Risk parity portfolios allocate capital based on the risk contribution of each asset, aiming for balanced volatility exposure and improved diversification across asset classes. Equal-weighted portfolios assign identical weights to each asset regardless of risk, potentially leading to disproportionate exposure to more volatile assets. Explore the key differences and advantages of these portfolio strategies to enhance investment decisions.
Why it is important
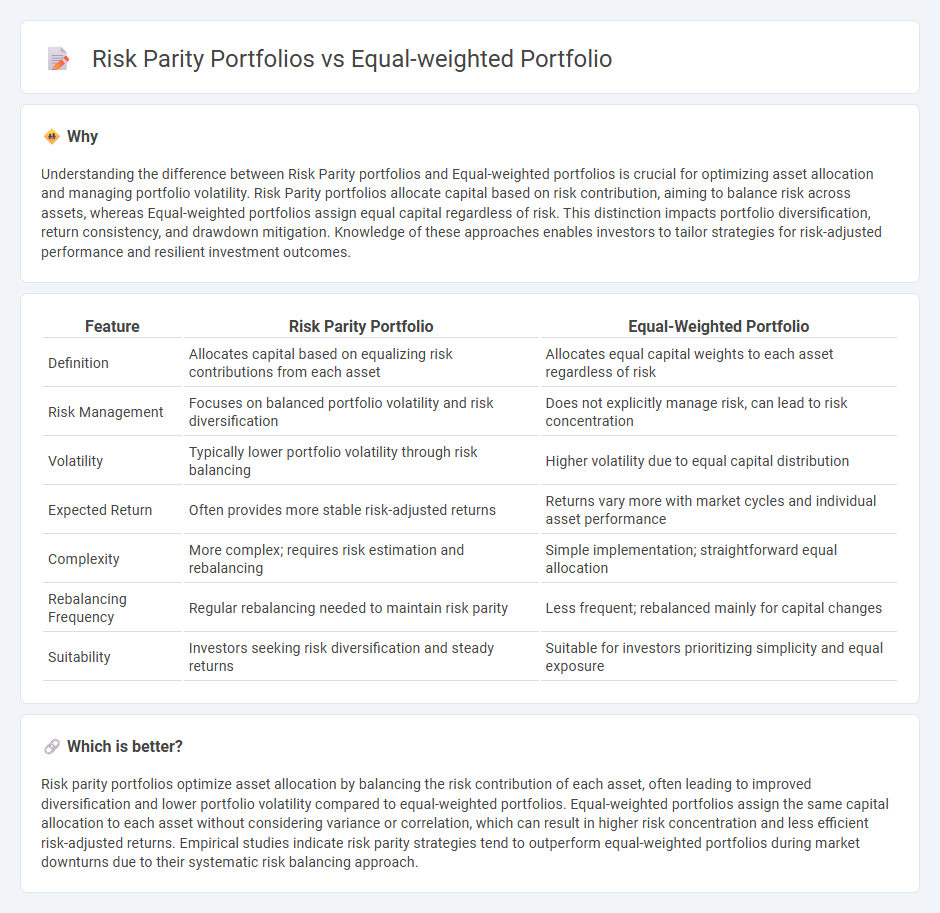
Understanding the difference between Risk Parity portfolios and Equal-weighted portfolios is crucial for optimizing asset allocation and managing portfolio volatility. Risk Parity portfolios allocate capital based on risk contribution, aiming to balance risk across assets, whereas Equal-weighted portfolios assign equal capital regardless of risk. This distinction impacts portfolio diversification, return consistency, and drawdown mitigation. Knowledge of these approaches enables investors to tailor strategies for risk-adjusted performance and resilient investment outcomes.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Risk Parity Portfolio | Equal-Weighted Portfolio |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Allocates capital based on equalizing risk contributions from each asset | Allocates equal capital weights to each asset regardless of risk |
| Risk Management | Focuses on balanced portfolio volatility and risk diversification | Does not explicitly manage risk, can lead to risk concentration |
| Volatility | Typically lower portfolio volatility through risk balancing | Higher volatility due to equal capital distribution |
| Expected Return | Often provides more stable risk-adjusted returns | Returns vary more with market cycles and individual asset performance |
| Complexity | More complex; requires risk estimation and rebalancing | Simple implementation; straightforward equal allocation |
| Rebalancing Frequency | Regular rebalancing needed to maintain risk parity | Less frequent; rebalanced mainly for capital changes |
| Suitability | Investors seeking risk diversification and steady returns | Suitable for investors prioritizing simplicity and equal exposure |
Which is better?
Risk parity portfolios optimize asset allocation by balancing the risk contribution of each asset, often leading to improved diversification and lower portfolio volatility compared to equal-weighted portfolios. Equal-weighted portfolios assign the same capital allocation to each asset without considering variance or correlation, which can result in higher risk concentration and less efficient risk-adjusted returns. Empirical studies indicate risk parity strategies tend to outperform equal-weighted portfolios during market downturns due to their systematic risk balancing approach.
Connection
Risk parity portfolios and equal-weighted portfolios both aim to diversify risk by allocating equal importance across assets or asset classes, but risk parity focuses on balancing risk contributions based on volatility and correlation, whereas equal-weighted portfolios assign uniform capital weights without adjusting for risk differences. Risk parity strategies typically use leverage to achieve target volatility, optimizing risk-adjusted returns, while equal-weighted portfolios inherently maintain simplicity and transparency in allocation. Investors seeking exposure to diversified risk may combine insights from both approaches to enhance portfolio resilience under varying market conditions.
Key Terms
Asset Allocation
Equal-weighted portfolios allocate capital uniformly across all assets, providing straightforward diversification but potentially ignoring individual asset risk profiles. Risk parity portfolios adjust weights based on asset volatility and correlations, aiming to balance risk contributions and enhance risk-adjusted returns. Explore in-depth analyses to understand which asset allocation strategy aligns best with your investment goals.
Volatility
Equal-weighted portfolios allocate assets uniformly, resulting in volatility primarily driven by the most volatile holdings. Risk parity portfolios adjust asset weights to balance contributions to portfolio volatility, aiming for more stable risk exposure across asset classes. Explore the performance differences and risk characteristics between these strategies to optimize your investment approach.
Portfolio Weights
Equal-weighted portfolios assign identical weights to each asset, ensuring uniform exposure regardless of volatility or correlation. Risk parity portfolios allocate weights based on the inverse of asset risk, balancing contributions to overall portfolio volatility by emphasizing lower-risk assets. Explore further to understand how these weighting methods impact diversification and risk-adjusted returns.
Source and External Links
Equal Weight Portfolio: A Simple Strategy for Diversified Investing - An equal-weighted portfolio assigns the same investment weight to every stock or asset, regardless of company size, allowing for a more balanced and diversified investment exposure, including smaller companies that market-cap-weighted portfolios may underrepresent.
How to Calculate Equal Weighted Index - SoFi - An equal-weighted index assigns the same weight to each stock in the index, requiring periodic rebalancing, and can offer increased diversification and reduced concentration risk compared to market-cap-weighted indexes.
What to consider when choosing between index-weighting ... - Equal weighting underweights large-cap stocks and overweights small-cap stocks relative to market-cap weighting, changing the risk profile and making it a more active, balanced approach than traditional passive market-cap weighting.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com