Flash loan attacks exploit instant, uncollateralized loans to manipulate DeFi protocols, often causing rapid price swings and financial losses. Market manipulation involves strategies like pump-and-dump or spoofing to distort asset prices and mislead investors, impacting market integrity. Discover how these tactics differ and their implications for financial security.
Why it is important
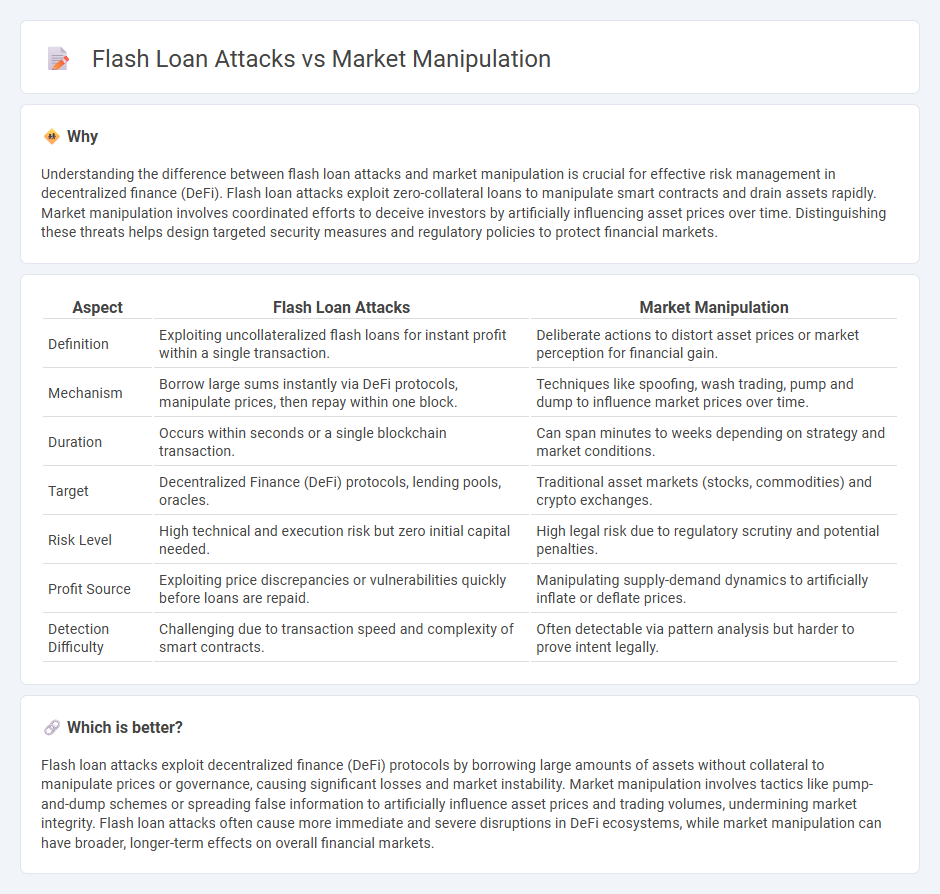
Understanding the difference between flash loan attacks and market manipulation is crucial for effective risk management in decentralized finance (DeFi). Flash loan attacks exploit zero-collateral loans to manipulate smart contracts and drain assets rapidly. Market manipulation involves coordinated efforts to deceive investors by artificially influencing asset prices over time. Distinguishing these threats helps design targeted security measures and regulatory policies to protect financial markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Flash Loan Attacks | Market Manipulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exploiting uncollateralized flash loans for instant profit within a single transaction. | Deliberate actions to distort asset prices or market perception for financial gain. |
| Mechanism | Borrow large sums instantly via DeFi protocols, manipulate prices, then repay within one block. | Techniques like spoofing, wash trading, pump and dump to influence market prices over time. |
| Duration | Occurs within seconds or a single blockchain transaction. | Can span minutes to weeks depending on strategy and market conditions. |
| Target | Decentralized Finance (DeFi) protocols, lending pools, oracles. | Traditional asset markets (stocks, commodities) and crypto exchanges. |
| Risk Level | High technical and execution risk but zero initial capital needed. | High legal risk due to regulatory scrutiny and potential penalties. |
| Profit Source | Exploiting price discrepancies or vulnerabilities quickly before loans are repaid. | Manipulating supply-demand dynamics to artificially inflate or deflate prices. |
| Detection Difficulty | Challenging due to transaction speed and complexity of smart contracts. | Often detectable via pattern analysis but harder to prove intent legally. |
Which is better?
Flash loan attacks exploit decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols by borrowing large amounts of assets without collateral to manipulate prices or governance, causing significant losses and market instability. Market manipulation involves tactics like pump-and-dump schemes or spreading false information to artificially influence asset prices and trading volumes, undermining market integrity. Flash loan attacks often cause more immediate and severe disruptions in DeFi ecosystems, while market manipulation can have broader, longer-term effects on overall financial markets.
Connection
Flash loan attacks exploit vulnerabilities in decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols by borrowing large amounts of capital without collateral, enabling attackers to manipulate market prices through rapid trades or oracle price manipulation. This artificial price distortion facilitates market manipulation tactics such as spoofing, pump-and-dump schemes, or liquidation attacks within DeFi ecosystems. The connection lies in the exploitation of flash loans to create temporary market imbalances that undermine liquidity pools and decentralized exchanges.
Key Terms
Price Manipulation
Price manipulation through flash loan attacks exploits the ability to borrow large sums instantly, creating artificial demand or supply that distorts asset prices on decentralized exchanges. Market manipulation often involves coordinated trades, wash trading, or spoofing to mislead other traders, but flash loans enable executing these strategies without upfront capital. Explore deeper insights into how price manipulation mechanisms differ and intersect within decentralized finance markets.
Liquidity
Market manipulation often exploits liquidity gaps to artificially influence asset prices, while flash loan attacks leverage large, instantaneous liquidity to execute rapid, uncollateralized trades that destabilize markets. Both tactics disrupt normal trading flows, with market manipulation targeting slower liquidity responses and flash loans exploiting immediate liquidity access to trigger price oracle manipulations or liquidations. Explore detailed case studies and defense mechanisms to better understand how liquidity plays a crucial role in these attack vectors.
Arbitrage
Market manipulation exploits price discrepancies through deceptive trading strategies, while flash loan attacks rapidly borrow large amounts of capital to execute arbitrage opportunities within a single blockchain transaction. Arbitrage in these contexts involves profiting from price differences across decentralized exchanges (DEXs) or blockchains, but flash loan attacks amplify the potential gains by temporarily accessing significant liquidity without collateral. Explore the mechanisms behind arbitrage, market manipulation, and flash loan exploits to understand their impact on decentralized finance security.
Source and External Links
Market Manipulation | EBSCO Research Starters - Market manipulation is the intentional interference with financial markets via deceptive practices like spreading false information or artificially inflating stock prices to gain financially, which is largely illegal under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 but remains challenging to detect.
Market Manipulation - Overview, How It Works, and Techniques - Market manipulation involves artificially inflating or deflating the price of securities for personal gain, often easier to execute with small companies' stocks, through methods such as placing misleading orders to influence investor perception and market price.
Market Manipulation - Investor.gov - Market manipulation artificially alters supply or demand for securities, using tactics like spreading false information, rigging trades, or creating fake trading volume, with microcap stocks being particularly vulnerable to these schemes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com