Basis trading exploits price discrepancies between futures contracts and their underlying assets, seeking arbitrage opportunities in bond markets. Yield curve trading focuses on capitalizing on changes in the interest rate term structure by taking strategic positions across different maturities. Explore deeper strategies and risk profiles to enhance your understanding of basis and yield curve trading.
Why it is important
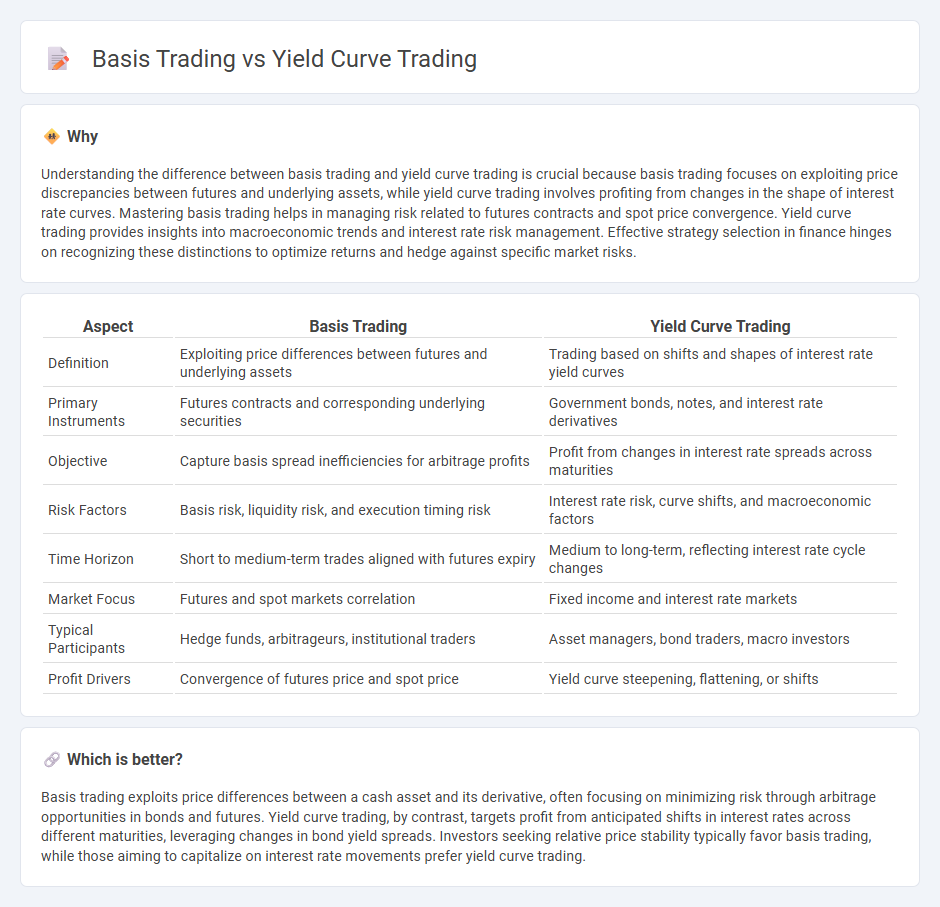
Understanding the difference between basis trading and yield curve trading is crucial because basis trading focuses on exploiting price discrepancies between futures and underlying assets, while yield curve trading involves profiting from changes in the shape of interest rate curves. Mastering basis trading helps in managing risk related to futures contracts and spot price convergence. Yield curve trading provides insights into macroeconomic trends and interest rate risk management. Effective strategy selection in finance hinges on recognizing these distinctions to optimize returns and hedge against specific market risks.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Basis Trading | Yield Curve Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exploiting price differences between futures and underlying assets | Trading based on shifts and shapes of interest rate yield curves |
| Primary Instruments | Futures contracts and corresponding underlying securities | Government bonds, notes, and interest rate derivatives |
| Objective | Capture basis spread inefficiencies for arbitrage profits | Profit from changes in interest rate spreads across maturities |
| Risk Factors | Basis risk, liquidity risk, and execution timing risk | Interest rate risk, curve shifts, and macroeconomic factors |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium-term trades aligned with futures expiry | Medium to long-term, reflecting interest rate cycle changes |
| Market Focus | Futures and spot markets correlation | Fixed income and interest rate markets |
| Typical Participants | Hedge funds, arbitrageurs, institutional traders | Asset managers, bond traders, macro investors |
| Profit Drivers | Convergence of futures price and spot price | Yield curve steepening, flattening, or shifts |
Which is better?
Basis trading exploits price differences between a cash asset and its derivative, often focusing on minimizing risk through arbitrage opportunities in bonds and futures. Yield curve trading, by contrast, targets profit from anticipated shifts in interest rates across different maturities, leveraging changes in bond yield spreads. Investors seeking relative price stability typically favor basis trading, while those aiming to capitalize on interest rate movements prefer yield curve trading.
Connection
Basis trading exploits the price differential between a financial instrument and its related derivative, often involving futures contracts on bonds or interest rates. Yield curve trading focuses on profiting from changes in the shape or slope of the yield curve, using strategies like bullet or barbell bond positioning. Both strategies intersect as basis traders monitor yield curve movements to identify mispricings between cash bonds and their futures, enabling arbitrage opportunities across maturities.
Key Terms
Interest Rate Differentials
Yield curve trading exploits variations in interest rates across different maturities within the Treasury market, aiming to profit from shifts in the yield curve's shape by buying and selling securities at different points. Basis trading centers on the spread between the yield on a Treasury security and the yield on a related futures contract, capitalizing on discrepancies caused by factors like delivery options or financing costs. Explore the nuances of interest rate differentials in these strategies to enhance your fixed-income trading insights.
Spread
Yield curve trading capitalizes on the relative movements between different maturities of the same issuer's bonds, aiming to profit from changes in the spread across the yield curve. Basis trading involves exploiting discrepancies between the cash bond yield and its corresponding futures contract, focusing on the basis spread to capture arbitrage opportunities. Explore detailed strategies and market conditions driving these spread-focused trades to enhance investment decisions.
Duration
Yield curve trading exploits interest rate movements across different maturities to optimize portfolio duration, targeting shifts in the slope or curvature of the yield curve for profit. Basis trading involves capitalizing on the price difference between a bond and its corresponding futures contract, focusing on duration risk and hedging efficiency. Explore in-depth strategies and performance metrics to enhance your fixed-income trading expertise.
Source and External Links
Yield Curve Shifts Create Trading Opportunities - CME Group - Yield curve trading involves taking positions based on expectations of the curve's shape changes, such as buying spreads if the curve steepens or selling spreads if it flattens, using techniques like DV01-weighted spread trades to isolate gains from curve shape movements.
Yield Curve Strategies | CFA Institute - Yield curve trading strategies include steepeners (long short-term bonds, short long-term bonds) and managing portfolio duration and convexity to exploit expected changes in yield curve slope and shape for excess returns.
Trading the Treasury Yield Curve - CME Group - Traders use Treasury futures across maturities to trade yield curve spreads, profiting from anticipated changes in curve shape driven by interest rate expectations and macroeconomic shifts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com