operations enhances supply chain responsiveness and decreases spoilage for perishable items.
Key Terms
Transshipment
Cross-docking in transshipment involves immediate transfer of goods from inbound to outbound transportation, minimizing storage time and reducing handling costs. Cold chain management ensures temperature-sensitive products maintain optimal conditions throughout transshipment to preserve quality and safety. Explore how integrating cross-docking with cold chain protocols enhances efficiency in temperature-controlled supply chains.
Temperature control
Cross-docking minimizes storage time by directly transferring goods from inbound to outbound transportation, requiring precise temperature control to maintain product quality during rapid handling. Cold chain management involves continuous temperature monitoring and regulation throughout the entire supply chain, ensuring perishable goods remain within strict thermal parameters. Explore further to understand how temperature control technologies impact both logistics strategies.
Perishability
Cross-docking minimizes product storage time by directly transferring goods from inbound to outbound transportation, ideal for highly perishable items requiring rapid distribution. Cold chain management ensures temperature-controlled storage and transportation, maintaining the quality and safety of perishable goods such as fresh produce, dairy, and pharmaceuticals throughout the supply chain. Explore further to understand how these strategies can optimize perishability management in logistics.
Source and External Links
Cross Docking: Definition, History, and Process - Inbound Logistics - Cross-docking is a shipping method that transfers goods directly from inbound to outbound transportation modes with minimal storage time, using methods like continuous cross-docking, consolidation, and de-consolidation to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
What Is Cross-Docking? Definition, Types & Advantages - NetSuite - Cross-docking is a supply chain technique that speeds up delivery and lowers costs by unloading goods from inbound trucks and loading them directly onto outbound trucks, minimizing warehouse storage and optimizing inventory control.
Understanding cross-docking: A comprehensive guide - Maersk - Cross-docking involves direct product transfer with little to no storage, and includes types such as pre-distribution and post-distribution, as well as continuous, consolidation, and deconsolidation processes tailored for industries like retail, manufacturing, and e-commerce.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com