Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) enable peer-to-peer trading of cryptocurrencies without intermediaries, enhancing security and transparency through blockchain technology. Cross-chain bridges facilitate the transfer of assets and data between different blockchain networks, improving interoperability and expanding liquidity options across ecosystems like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Solana. Discover the key differences, benefits, and risks of DEXs and cross-chain bridges to optimize your blockchain trading strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between decentralized exchanges (DEXs) and cross-chain bridges is crucial for secure and efficient asset transfers in the blockchain ecosystem. DEXs facilitate peer-to-peer trading within a single blockchain, minimizing reliance on intermediaries and reducing counterparty risk. Cross-chain bridges enable interoperability by allowing assets and data to move between different blockchain networks, expanding liquidity and use cases. Knowing their distinct mechanisms helps users optimize transaction costs, enhance security, and leverage the full potential of decentralized finance (DeFi).
Comparison Table
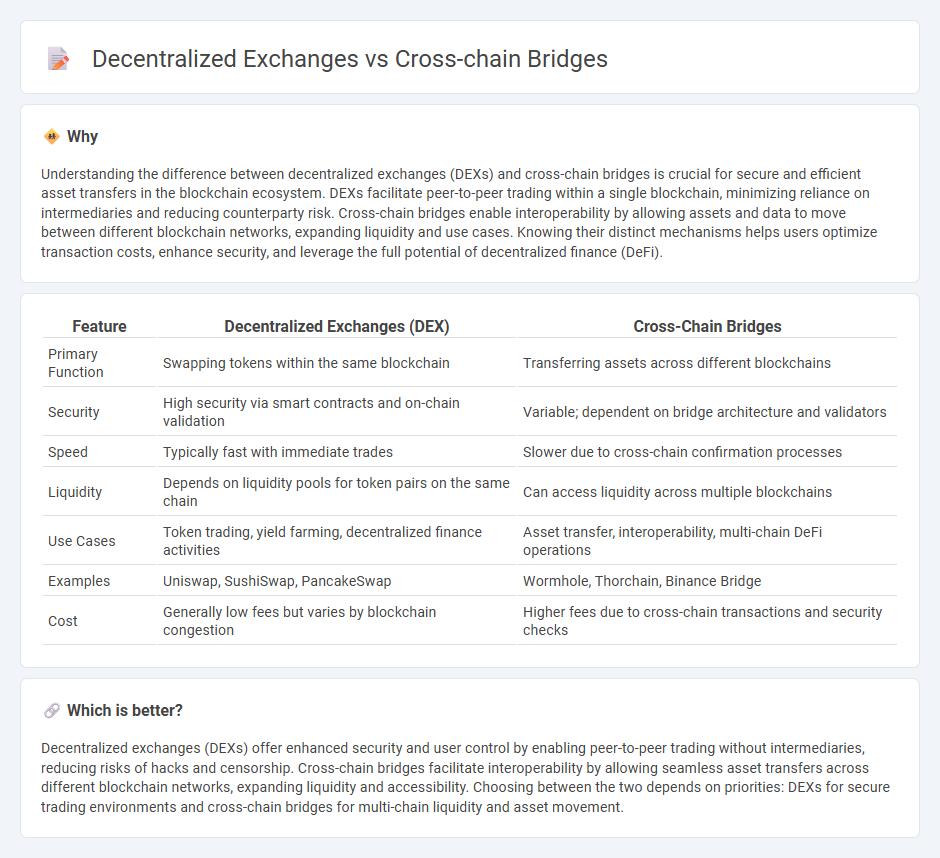
| Feature | Decentralized Exchanges (DEX) | Cross-Chain Bridges |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Swapping tokens within the same blockchain | Transferring assets across different blockchains |
| Security | High security via smart contracts and on-chain validation | Variable; dependent on bridge architecture and validators |
| Speed | Typically fast with immediate trades | Slower due to cross-chain confirmation processes |
| Liquidity | Depends on liquidity pools for token pairs on the same chain | Can access liquidity across multiple blockchains |
| Use Cases | Token trading, yield farming, decentralized finance activities | Asset transfer, interoperability, multi-chain DeFi operations |
| Examples | Uniswap, SushiSwap, PancakeSwap | Wormhole, Thorchain, Binance Bridge |
| Cost | Generally low fees but varies by blockchain congestion | Higher fees due to cross-chain transactions and security checks |
Which is better?
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) offer enhanced security and user control by enabling peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries, reducing risks of hacks and censorship. Cross-chain bridges facilitate interoperability by allowing seamless asset transfers across different blockchain networks, expanding liquidity and accessibility. Choosing between the two depends on priorities: DEXs for secure trading environments and cross-chain bridges for multi-chain liquidity and asset movement.
Connection
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) leverage cross-chain bridges to enable seamless asset swaps between different blockchain networks without relying on centralized intermediaries. Cross-chain bridges facilitate interoperability by securely transferring tokens and data across multiple blockchains, expanding liquidity pools available on DEX platforms. This integration enhances decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems by promoting efficient cross-chain trading and reducing transaction friction.
Key Terms
Interoperability
Cross-chain bridges enable interoperability by facilitating direct asset transfers across different blockchain networks, overcoming isolated ledgers' limitations. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) offer cross-chain token swaps but rely on smart contract protocols within specific chains, which can introduce liquidity fragmentation. Explore how cross-chain solutions enhance seamless asset movement and improve decentralized finance efficiency.
Liquidity
Cross-chain bridges enable seamless asset transfers between different blockchain networks, significantly enhancing liquidity accessibility by connecting otherwise isolated ecosystems. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) provide liquidity pools within specific blockchains but face limitations in cross-chain asset interoperability. Explore how leveraging both technologies can optimize liquidity strategies across the evolving decentralized finance landscape.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts in cross-chain bridges enable secure asset transfers between different blockchains by automatically verifying and executing transactions without intermediaries. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) utilize smart contracts to facilitate peer-to-peer token swaps on a single blockchain, ensuring transparency and reducing custody risks. Explore deeper insights into how smart contracts power cross-chain bridges and DEXs for seamless decentralized finance.
Source and External Links
What Is A Cross Chain Bridge? - A cross-chain bridge is a decentralized application that enables transferring assets between blockchains using mechanisms like lock and mint, burn and mint, or lock and unlock, and can also carry arbitrary data for more complex cross-chain functions.
Introduction to Cross-Chain Bridges - Cross-chain bridges provide interoperability by allowing blockchains to securely share assets and data, expanding DeFi opportunities and enabling multi-chain decentralized applications with high transaction volumes.
What are cross-chain bridges? How interoperable crypto ... - Cross-chain bridges facilitate asset transfers between blockchains improving efficiency, scalability, and transaction speed while reducing reliance on single chains, but carry some inherent risks.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com