Middle mile automation optimizes the transportation and handling of goods between warehouses and distribution centers using advanced robotics and AI-driven systems to reduce transit times and operational costs. Reverse logistics focuses on the efficient management of returned products, recycling, and refurbishment processes to minimize waste and recover value from returned inventory. Explore the key differences and benefits of middle mile automation versus reverse logistics to enhance your supply chain strategy.
Why it is important
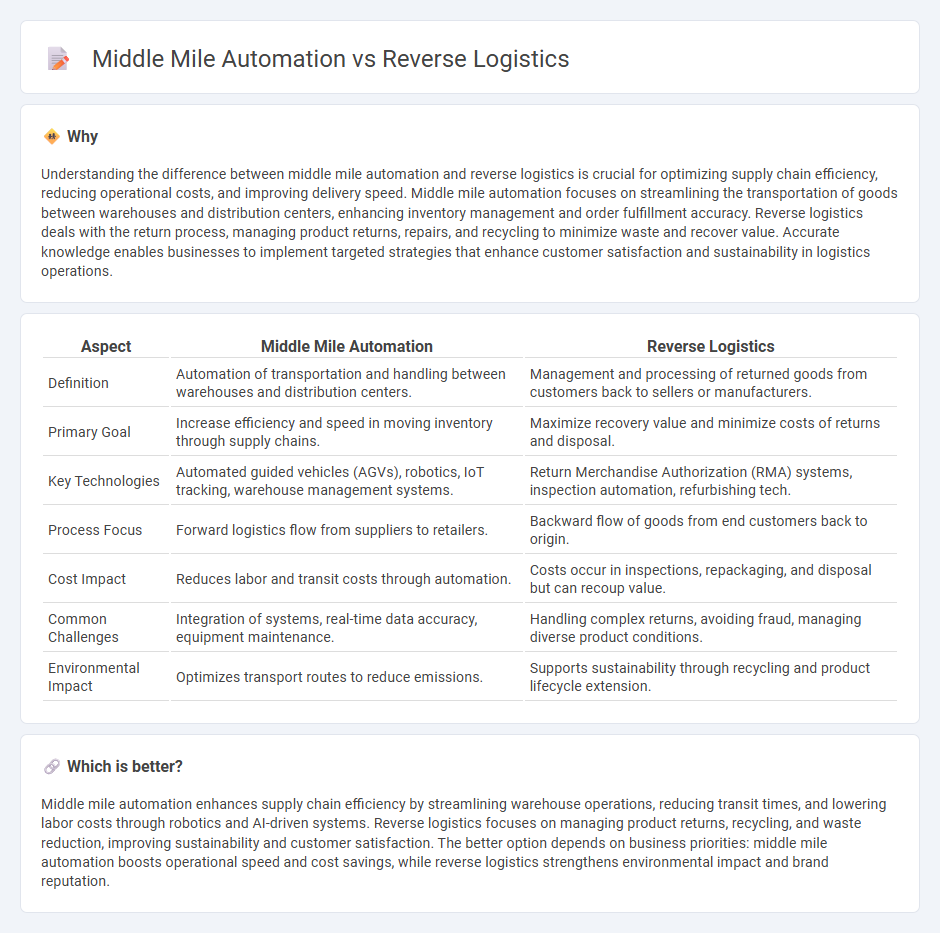
Understanding the difference between middle mile automation and reverse logistics is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency, reducing operational costs, and improving delivery speed. Middle mile automation focuses on streamlining the transportation of goods between warehouses and distribution centers, enhancing inventory management and order fulfillment accuracy. Reverse logistics deals with the return process, managing product returns, repairs, and recycling to minimize waste and recover value. Accurate knowledge enables businesses to implement targeted strategies that enhance customer satisfaction and sustainability in logistics operations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Middle Mile Automation | Reverse Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automation of transportation and handling between warehouses and distribution centers. | Management and processing of returned goods from customers back to sellers or manufacturers. |
| Primary Goal | Increase efficiency and speed in moving inventory through supply chains. | Maximize recovery value and minimize costs of returns and disposal. |
| Key Technologies | Automated guided vehicles (AGVs), robotics, IoT tracking, warehouse management systems. | Return Merchandise Authorization (RMA) systems, inspection automation, refurbishing tech. |
| Process Focus | Forward logistics flow from suppliers to retailers. | Backward flow of goods from end customers back to origin. |
| Cost Impact | Reduces labor and transit costs through automation. | Costs occur in inspections, repackaging, and disposal but can recoup value. |
| Common Challenges | Integration of systems, real-time data accuracy, equipment maintenance. | Handling complex returns, avoiding fraud, managing diverse product conditions. |
| Environmental Impact | Optimizes transport routes to reduce emissions. | Supports sustainability through recycling and product lifecycle extension. |
Which is better?
Middle mile automation enhances supply chain efficiency by streamlining warehouse operations, reducing transit times, and lowering labor costs through robotics and AI-driven systems. Reverse logistics focuses on managing product returns, recycling, and waste reduction, improving sustainability and customer satisfaction. The better option depends on business priorities: middle mile automation boosts operational speed and cost savings, while reverse logistics strengthens environmental impact and brand reputation.
Connection
Middle mile automation enhances supply chain efficiency by streamlining the transportation and handling of goods between warehouses and distribution centers, which directly impacts reverse logistics by making product returns, refurbishments, and recycling processes faster and more accurate. Automated systems enable real-time tracking and optimized routing, reducing delays and operational costs in returning products back through the supply chain. Integration of middle mile automation with reverse logistics facilitates seamless inventory management and improves sustainability efforts through more efficient waste reduction and resource recovery.
Key Terms
**Reverse Logistics:**
Reverse logistics optimizes the process of returning products from consumers to manufacturers or warehouses, reducing waste and improving sustainability. Automated systems streamline inspection, sorting, and refurbishing, enhancing efficiency and cost savings. Explore how reverse logistics automation revolutionizes supply chain management and sustainability practices.
Returns Management
Reverse logistics in returns management streamlines the process of returning products from customers back to sellers, emphasizing cost reduction and sustainability. Middle mile automation enhances inventory movement between distribution centers, improving efficiency and accuracy before products reach the last mile. Explore how integrating both strategies optimizes overall returns management and boosts operational performance.
Refurbishment
Reverse logistics involves the process of returning products from customers back to the warehouse for refurbishment, repair, or recycling, optimizing product lifecycle management. Middle mile automation streamlines the transportation and handling of goods between distribution centers, enhancing efficiency in inventory management and refurbishment operations. Discover more about how these strategies improve refurbishment outcomes and operational performance.
Source and External Links
What is Reverse Logistics? - c3controls - Reverse logistics is the process of planning, controlling, and implementing a cost-effective flow of goods from the customer back to the manufacturer for returns, repairs, remanufacturing, recycling, or disposal, playing a strategic role in creating a leaner, more efficient supply chain aligned with sustainability goals.
A Guide to Reverse Logistics: How It Works, Types and Strategies - Reverse logistics manages the return flow of goods from customers to sellers or manufacturers, encompassing processing returns, refurbishments, and materials recovery across various industries like beverage, construction, and food for economic and environmental benefits.
What Is Reverse Logistics in Supply Chain Management? - Flowspace - Reverse logistics involves handling the flow of products from consumers back to manufacturers, focusing on returns management, refurbishment, recycling, and packaging management to reduce waste and recapture product value while improving customer experience and brand loyalty.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com