Climate-linked derivatives provide financial instruments that hedge risks related to climate variables like temperature and rainfall, offering tailored solutions for sectors vulnerable to climate change. Green bonds fund environmentally sustainable projects, delivering fixed returns while supporting renewable energy, conservation, and clean transportation initiatives. Discover how these innovative finance tools can optimize your investment strategy and drive impactful climate action.
Why it is important
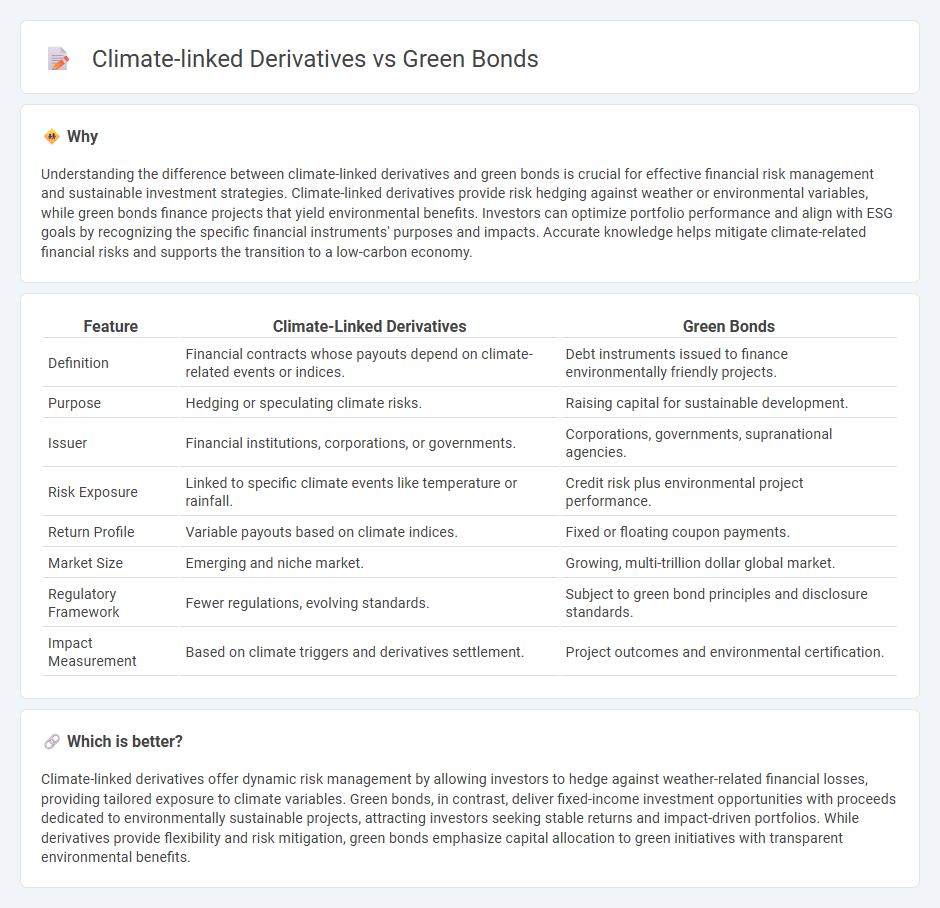
Understanding the difference between climate-linked derivatives and green bonds is crucial for effective financial risk management and sustainable investment strategies. Climate-linked derivatives provide risk hedging against weather or environmental variables, while green bonds finance projects that yield environmental benefits. Investors can optimize portfolio performance and align with ESG goals by recognizing the specific financial instruments' purposes and impacts. Accurate knowledge helps mitigate climate-related financial risks and supports the transition to a low-carbon economy.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Climate-Linked Derivatives | Green Bonds |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial contracts whose payouts depend on climate-related events or indices. | Debt instruments issued to finance environmentally friendly projects. |
| Purpose | Hedging or speculating climate risks. | Raising capital for sustainable development. |
| Issuer | Financial institutions, corporations, or governments. | Corporations, governments, supranational agencies. |
| Risk Exposure | Linked to specific climate events like temperature or rainfall. | Credit risk plus environmental project performance. |
| Return Profile | Variable payouts based on climate indices. | Fixed or floating coupon payments. |
| Market Size | Emerging and niche market. | Growing, multi-trillion dollar global market. |
| Regulatory Framework | Fewer regulations, evolving standards. | Subject to green bond principles and disclosure standards. |
| Impact Measurement | Based on climate triggers and derivatives settlement. | Project outcomes and environmental certification. |
Which is better?
Climate-linked derivatives offer dynamic risk management by allowing investors to hedge against weather-related financial losses, providing tailored exposure to climate variables. Green bonds, in contrast, deliver fixed-income investment opportunities with proceeds dedicated to environmentally sustainable projects, attracting investors seeking stable returns and impact-driven portfolios. While derivatives provide flexibility and risk mitigation, green bonds emphasize capital allocation to green initiatives with transparent environmental benefits.
Connection
Climate-linked derivatives and green bonds are connected through their shared purpose of managing environmental risks and financing sustainable projects. Climate-linked derivatives provide financial instruments that hedge against climate-related risks, while green bonds raise capital specifically for environmentally beneficial initiatives. Both tools contribute to the growth of sustainable finance markets by aligning investment strategies with climate resilience and carbon reduction goals.
Key Terms
Issuance Purpose
Green bonds are debt instruments specifically issued to finance projects with environmental benefits such as renewable energy, clean transportation, or sustainable water management, aiming to attract investors committed to sustainability goals. Climate-linked derivatives serve as financial tools designed to hedge or speculate on climate-related risks like temperature variations or carbon prices, facilitating risk management for businesses impacted by climate change. Explore detailed comparisons on issuance purpose and market implications of these instruments to enhance your sustainable finance strategy.
Risk Management
Green bonds provide investors with fixed-income opportunities directly financing environmentally sustainable projects, reducing exposure to regulatory and market risks associated with climate change. Climate-linked derivatives offer dynamic risk management by allowing hedging against future climate-related financial losses through instruments tied to weather events or emission targets. Explore the nuances of how each tool enhances financial resilience in the face of climate risks to optimize your investment strategy.
Environmental Impact
Green bonds finance projects with measurable positive environmental outcomes, such as renewable energy or pollution reduction initiatives, ensuring capital supports sustainability goals. Climate-linked derivatives provide financial instruments to hedge risks tied to environmental variables, enabling companies to manage climate-related financial exposure more effectively. Explore how these financial tools drive environmental impact by learning more about their mechanisms and benefits.
Source and External Links
Green bond - Wikipedia - A green bond is a fixed-income financial instrument used exclusively to fund projects with positive environmental benefits, such as renewable energy, clean transportation, and climate change adaptation, enabling investors to meet environmental, social, and governance goals.
What are Green Bonds and what projects do they finance? - Iberdrola - Green bonds are debt instruments issued by public or private entities committing funds solely to environmental or climate change projects, such as renewable energy and energy efficiency, supporting Sustainable Development Goals like affordable energy and climate action.
Green Bond Principles (GBP) - ICMA - The Green Bond Principles are voluntary guidelines promoting transparency, disclosure, and integrity in green bond issuance to finance projects fostering a net-zero emissions economy and environmental protection, with a focus on clear reporting of use of proceeds and impact.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com