Climate-linked derivatives offer financial instruments that hedge risks related to climate change, enabling companies to manage exposure to environmental factors with tailored contracts. Sustainability-linked bonds incentivize issuers to meet specific environmental, social, and governance (ESG) targets by linking bond terms to performance metrics. Explore the distinctions and benefits of these innovative finance tools to optimize your sustainability strategy.
Why it is important
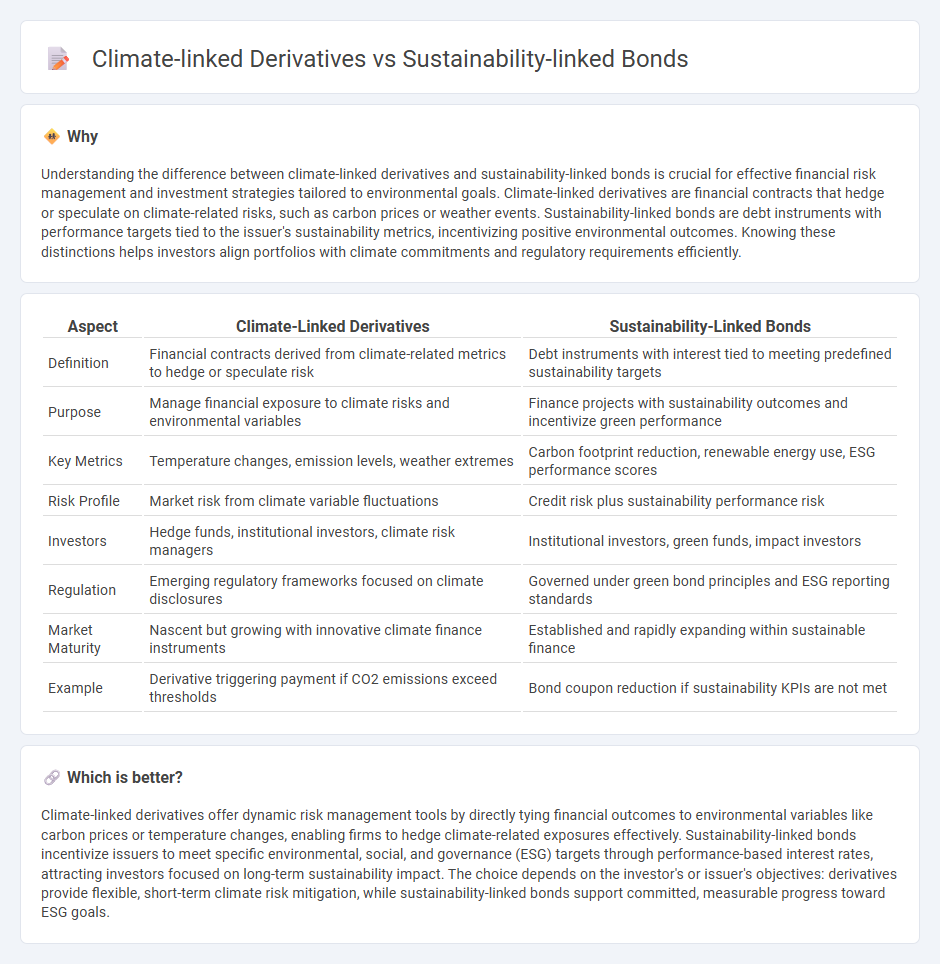
Understanding the difference between climate-linked derivatives and sustainability-linked bonds is crucial for effective financial risk management and investment strategies tailored to environmental goals. Climate-linked derivatives are financial contracts that hedge or speculate on climate-related risks, such as carbon prices or weather events. Sustainability-linked bonds are debt instruments with performance targets tied to the issuer's sustainability metrics, incentivizing positive environmental outcomes. Knowing these distinctions helps investors align portfolios with climate commitments and regulatory requirements efficiently.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Climate-Linked Derivatives | Sustainability-Linked Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial contracts derived from climate-related metrics to hedge or speculate risk | Debt instruments with interest tied to meeting predefined sustainability targets |
| Purpose | Manage financial exposure to climate risks and environmental variables | Finance projects with sustainability outcomes and incentivize green performance |
| Key Metrics | Temperature changes, emission levels, weather extremes | Carbon footprint reduction, renewable energy use, ESG performance scores |
| Risk Profile | Market risk from climate variable fluctuations | Credit risk plus sustainability performance risk |
| Investors | Hedge funds, institutional investors, climate risk managers | Institutional investors, green funds, impact investors |
| Regulation | Emerging regulatory frameworks focused on climate disclosures | Governed under green bond principles and ESG reporting standards |
| Market Maturity | Nascent but growing with innovative climate finance instruments | Established and rapidly expanding within sustainable finance |
| Example | Derivative triggering payment if CO2 emissions exceed thresholds | Bond coupon reduction if sustainability KPIs are not met |
Which is better?
Climate-linked derivatives offer dynamic risk management tools by directly tying financial outcomes to environmental variables like carbon prices or temperature changes, enabling firms to hedge climate-related exposures effectively. Sustainability-linked bonds incentivize issuers to meet specific environmental, social, and governance (ESG) targets through performance-based interest rates, attracting investors focused on long-term sustainability impact. The choice depends on the investor's or issuer's objectives: derivatives provide flexible, short-term climate risk mitigation, while sustainability-linked bonds support committed, measurable progress toward ESG goals.
Connection
Climate-linked derivatives provide financial instruments that hedge risks associated with environmental factors, while sustainability-linked bonds incentivize companies to achieve specific environmental, social, and governance (ESG) targets. Both tools support corporate strategies aimed at mitigating climate risk and promoting sustainable development by aligning financial performance with climate goals. Integrating these instruments enhances market confidence in transitioning to a low-carbon economy and attracts investment toward sustainable projects.
Key Terms
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Sustainability-linked bonds (SLBs) use Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as carbon emissions reduction, renewable energy adoption, and water usage efficiency to determine financial incentives or penalties, aligning investor returns with issuer sustainability targets. Climate-linked derivatives, including weather derivatives and carbon credit options, employ KPIs related to temperature changes, precipitation levels, and greenhouse gas emission metrics to hedge risks connected to climate variability and policy shifts. Explore the distinct roles and mechanisms of KPIs in these financial instruments to better understand their impact on sustainable finance.
Emissions Reduction Targets
Sustainability-linked bonds (SLBs) directly tie financial performance to emissions reduction targets, incentivizing issuers to meet predefined environmental goals through interest rate adjustments. Climate-linked derivatives serve as risk management tools that hedge against climate-related financial risks by referencing environmental indicators without necessarily setting binding reduction commitments. Explore further to understand how these instruments uniquely support corporate strategies in achieving net-zero emissions.
Hedging Mechanisms
Sustainability-linked bonds provide issuers with flexible capital aligned to ESG targets, incentivizing performance through coupon adjustments tied to sustainability KPIs. Climate-linked derivatives function as financial instruments for hedging climate-related risks, offering protection against adverse price movements in carbon markets or weather fluctuations. Explore how these hedging mechanisms can enhance financial resilience and drive sustainable investment strategies.
Source and External Links
Understanding Green, Social and Sustainability Bonds - PIMCO - Sustainability-linked bonds finance the general functioning of an issuer and link bond coupon rates to the achievement of explicit sustainability targets, encouraging corporate commitments to climate and SDG goals.
Sustainability linked bonds: how they can support net-zero - SLBs adjust financial terms based on whether issuers meet predefined ESG metrics, offering lower interest rates when targets are met and encouraging a wide range of companies to improve sustainability without restricting fund use to specific projects.
Sustainability-Linked Bond Principles (SLBP) - ICMA - The SLBP provide market guidelines on structuring, disclosure, and reporting for sustainability-linked bonds, promoting transparency and aligning debt markets with sustainability goals across all issuer types and financial instruments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com