Shadow banking encompasses financial intermediaries like hedge funds and money market funds that operate outside traditional banking regulations, providing credit and liquidity services. Non-bank financial institutions include entities such as insurance companies, pension funds, and finance companies that offer financial products but do not hold a banking license. Explore the distinctions and roles of shadow banking and non-bank financial institutions to understand their impact on the financial system.
Why it is important
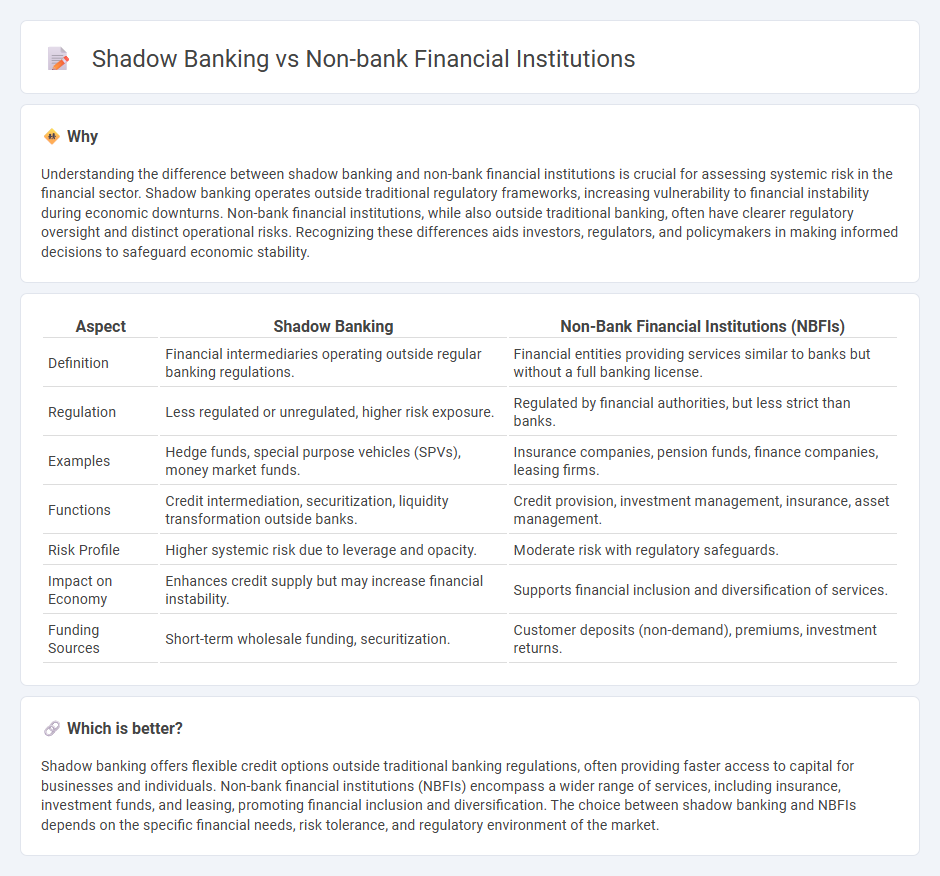
Understanding the difference between shadow banking and non-bank financial institutions is crucial for assessing systemic risk in the financial sector. Shadow banking operates outside traditional regulatory frameworks, increasing vulnerability to financial instability during economic downturns. Non-bank financial institutions, while also outside traditional banking, often have clearer regulatory oversight and distinct operational risks. Recognizing these differences aids investors, regulators, and policymakers in making informed decisions to safeguard economic stability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Shadow Banking | Non-Bank Financial Institutions (NBFIs) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial intermediaries operating outside regular banking regulations. | Financial entities providing services similar to banks but without a full banking license. |
| Regulation | Less regulated or unregulated, higher risk exposure. | Regulated by financial authorities, but less strict than banks. |
| Examples | Hedge funds, special purpose vehicles (SPVs), money market funds. | Insurance companies, pension funds, finance companies, leasing firms. |
| Functions | Credit intermediation, securitization, liquidity transformation outside banks. | Credit provision, investment management, insurance, asset management. |
| Risk Profile | Higher systemic risk due to leverage and opacity. | Moderate risk with regulatory safeguards. |
| Impact on Economy | Enhances credit supply but may increase financial instability. | Supports financial inclusion and diversification of services. |
| Funding Sources | Short-term wholesale funding, securitization. | Customer deposits (non-demand), premiums, investment returns. |
Which is better?
Shadow banking offers flexible credit options outside traditional banking regulations, often providing faster access to capital for businesses and individuals. Non-bank financial institutions (NBFIs) encompass a wider range of services, including insurance, investment funds, and leasing, promoting financial inclusion and diversification. The choice between shadow banking and NBFIs depends on the specific financial needs, risk tolerance, and regulatory environment of the market.
Connection
Shadow banking and non-bank financial institutions are interconnected through their roles in providing credit and liquidity outside traditional banking regulations. These entities, including investment funds, hedge funds, and money market funds, facilitate lending and financial services without direct oversight from central banks, increasing systemic risk. Their activities amplify credit availability but often lack the transparency and safeguards characteristic of regulated banks, impacting financial stability.
Key Terms
Regulatory Oversight
Non-bank financial institutions operate under formal regulatory frameworks designed to ensure transparency, consumer protection, and financial stability, while shadow banking entities typically function with limited oversight, increasing systemic risk due to their opaque operations and reliance on short-term funding. Regulatory bodies monitor non-bank institutions through capital requirements, reporting standards, and compliance audits, whereas shadow banking activities often circumvent traditional regulations, posing challenges for regulators in risk assessment and control. Explore detailed strategies and case studies on regulatory measures to understand how oversight impacts financial sector resilience.
Credit Intermediation
Non-bank financial institutions (NBFIs) provide credit intermediation through regulated entities such as finance companies, leasing firms, and insurance companies, focusing on serving niche markets with specialized lending products. Shadow banking involves credit intermediation activities conducted by unregulated or loosely regulated entities like hedge funds and money market funds, often engaging in maturity transformation and leveraging off-balance sheet operations, which can pose systemic risks. Explore further to understand the regulatory implications and risk profiles distinguishing these two credit intermediation channels.
Systemic Risk
Non-bank financial institutions (NBFIs) provide critical credit and liquidity services but operate with less regulatory oversight, increasing systemic risk in financial markets. Shadow banking comprises a subset of NBFIs engaging in credit intermediation through non-bank channels, amplifying vulnerabilities due to opacity and leverage. Explore the nuances of how systemic risk emerges in these entities and their impact on global financial stability.
Source and External Links
Nonbank Financial Institution - Non-bank financial institutions (NBFIs) do not have banking licenses and cannot accept public deposits; they provide alternative financial services including insurance, venture capital, currency exchanges, and microloans, specializing in sectors or groups that banks may not serve.
Non-Bank Financial Intermediation - NBFIs like investment funds, pension funds, and insurance companies play a crucial role in financing the real economy and managing savings but may also pose systemic risks due to maturity and liquidity transformation or leverage.
Non-bank financial institution - NBFIs supplement banks by unbundling and tailoring financial services, specializing in sectors, and typically do not take deposits or offer checking accounts but provide loans, credit, wealth management, and underwriting activities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com