Omnichannel fulfillment integrates multiple sales channels, allowing inventory to be shipped directly from warehouses, stores, or fulfillment centers to customers, enhancing flexibility and customer experience. Cross-docking minimizes storage time by transferring goods directly from inbound to outbound transportation, reducing handling costs and speeding up delivery. Explore the differences and advantages of each method to optimize your supply chain strategy.
Why it is important
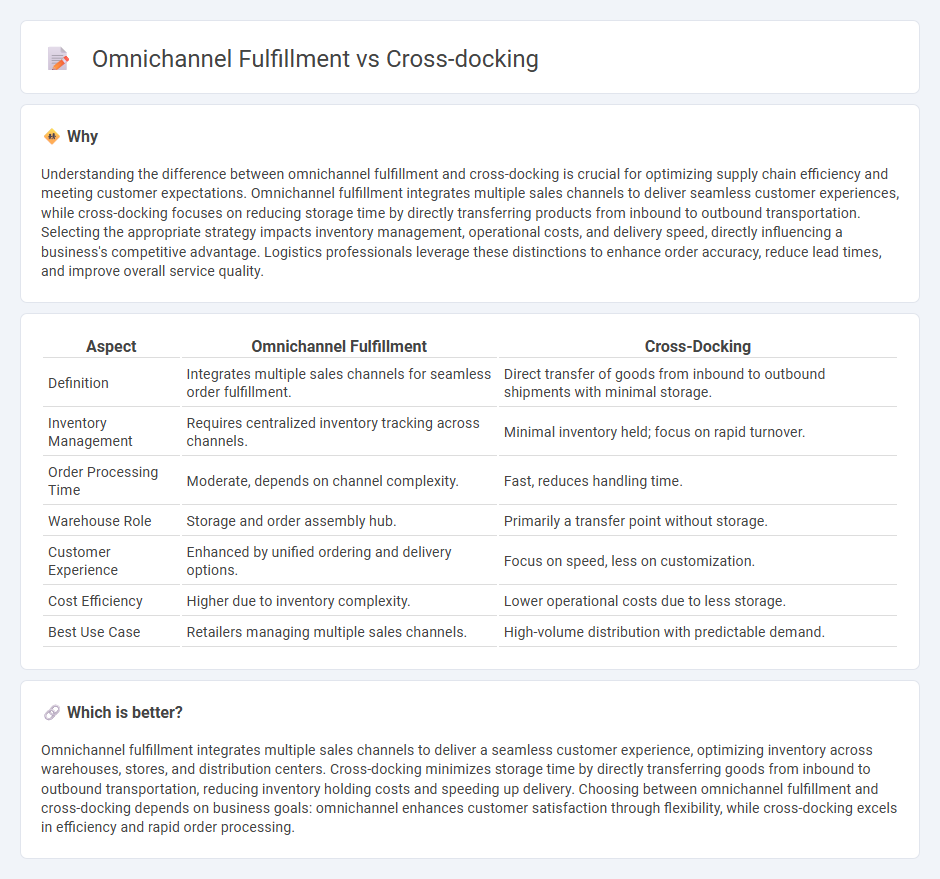
Understanding the difference between omnichannel fulfillment and cross-docking is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and meeting customer expectations. Omnichannel fulfillment integrates multiple sales channels to deliver seamless customer experiences, while cross-docking focuses on reducing storage time by directly transferring products from inbound to outbound transportation. Selecting the appropriate strategy impacts inventory management, operational costs, and delivery speed, directly influencing a business's competitive advantage. Logistics professionals leverage these distinctions to enhance order accuracy, reduce lead times, and improve overall service quality.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Omnichannel Fulfillment | Cross-Docking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrates multiple sales channels for seamless order fulfillment. | Direct transfer of goods from inbound to outbound shipments with minimal storage. |
| Inventory Management | Requires centralized inventory tracking across channels. | Minimal inventory held; focus on rapid turnover. |
| Order Processing Time | Moderate, depends on channel complexity. | Fast, reduces handling time. |
| Warehouse Role | Storage and order assembly hub. | Primarily a transfer point without storage. |
| Customer Experience | Enhanced by unified ordering and delivery options. | Focus on speed, less on customization. |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher due to inventory complexity. | Lower operational costs due to less storage. |
| Best Use Case | Retailers managing multiple sales channels. | High-volume distribution with predictable demand. |
Which is better?
Omnichannel fulfillment integrates multiple sales channels to deliver a seamless customer experience, optimizing inventory across warehouses, stores, and distribution centers. Cross-docking minimizes storage time by directly transferring goods from inbound to outbound transportation, reducing inventory holding costs and speeding up delivery. Choosing between omnichannel fulfillment and cross-docking depends on business goals: omnichannel enhances customer satisfaction through flexibility, while cross-docking excels in efficiency and rapid order processing.
Connection
Omnichannel fulfillment relies heavily on cross-docking to streamline inventory flow, reduce storage time, and accelerate order processing across multiple sales channels. Cross-docking facilitates real-time inventory redistribution by transferring goods directly from inbound to outbound transportation, supporting the rapid delivery demands of omnichannel strategies. This integration enhances supply chain efficiency, minimizes handling costs, and improves customer satisfaction through faster, more accurate order fulfillment.
Key Terms
Inventory Flow
Cross-docking minimizes inventory holding by transferring products directly from inbound to outbound shipments, accelerating inventory turnover and reducing storage costs. Omnichannel fulfillment integrates multiple sales channels, requiring sophisticated inventory management to balance stock availability across physical stores, warehouses, and online platforms. Explore detailed strategies to optimize inventory flow in both models for enhanced supply chain efficiency.
Distribution Channels
Cross-docking streamlines inventory flow by minimizing storage time, directly transferring goods from inbound to outbound transportation, optimizing distribution channels for rapid delivery. Omnichannel fulfillment integrates multiple sales channels, ensuring seamless customer experiences by synchronizing inventory, orders, and fulfillment across physical stores, e-commerce, and third-party platforms. Discover how mastering these strategies transforms distribution channels and boosts supply chain efficiency.
Order Consolidation
Cross-docking accelerates order consolidation by directly transferring inbound shipments to outbound carriers, minimizing storage time and reducing handling costs. Omnichannel fulfillment integrates multiple sales channels, requiring sophisticated order consolidation systems to combine product quantities from various sources like warehouses, stores, and drop-shippers. Discover the detailed strategies and technologies that optimize order consolidation in both cross-docking and omnichannel fulfillment to enhance supply chain efficiency.
Source and External Links
Cross Docking: Definition, History, and Process - This article provides an overview of cross-docking methods, including continuous cross-docking, consolidation arrangements, and de-consolidation.
What Is Cross-Docking? Definition, Types & Advantages - This resource explains how cross-docking accelerates delivery and increases supply chain efficiency by transferring goods directly from inbound to outbound vehicles.
Understanding cross-docking: A comprehensive guide - This comprehensive guide covers types of cross-docking, including pre-distribution, post-distribution, continuous, consolidation, and deconsolidation, focusing on different logistical needs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com