Risk parity portfolios balance asset risk levels by allocating capital according to volatility rather than traditional asset weights, enhancing diversification and stability across market conditions. Endowment model portfolios emphasize alternative assets such as private equity, real estate, and hedge funds to achieve long-term growth with a focus on illiquidity premiums and active management. Explore deeper insights into their risk-return profiles and strategic applications.
Why it is important
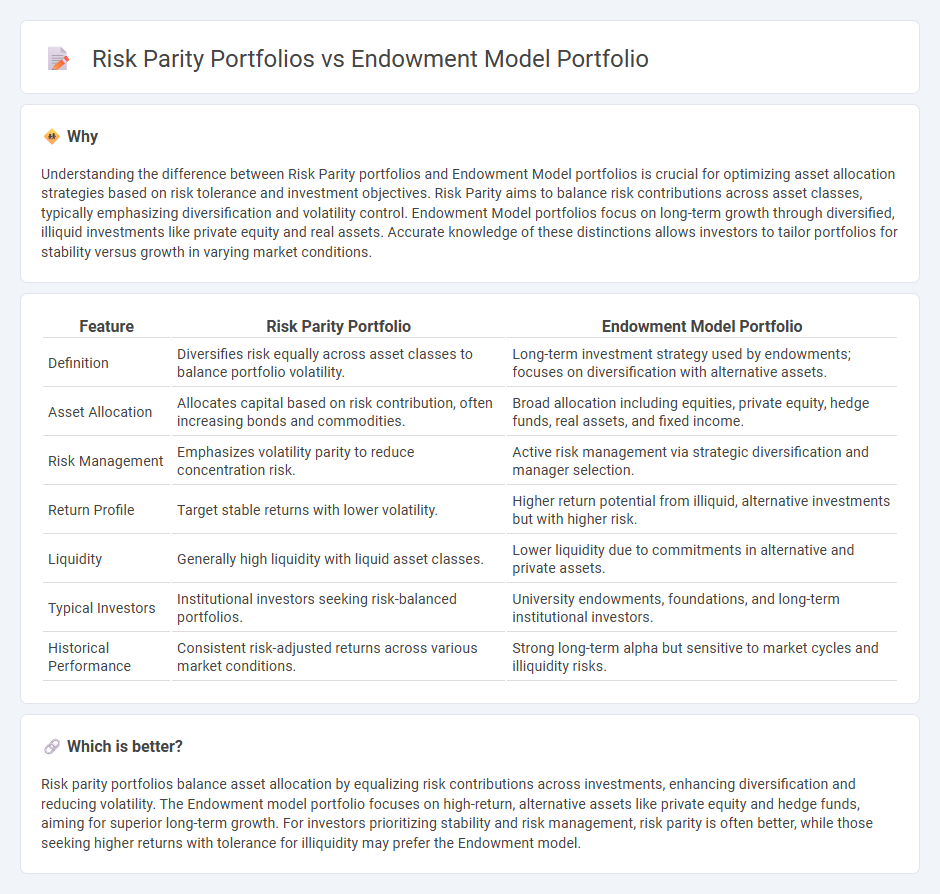
Understanding the difference between Risk Parity portfolios and Endowment Model portfolios is crucial for optimizing asset allocation strategies based on risk tolerance and investment objectives. Risk Parity aims to balance risk contributions across asset classes, typically emphasizing diversification and volatility control. Endowment Model portfolios focus on long-term growth through diversified, illiquid investments like private equity and real assets. Accurate knowledge of these distinctions allows investors to tailor portfolios for stability versus growth in varying market conditions.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Risk Parity Portfolio | Endowment Model Portfolio |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Diversifies risk equally across asset classes to balance portfolio volatility. | Long-term investment strategy used by endowments; focuses on diversification with alternative assets. |
| Asset Allocation | Allocates capital based on risk contribution, often increasing bonds and commodities. | Broad allocation including equities, private equity, hedge funds, real assets, and fixed income. |
| Risk Management | Emphasizes volatility parity to reduce concentration risk. | Active risk management via strategic diversification and manager selection. |
| Return Profile | Target stable returns with lower volatility. | Higher return potential from illiquid, alternative investments but with higher risk. |
| Liquidity | Generally high liquidity with liquid asset classes. | Lower liquidity due to commitments in alternative and private assets. |
| Typical Investors | Institutional investors seeking risk-balanced portfolios. | University endowments, foundations, and long-term institutional investors. |
| Historical Performance | Consistent risk-adjusted returns across various market conditions. | Strong long-term alpha but sensitive to market cycles and illiquidity risks. |
Which is better?
Risk parity portfolios balance asset allocation by equalizing risk contributions across investments, enhancing diversification and reducing volatility. The Endowment model portfolio focuses on high-return, alternative assets like private equity and hedge funds, aiming for superior long-term growth. For investors prioritizing stability and risk management, risk parity is often better, while those seeking higher returns with tolerance for illiquidity may prefer the Endowment model.
Connection
Risk parity portfolios and Endowment model portfolios are connected through their shared goal of diversification and risk management by allocating assets across multiple uncorrelated classes. Risk parity emphasizes equal risk contribution from each asset class, while the Endowment model focuses on long-term growth by investing in diversified alternatives like private equity, real estate, and hedge funds. Both approaches leverage asset allocation strategies designed to optimize risk-adjusted returns and enhance portfolio resilience in volatile markets.
Key Terms
Asset Allocation
Endowment model portfolios emphasize diversification across alternative assets such as private equity, hedge funds, and real assets to achieve long-term growth with controlled risk. Risk parity portfolios allocate capital based on risk contribution from asset classes, often balancing equities, bonds, and commodities to minimize volatility and enhance risk-adjusted returns. Explore deeper insights into these asset allocation strategies to optimize portfolio performance.
Leverage
Endowment model portfolios typically utilize significant leverage through alternative assets like private equity and hedge funds to enhance returns and diversification. Risk parity portfolios balance asset allocation by equalizing risk contributions, often employing leverage on low-volatility assets such as bonds to achieve target risk levels. Explore detailed comparisons and strategies to optimize leverage use in both portfolio approaches.
Risk Budgeting
Endowment model portfolios prioritize diversified asset allocations including private equity, real assets, and absolute return strategies to maximize long-term risk-adjusted returns by leveraging illiquidity premiums. Risk parity portfolios focus on equalizing risk contributions across asset classes, often favoring liquid bonds and equities to minimize portfolio volatility through balanced risk budgeting. Explore detailed comparisons and practical implementations to understand their impact on portfolio risk management.
Source and External Links
Endowment Model: Explained - The Family Office - The Endowment Model portfolio emphasizes diversification across asset classes with low correlation, heavy allocation to illiquid alternative assets like private equity and venture capital for higher expected returns, and accepts short-term underperformance for long-term gains.
The importance of the endowment model investing for families - This model aims to preserve and grow capital faster than inflation by investing in a broad mix of alternatives such as private equity, real assets, infrastructure, and commodities, with an inflation+5% return benchmark.
The Endowment Model and Modern Portfolio Theory - The model uses a dynamic portfolio choice including illiquid alternative assets with staggered lock-up periods to optimize asset allocation, balancing liquidity costs and increasing overall investor welfare based on modern portfolio theory advances.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com