Climate-linked derivatives provide financial instruments that allow investors to hedge risks related to climate change, such as temperature fluctuations or carbon credit price volatility. Emissions allowances, often traded under cap-and-trade systems, represent the legal right to emit a specific amount of greenhouse gases, influencing corporate environmental strategy and regulatory compliance. Explore how these market tools drive climate finance efficiency and risk management.
Why it is important
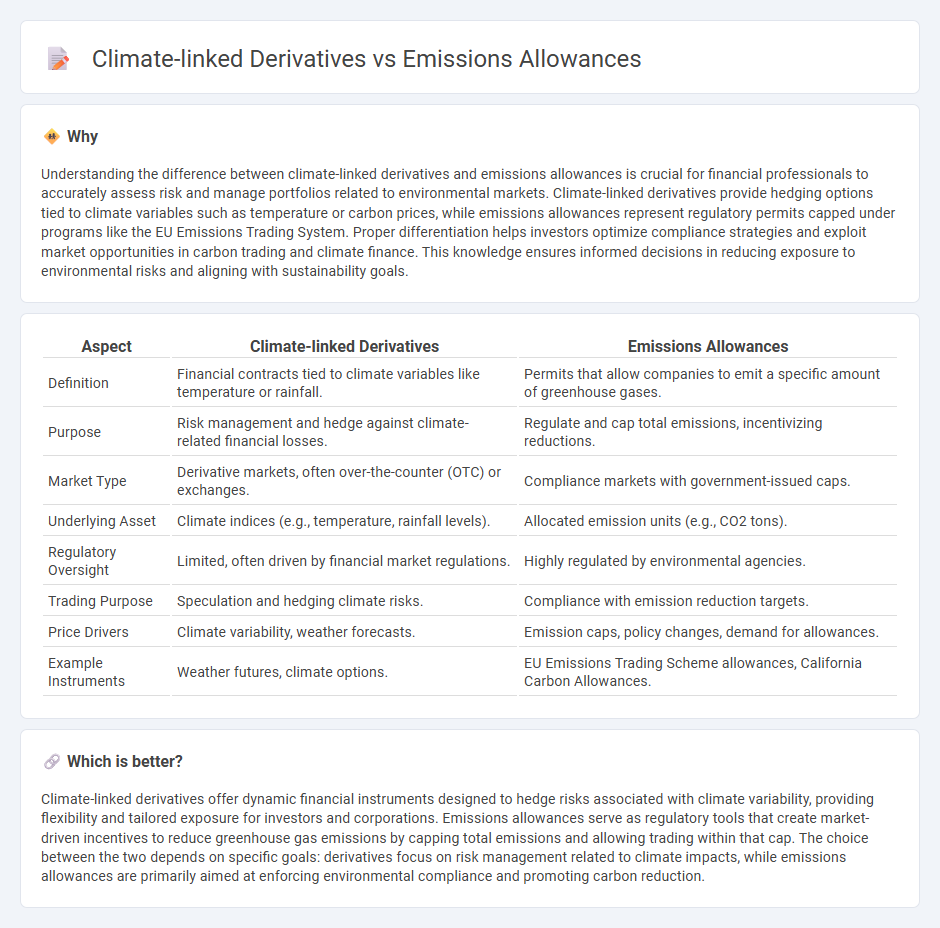
Understanding the difference between climate-linked derivatives and emissions allowances is crucial for financial professionals to accurately assess risk and manage portfolios related to environmental markets. Climate-linked derivatives provide hedging options tied to climate variables such as temperature or carbon prices, while emissions allowances represent regulatory permits capped under programs like the EU Emissions Trading System. Proper differentiation helps investors optimize compliance strategies and exploit market opportunities in carbon trading and climate finance. This knowledge ensures informed decisions in reducing exposure to environmental risks and aligning with sustainability goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Climate-linked Derivatives | Emissions Allowances |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial contracts tied to climate variables like temperature or rainfall. | Permits that allow companies to emit a specific amount of greenhouse gases. |
| Purpose | Risk management and hedge against climate-related financial losses. | Regulate and cap total emissions, incentivizing reductions. |
| Market Type | Derivative markets, often over-the-counter (OTC) or exchanges. | Compliance markets with government-issued caps. |
| Underlying Asset | Climate indices (e.g., temperature, rainfall levels). | Allocated emission units (e.g., CO2 tons). |
| Regulatory Oversight | Limited, often driven by financial market regulations. | Highly regulated by environmental agencies. |
| Trading Purpose | Speculation and hedging climate risks. | Compliance with emission reduction targets. |
| Price Drivers | Climate variability, weather forecasts. | Emission caps, policy changes, demand for allowances. |
| Example Instruments | Weather futures, climate options. | EU Emissions Trading Scheme allowances, California Carbon Allowances. |
Which is better?
Climate-linked derivatives offer dynamic financial instruments designed to hedge risks associated with climate variability, providing flexibility and tailored exposure for investors and corporations. Emissions allowances serve as regulatory tools that create market-driven incentives to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by capping total emissions and allowing trading within that cap. The choice between the two depends on specific goals: derivatives focus on risk management related to climate impacts, while emissions allowances are primarily aimed at enforcing environmental compliance and promoting carbon reduction.
Connection
Climate-linked derivatives are financial instruments designed to hedge or speculate on risks associated with climate change, often tied to emissions metrics. Emissions allowances represent permits to emit a certain amount of greenhouse gases, trading within carbon markets that influence the pricing and demand of these derivatives. The intersection of both creates a dynamic ecosystem where financial markets actively manage climate-related regulatory risks and carbon credit valuations.
Key Terms
Cap-and-Trade
Emissions allowances represent permits that allow companies to emit a specific amount of greenhouse gases under cap-and-trade systems, providing a market-driven approach to reducing overall emissions. Climate-linked derivatives, such as futures and options, offer financial instruments tied to these allowances, enabling firms to hedge risks related to fluctuating carbon prices and regulatory changes. Explore how combining emissions allowances and climate-linked derivatives can optimize risk management and compliance strategies in cap-and-trade programs.
Carbon Credits
Emissions allowances represent government-issued permits that cap the amount of greenhouse gases a company can emit, serving as a regulatory tool within cap-and-trade systems. Climate-linked derivatives, particularly those tied to carbon credits, are financial instruments allowing investors to hedge or speculate on carbon pricing fluctuations, enhancing market liquidity for emission reductions. Explore how carbon credits function as both compliance mechanisms and investment opportunities in the evolving carbon markets.
Hedging
Emissions allowances provide a regulatory framework for companies to limit greenhouse gas outputs, serving as a direct tool for compliance and hedging against carbon price volatility. Climate-linked derivatives, such as carbon futures and options, offer financial instruments designed to hedge risks associated with fluctuating carbon markets and climate policies. Explore how integrating these tools can optimize your climate risk management strategy.
Source and External Links
About Carbon Credits, Carbon Allowances, and Emission Allowances - Emissions allowances are permits allowing organizations to emit a specific amount of greenhouse gases, which can be complemented by carbon credits from offset projects to achieve net-zero emissions goals.
Are you receiving emissions allowances from the government? - Under cap-and-trade schemes, governments allocate emission allowances that companies must match with their emissions during compliance periods, allowing trading of allowances to meet limits.
Understanding & Accounting For Emission Allowances - Emission allowances are tradable rights to emit certain gases, typically accounted for as inventory or intangible assets, with specific accounting treatments for cost, impairment, and sales gains or losses.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com