Tokenization of real-world assets leverages blockchain technology to convert physical assets like real estate, art, or commodities into digital tokens, enabling fractional ownership and enhanced liquidity. Private equity involves investing in privately-held companies through direct equity stakes, often requiring substantial capital and long-term commitments with limited liquidity. Explore the transformative impact of tokenization on traditional private equity markets and how it is reshaping investment opportunities.
Why it is important
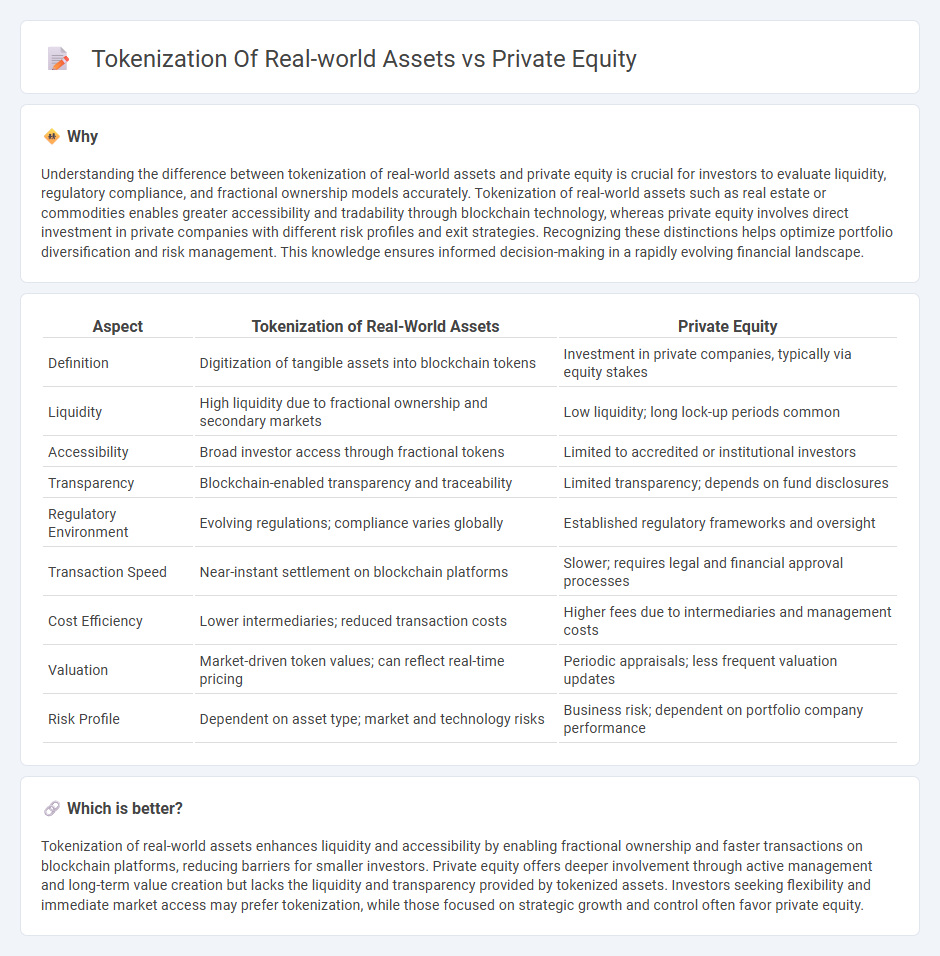
Understanding the difference between tokenization of real-world assets and private equity is crucial for investors to evaluate liquidity, regulatory compliance, and fractional ownership models accurately. Tokenization of real-world assets such as real estate or commodities enables greater accessibility and tradability through blockchain technology, whereas private equity involves direct investment in private companies with different risk profiles and exit strategies. Recognizing these distinctions helps optimize portfolio diversification and risk management. This knowledge ensures informed decision-making in a rapidly evolving financial landscape.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tokenization of Real-World Assets | Private Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Digitization of tangible assets into blockchain tokens | Investment in private companies, typically via equity stakes |
| Liquidity | High liquidity due to fractional ownership and secondary markets | Low liquidity; long lock-up periods common |
| Accessibility | Broad investor access through fractional tokens | Limited to accredited or institutional investors |
| Transparency | Blockchain-enabled transparency and traceability | Limited transparency; depends on fund disclosures |
| Regulatory Environment | Evolving regulations; compliance varies globally | Established regulatory frameworks and oversight |
| Transaction Speed | Near-instant settlement on blockchain platforms | Slower; requires legal and financial approval processes |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower intermediaries; reduced transaction costs | Higher fees due to intermediaries and management costs |
| Valuation | Market-driven token values; can reflect real-time pricing | Periodic appraisals; less frequent valuation updates |
| Risk Profile | Dependent on asset type; market and technology risks | Business risk; dependent on portfolio company performance |
Which is better?
Tokenization of real-world assets enhances liquidity and accessibility by enabling fractional ownership and faster transactions on blockchain platforms, reducing barriers for smaller investors. Private equity offers deeper involvement through active management and long-term value creation but lacks the liquidity and transparency provided by tokenized assets. Investors seeking flexibility and immediate market access may prefer tokenization, while those focused on strategic growth and control often favor private equity.
Connection
Tokenization of real-world assets transforms traditional private equity investments into digital tokens, enhancing liquidity and accessibility for a broader range of investors. By leveraging blockchain technology, private equity firms can fractionalize ownership stakes, reduce transaction costs, and enable faster settlement times. This integration improves transparency, increases market efficiency, and opens new avenues for capital raising within private equity markets.
Key Terms
Liquidity
Tokenization of real-world assets significantly enhances liquidity by enabling fractional ownership and 24/7 trading on blockchain platforms, unlike traditional private equity investments which often involve lengthy lock-up periods and limited secondary market options. Private equity typically restricts investor exit strategies due to regulatory and market constraints, whereas tokenization facilitates faster asset transfer and broader investor participation. Explore how these innovations redefine asset liquidity and investor access in modern finance.
Ownership structure
Private equity typically involves direct ownership through equity shares, granting investors voting rights and control over business decisions. Tokenization of real-world assets digitizes ownership into blockchain-based tokens, enabling fractional ownership and increased liquidity without traditional intermediaries. Explore how these ownership structures impact investor rights and market accessibility.
Regulatory compliance
Private equity investments are heavily regulated, requiring adherence to securities laws, investor accreditation standards, and extensive reporting to ensure compliance and protect investors. Tokenization of real-world assets introduces new regulatory challenges, including navigating evolving frameworks for digital securities, anti-money laundering (AML) protocols, and cross-border jurisdictional issues. Explore the latest regulatory trends and compliance strategies to understand how these investment models coexist and evolve.
Source and External Links
Private equity - Wikipedia - Private equity involves investment firms raising capital from institutional investors to buy stakes in private companies, focusing on strategies like revenue growth, margin expansion, and debt paydown to generate returns over a typical 4-7 year horizon.
What is Private Equity? - BVCA - Private equity provides medium to long-term capital to mature companies, enhancing value through active management partnerships that improve operations, growth, and governance before exiting investments typically after four to seven years.
Private Equity: What You Need to Know - KKR - Private equity strategies focus on investing in non-public companies, improving their operations and capital structure, with the goal of generating returns and diversifying portfolios beyond the shrinking public company universe.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com