Basis trading exploits the price difference between a futures contract and its underlying asset, capitalizing on convergence at contract expiration, while spread trading involves simultaneously buying and selling related securities to profit from relative price movements. Basis trading focuses on arbitrage opportunities within the same asset class, whereas spread trading leverages correlations between different but related instruments such as commodities, bonds, or equities. Explore the nuances and strategies of basis trading versus spread trading to enhance your financial expertise.
Why it is important
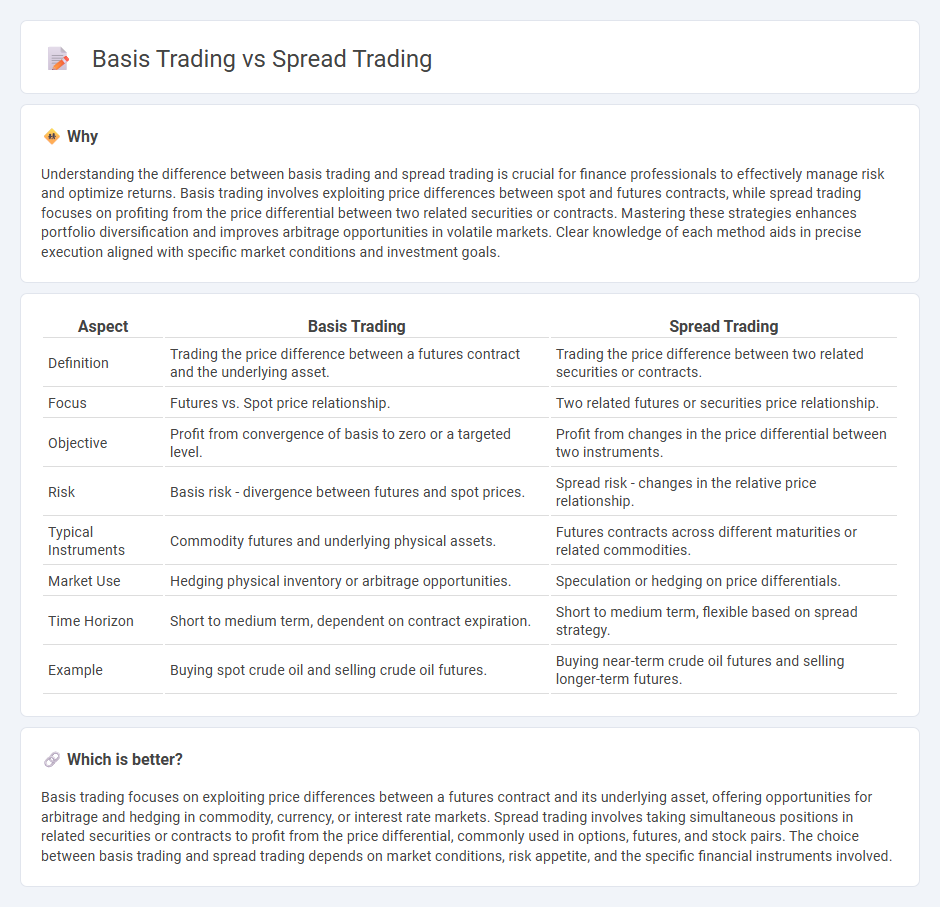
Understanding the difference between basis trading and spread trading is crucial for finance professionals to effectively manage risk and optimize returns. Basis trading involves exploiting price differences between spot and futures contracts, while spread trading focuses on profiting from the price differential between two related securities or contracts. Mastering these strategies enhances portfolio diversification and improves arbitrage opportunities in volatile markets. Clear knowledge of each method aids in precise execution aligned with specific market conditions and investment goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Basis Trading | Spread Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading the price difference between a futures contract and the underlying asset. | Trading the price difference between two related securities or contracts. |
| Focus | Futures vs. Spot price relationship. | Two related futures or securities price relationship. |
| Objective | Profit from convergence of basis to zero or a targeted level. | Profit from changes in the price differential between two instruments. |
| Risk | Basis risk - divergence between futures and spot prices. | Spread risk - changes in the relative price relationship. |
| Typical Instruments | Commodity futures and underlying physical assets. | Futures contracts across different maturities or related commodities. |
| Market Use | Hedging physical inventory or arbitrage opportunities. | Speculation or hedging on price differentials. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term, dependent on contract expiration. | Short to medium term, flexible based on spread strategy. |
| Example | Buying spot crude oil and selling crude oil futures. | Buying near-term crude oil futures and selling longer-term futures. |
Which is better?
Basis trading focuses on exploiting price differences between a futures contract and its underlying asset, offering opportunities for arbitrage and hedging in commodity, currency, or interest rate markets. Spread trading involves taking simultaneous positions in related securities or contracts to profit from the price differential, commonly used in options, futures, and stock pairs. The choice between basis trading and spread trading depends on market conditions, risk appetite, and the specific financial instruments involved.
Connection
Basis trading and spread trading are interconnected strategies in finance that exploit price differentials between related securities. Basis trading focuses on the price difference between a futures contract and its underlying asset, while spread trading involves simultaneously buying and selling two correlated instruments to profit from the relative price movement. Both techniques aim to capitalize on market inefficiencies and manage risk by leveraging the relationship between related financial instruments.
Key Terms
Price Differential
Spread trading involves simultaneously buying and selling related securities to profit from the price differential between them, often in futures or options markets. Basis trading focuses on exploiting the price gap between the spot price and futures price of the same asset, capitalizing on convergence as the contract nears expiration. Explore the nuances of price differentials in financial markets to understand these trading strategies in depth.
Underlying Assets
Spread trading involves taking opposing positions in related futures contracts to capitalize on price differentials, often within the same commodity or asset class, such as crude oil or gold. Basis trading focuses on the price difference between a futures contract and the underlying asset's spot price, typically leveraging disparities in supply, demand, or storage costs. Discover more about how these strategies optimize risk management and profit potential in commodity markets.
Convergence
Spread trading and basis trading both capitalize on price convergence, but they target different markets and instruments. Spread trading typically involves taking opposing positions in related futures contracts to profit from the narrowing price gap between them, while basis trading exploits the difference between spot prices and futures prices in the same commodity. Explore these strategies further to understand how convergence drives profitable arbitrage opportunities in diverse financial markets.
Source and External Links
What is Spread Trading: Meaning and Types - Spread trading involves simultaneously buying one security and selling another to profit from changes in the price difference, with common types including intermarket, intracommodity, intercommodity, calendar, and options spreads, while factors like market volatility and liquidity affect profitability.
What is Spread Trading? Meaning, Strategies and Benefits - Spread trading is buying and selling two financial instruments simultaneously to profit from their price difference, exemplified by calendar spreads, and reduces risk compared to outright positions.
A Guide to Spread Trading Futures - Futures spread trading involves taking a long and short position simultaneously to benefit from price discrepancies, functioning as a hedge or arbitrage strategy that lowers risk compared to directional bets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com