Latency arbitrage exploits temporary price discrepancies between markets caused by speed advantages in executing trades, primarily in high-frequency trading environments. Merger arbitrage involves profiting from the price differences between a company's stock before and after a merger or acquisition announcement, typically by buying the target's stock and shorting the acquirer's stock. Explore the nuances and strategies behind latency arbitrage and merger arbitrage to deepen your understanding of advanced financial trading techniques.
Why it is important
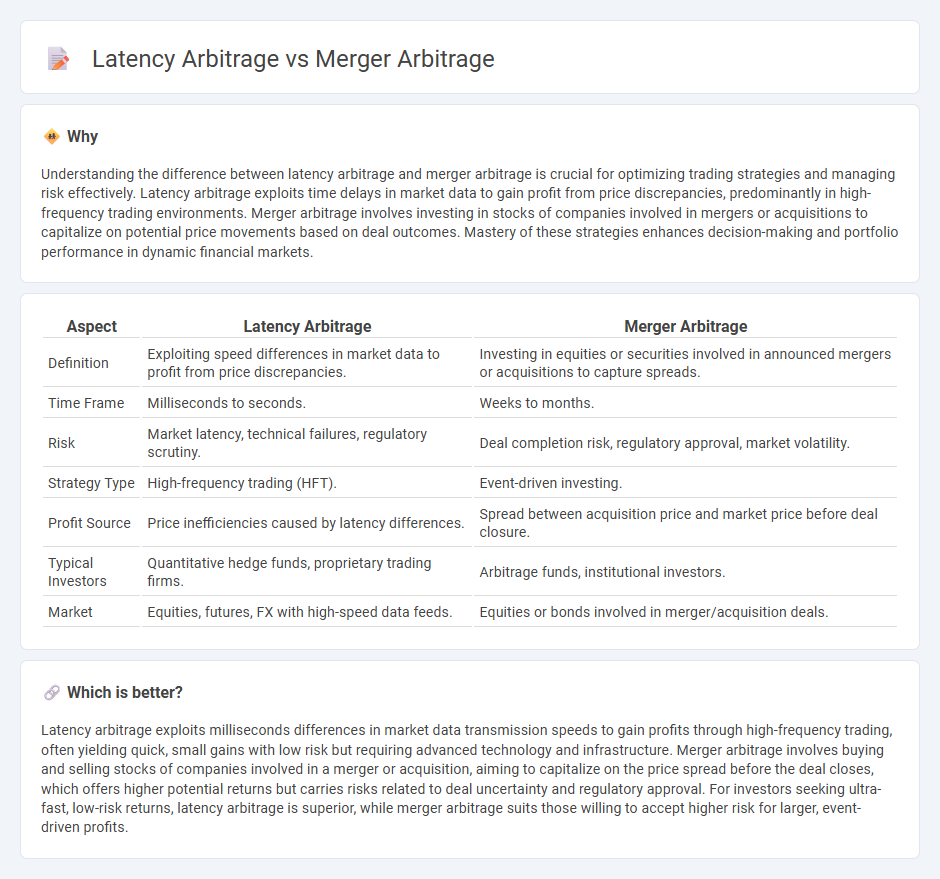
Understanding the difference between latency arbitrage and merger arbitrage is crucial for optimizing trading strategies and managing risk effectively. Latency arbitrage exploits time delays in market data to gain profit from price discrepancies, predominantly in high-frequency trading environments. Merger arbitrage involves investing in stocks of companies involved in mergers or acquisitions to capitalize on potential price movements based on deal outcomes. Mastery of these strategies enhances decision-making and portfolio performance in dynamic financial markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Latency Arbitrage | Merger Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exploiting speed differences in market data to profit from price discrepancies. | Investing in equities or securities involved in announced mergers or acquisitions to capture spreads. |
| Time Frame | Milliseconds to seconds. | Weeks to months. |
| Risk | Market latency, technical failures, regulatory scrutiny. | Deal completion risk, regulatory approval, market volatility. |
| Strategy Type | High-frequency trading (HFT). | Event-driven investing. |
| Profit Source | Price inefficiencies caused by latency differences. | Spread between acquisition price and market price before deal closure. |
| Typical Investors | Quantitative hedge funds, proprietary trading firms. | Arbitrage funds, institutional investors. |
| Market | Equities, futures, FX with high-speed data feeds. | Equities or bonds involved in merger/acquisition deals. |
Which is better?
Latency arbitrage exploits milliseconds differences in market data transmission speeds to gain profits through high-frequency trading, often yielding quick, small gains with low risk but requiring advanced technology and infrastructure. Merger arbitrage involves buying and selling stocks of companies involved in a merger or acquisition, aiming to capitalize on the price spread before the deal closes, which offers higher potential returns but carries risks related to deal uncertainty and regulatory approval. For investors seeking ultra-fast, low-risk returns, latency arbitrage is superior, while merger arbitrage suits those willing to accept higher risk for larger, event-driven profits.
Connection
Latency arbitrage and merger arbitrage both exploit timing inefficiencies in financial markets to generate profit. Latency arbitrage leverages speed advantages in trade execution to capitalize on minor price discrepancies, while merger arbitrage focuses on trading securities of companies involved in mergers and acquisitions by analyzing deal announcement and completion timelines. The connection lies in their reliance on information asymmetry and precise timing to achieve arbitrage opportunities in dynamic market conditions.
Key Terms
**Merger Arbitrage:**
Merger arbitrage involves capitalizing on the price inefficiencies of acquiring target companies during merger and acquisition deals, typically by purchasing the target's stock at a discount to the proposed acquisition price and profiting when the deal closes. This strategy requires deep analysis of deal terms, regulatory risks, and potential obstacles that could delay or derail the merger. Explore the nuances and risk management strategies behind merger arbitrage for a comprehensive understanding.
Tender Offer
Merger arbitrage involves profiting from the price discrepancy between a target company's stock and the offer price in a tender offer, typically exploiting the uncertainty during the deal's closing process. Latency arbitrage capitalizes on speed advantages by executing trades faster than competitors during the tender offer period, capturing fleeting price inefficiencies caused by information delays. Explore deeper insights into how these strategies operate in tender offers to enhance your trading approaches.
Spread
Merger arbitrage typically exploits price discrepancies between a target company's stock and its acquisition offer, with the spread reflecting the deal's risk and expected completion time. Latency arbitrage capitalizes on minute delays in market data transmission, profiting from transient spreads caused by speed differentials in accessing price information. Explore the nuances of spreads in these arbitrage strategies to understand their distinct risk-return profiles.
Source and External Links
Merger arbitrage: Process, examples, types, and risks - Merger arbitrage is an event-driven investment strategy focused on buying the target company's stock at a price below its expected value after a successful merger, with key steps including researching the target, understanding the merger agreement, and analyzing risk/reward.
An Introduction to Merger Arbitrage - This strategy involves profiting from the spread between the target's stock price and the acquisition price in mergers, with common types including stock-for-stock, cash, and mixed consideration mergers.
Risk arbitrage - Merger arbitrage speculates on successful merger completions by buying target stock and, in stock mergers, shorting acquirer stock to profit from price convergence upon deal closure.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com