Investment in art tokenization leverages blockchain technology to fractionalize ownership of physical artworks, providing liquidity and broader access to high-value pieces. Unlike NFTs, which represent unique digital assets or ownership certificates tied to digital art, art tokenization links digital tokens directly to tangible art assets, enabling real-world value transfer. Explore the transformative potential of art tokenization and how it can reshape your investment portfolio.
Why it is important
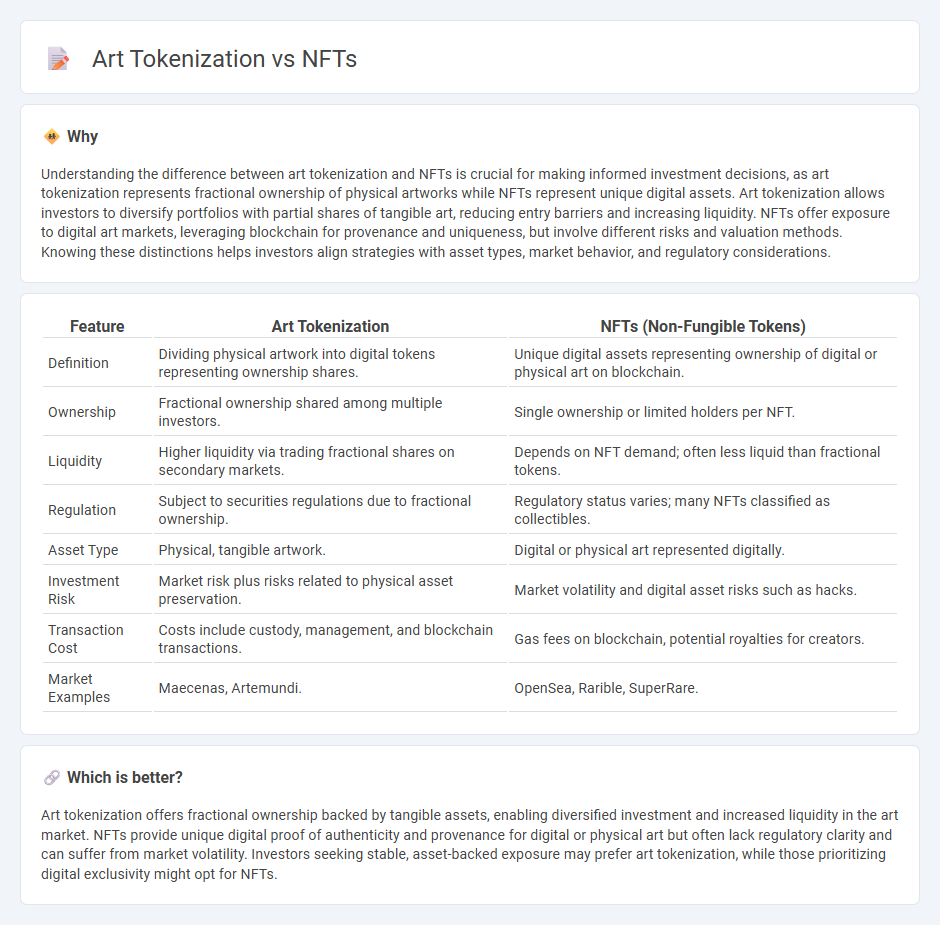
Understanding the difference between art tokenization and NFTs is crucial for making informed investment decisions, as art tokenization represents fractional ownership of physical artworks while NFTs represent unique digital assets. Art tokenization allows investors to diversify portfolios with partial shares of tangible art, reducing entry barriers and increasing liquidity. NFTs offer exposure to digital art markets, leveraging blockchain for provenance and uniqueness, but involve different risks and valuation methods. Knowing these distinctions helps investors align strategies with asset types, market behavior, and regulatory considerations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Art Tokenization | NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dividing physical artwork into digital tokens representing ownership shares. | Unique digital assets representing ownership of digital or physical art on blockchain. |
| Ownership | Fractional ownership shared among multiple investors. | Single ownership or limited holders per NFT. |
| Liquidity | Higher liquidity via trading fractional shares on secondary markets. | Depends on NFT demand; often less liquid than fractional tokens. |
| Regulation | Subject to securities regulations due to fractional ownership. | Regulatory status varies; many NFTs classified as collectibles. |
| Asset Type | Physical, tangible artwork. | Digital or physical art represented digitally. |
| Investment Risk | Market risk plus risks related to physical asset preservation. | Market volatility and digital asset risks such as hacks. |
| Transaction Cost | Costs include custody, management, and blockchain transactions. | Gas fees on blockchain, potential royalties for creators. |
| Market Examples | Maecenas, Artemundi. | OpenSea, Rarible, SuperRare. |
Which is better?
Art tokenization offers fractional ownership backed by tangible assets, enabling diversified investment and increased liquidity in the art market. NFTs provide unique digital proof of authenticity and provenance for digital or physical art but often lack regulatory clarity and can suffer from market volatility. Investors seeking stable, asset-backed exposure may prefer art tokenization, while those prioritizing digital exclusivity might opt for NFTs.
Connection
Art tokenization leverages blockchain technology to convert physical artworks into digital tokens, enabling fractional ownership and enhanced liquidity in the investment market. Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) represent unique digital assets, often linked to art pieces, providing verifiable provenance and authenticity on decentralized platforms. This connection transforms traditional art investment by facilitating secure, transparent trading and expanding access to a broader range of investors globally.
Key Terms
Ownership
NFTs provide unique, indivisible ownership of digital artworks secured by blockchain technology, ensuring provenance and authenticity. Art tokenization divides ownership into fractional shares, allowing multiple investors to hold a stake in high-value physical or digital art pieces. Explore how these ownership models are transforming art investment and collector experiences.
Provenance
NFTs provide unique digital certificates ensuring undeniable provenance by recording ownership history on a blockchain. Art tokenization divides physical artwork into tradable digital shares, offering fractional ownership but requiring robust provenance tracking mechanisms to validate authenticity. Explore deeper insights into how provenance impacts value and trust in digital and tokenized art markets.
Fractionalization
NFTs represent unique digital assets on the blockchain, allowing for exclusive ownership and provenance verification, while art tokenization breaks down artworks into smaller fractions, enabling multiple investors to hold shared ownership through divisible tokens. Fractionalization increases liquidity and democratizes access to high-value art pieces by allowing investment with lower capital compared to purchasing entire NFTs or physical artworks outright. Explore how fractionalization is reshaping art investment and creating new opportunities for collectors and investors.
Source and External Links
Non-fungible token - Wikipedia - NFTs are unique digital identifiers recorded on a blockchain that certify ownership and authenticity of digital assets like artworks or videos, but they do not inherently grant copyright or legal rights; the market experienced explosive growth and a subsequent collapse after 2021.
NFTs Definition & Explanation - Kaspersky - NFTs are cryptographic digital assets with unique signatures stored on a blockchain representing ownership of unique items such as art, collectibles, or real estate, enabling easy transfer and fraud reduction through verified ownership.
What are NFTs? A beginner's guide to non-fungible tokens - NFTs link blockchain-verified ownership to one-of-a-kind digital or physical goods including digital art, gaming items, music, and virtual real estate, and they hold potential for applications like education credentials and event ticketing.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com