Fractional ownership in real estate allows investors to purchase a share of a property, reducing upfront costs and spreading risk among co-owners, unlike direct property investment which requires full capital commitment and sole responsibility for management. This model provides access to high-value assets and professional management, appealing to those seeking diversification without the complexities of sole ownership. Explore the benefits and considerations of each approach to make informed investment decisions.
Why it is important
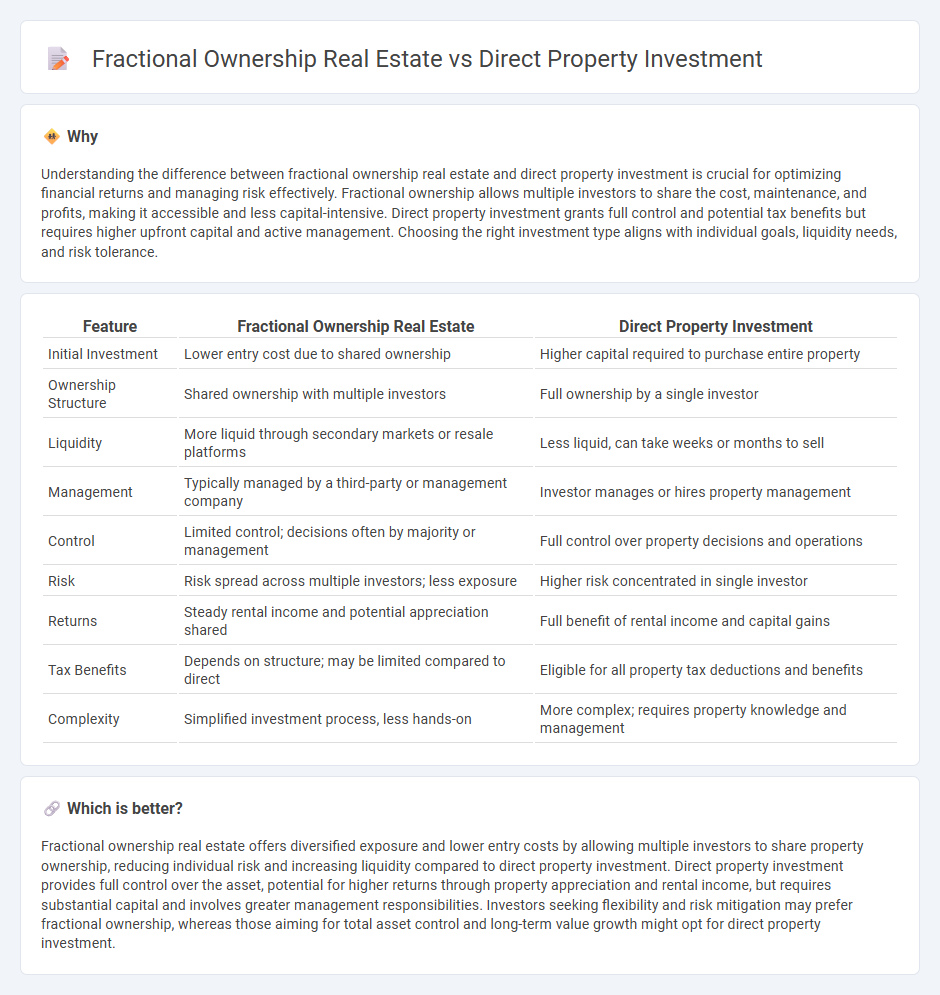
Understanding the difference between fractional ownership real estate and direct property investment is crucial for optimizing financial returns and managing risk effectively. Fractional ownership allows multiple investors to share the cost, maintenance, and profits, making it accessible and less capital-intensive. Direct property investment grants full control and potential tax benefits but requires higher upfront capital and active management. Choosing the right investment type aligns with individual goals, liquidity needs, and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Fractional Ownership Real Estate | Direct Property Investment |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Lower entry cost due to shared ownership | Higher capital required to purchase entire property |
| Ownership Structure | Shared ownership with multiple investors | Full ownership by a single investor |
| Liquidity | More liquid through secondary markets or resale platforms | Less liquid, can take weeks or months to sell |
| Management | Typically managed by a third-party or management company | Investor manages or hires property management |
| Control | Limited control; decisions often by majority or management | Full control over property decisions and operations |
| Risk | Risk spread across multiple investors; less exposure | Higher risk concentrated in single investor |
| Returns | Steady rental income and potential appreciation shared | Full benefit of rental income and capital gains |
| Tax Benefits | Depends on structure; may be limited compared to direct | Eligible for all property tax deductions and benefits |
| Complexity | Simplified investment process, less hands-on | More complex; requires property knowledge and management |
Which is better?
Fractional ownership real estate offers diversified exposure and lower entry costs by allowing multiple investors to share property ownership, reducing individual risk and increasing liquidity compared to direct property investment. Direct property investment provides full control over the asset, potential for higher returns through property appreciation and rental income, but requires substantial capital and involves greater management responsibilities. Investors seeking flexibility and risk mitigation may prefer fractional ownership, whereas those aiming for total asset control and long-term value growth might opt for direct property investment.
Connection
Fractional ownership real estate and direct property investment both involve acquiring equity in real estate assets, enabling investors to benefit from property appreciation and rental income streams. Fractional ownership allows multiple investors to co-own a single property proportionally, reducing capital requirements compared to full direct investment. Both strategies provide opportunities for portfolio diversification, yet fractional ownership offers enhanced liquidity and lower entry barriers relative to traditional direct property investment.
Key Terms
Ownership Structure
Direct property investment involves acquiring full ownership of a real estate asset, granting investors complete control over decision-making, management, and potential income. Fractional ownership divides the property into shares, allowing multiple investors to own a percentage, reducing individual costs and risks but limiting control and requiring coordinated management. Explore the benefits and challenges of each ownership structure to determine the best fit for your investment goals.
Liquidity
Direct property investment often requires significant capital and can be illiquid due to lengthy selling processes and market fluctuations. Fractional ownership real estate offers enhanced liquidity by allowing investors to buy and sell shares more easily, sometimes through secondary markets or platforms. Explore the benefits of each approach to determine which liquidity option suits your investment goals.
Capital Requirement
Direct property investment typically demands a significant capital outlay, often requiring full payment for the property or a large mortgage down payment. Fractional ownership real estate allows investors to purchase a share of a property at a fraction of the total cost, lowering the entry barrier and enabling diversification with less capital. Explore detailed comparisons and financial implications to determine which investment suits your capital goals best.
Source and External Links
Understanding Direct vs. Indirect Real Estate Investments - Direct property investment involves acquiring physical real estate, giving investors full control over management and decisions, but requiring higher capital and carrying higher risks, alongside potential tax benefits and lower liquidity compared to indirect investments.
Direct vs Indirect Real Estate Investing - Direct property investment means buying, controlling, and managing real estate directly, allowing for full profit retention and flexibility in strategies such as renting or renovating for resale, though it may require mortgage financing and is cash flow dependent.
The Pros and Cons of Direct Real Estate Investments - Direct real estate investment offers benefits including asset control, potential appreciation, steady cash flow, and tax advantages but also involves challenges in property management and liquidity that investors should carefully consider.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com