Risk parity portfolios allocate risk equally across asset classes to achieve diversification, while minimum variance portfolios focus on minimizing overall portfolio volatility by selecting low-correlation, low-volatility assets. Risk parity emphasizes balanced risk contributions, often leveraging fixed income and equities, whereas minimum variance prioritizes the lowest possible portfolio variance regardless of asset allocation constraints. Explore these strategies further to understand their implications for portfolio risk management and return optimization.
Why it is important
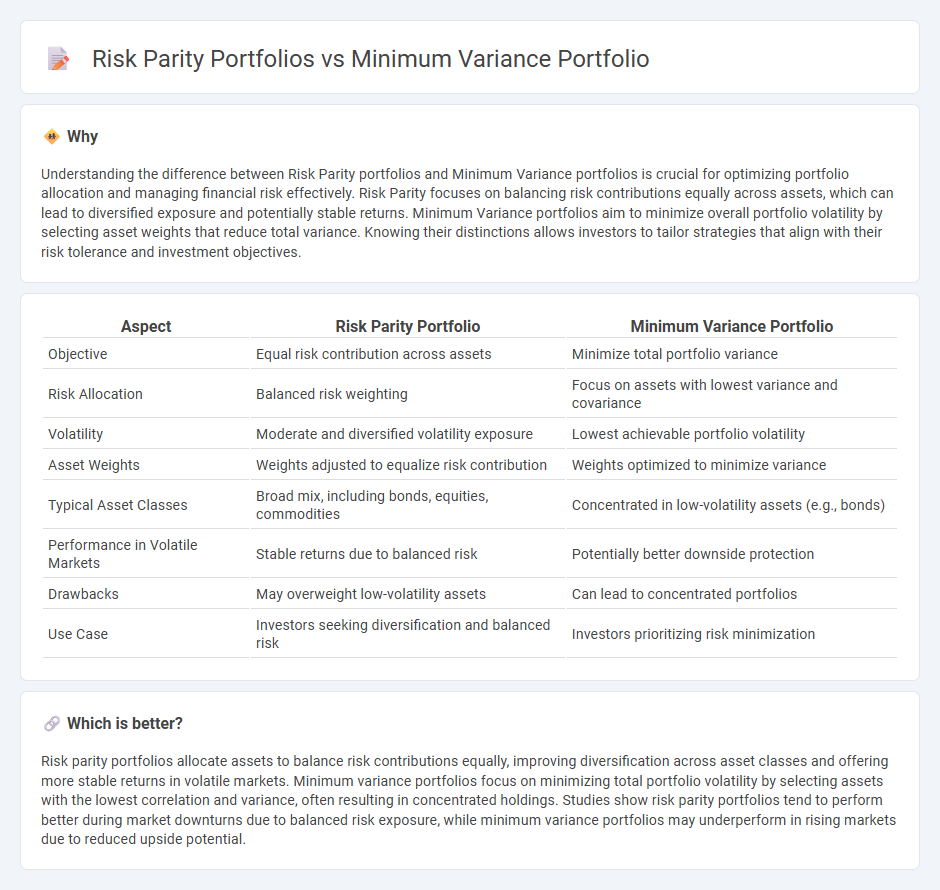
Understanding the difference between Risk Parity portfolios and Minimum Variance portfolios is crucial for optimizing portfolio allocation and managing financial risk effectively. Risk Parity focuses on balancing risk contributions equally across assets, which can lead to diversified exposure and potentially stable returns. Minimum Variance portfolios aim to minimize overall portfolio volatility by selecting asset weights that reduce total variance. Knowing their distinctions allows investors to tailor strategies that align with their risk tolerance and investment objectives.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Risk Parity Portfolio | Minimum Variance Portfolio |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | Equal risk contribution across assets | Minimize total portfolio variance |
| Risk Allocation | Balanced risk weighting | Focus on assets with lowest variance and covariance |
| Volatility | Moderate and diversified volatility exposure | Lowest achievable portfolio volatility |
| Asset Weights | Weights adjusted to equalize risk contribution | Weights optimized to minimize variance |
| Typical Asset Classes | Broad mix, including bonds, equities, commodities | Concentrated in low-volatility assets (e.g., bonds) |
| Performance in Volatile Markets | Stable returns due to balanced risk | Potentially better downside protection |
| Drawbacks | May overweight low-volatility assets | Can lead to concentrated portfolios |
| Use Case | Investors seeking diversification and balanced risk | Investors prioritizing risk minimization |
Which is better?
Risk parity portfolios allocate assets to balance risk contributions equally, improving diversification across asset classes and offering more stable returns in volatile markets. Minimum variance portfolios focus on minimizing total portfolio volatility by selecting assets with the lowest correlation and variance, often resulting in concentrated holdings. Studies show risk parity portfolios tend to perform better during market downturns due to balanced risk exposure, while minimum variance portfolios may underperform in rising markets due to reduced upside potential.
Connection
Risk parity portfolios and minimum variance portfolios both aim to optimize risk allocation by balancing asset contributions to overall portfolio volatility. Risk parity focuses on equalizing risk contributions across asset classes, often resulting in diversified exposures, while minimum variance portfolios emphasize minimizing total portfolio variance through asset weight optimization. Their connection lies in the shared objective of reducing portfolio risk through strategic asset allocation based on covariance and volatility measures.
Key Terms
Covariance Matrix
Minimum variance portfolios directly optimize asset weights to minimize portfolio variance based on the covariance matrix, emphasizing assets with lower volatility and correlations. Risk parity portfolios allocate weights to equalize risk contributions across assets, relying on the covariance matrix to balance the marginal risk per asset, often resulting in more diversified allocations. Explore further to understand how covariance matrix estimation impacts portfolio performance and robustness.
Portfolio Weights
Minimum variance portfolios prioritize assets with the lowest individual variances and covariances to construct weights that minimize overall portfolio volatility, often resulting in concentrated allocations. Risk parity portfolios allocate weights inversely proportional to asset risk contributions, promoting balanced exposure across asset classes and diversifying risk more evenly. Explore detailed comparisons of portfolio weights and their implications for optimized asset allocation strategies.
Risk Contribution
Minimum variance portfolios aim to minimize total portfolio variance by assigning weights that reduce overall risk, often resulting in concentrated positions in low-volatility assets. Risk parity portfolios balance risk contributions from each asset, ensuring that each component contributes equally to portfolio volatility, promoting diversification across asset classes regardless of their individual variances. Explore the detailed methodologies and comparative benefits of these portfolio strategies to optimize your investment risk management.
Source and External Links
Minimum Variance Portfolio - Meaning, Formula, Calculation - A minimum variance portfolio is an investment strategy that uses diversification to minimize risk and maximize profits, calculated using a formula involving the weights, standard deviations, and covariance of the assets in the portfolio.
Minimum-Variance Portfolio | Meaning, Construction, Applications - This portfolio aims to minimize overall risk by choosing assets with low or negative correlations, using techniques such as covariance matrix creation and mean-variance optimization to find the asset allocation that minimizes portfolio variance.
Minimum-Variance Portfolios | CFA Level 1 - AnalystPrep - The global minimum-variance portfolio represents the portfolio of risky assets with the lowest possible risk, lying at the extreme left of the efficient frontier and providing the minimum risk achievable without including risk-free assets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com