Dark pool routing enables large institutional investors to execute sizable orders privately, minimizing market impact and price slippage by avoiding public exchanges. Algorithmic trading leverages complex mathematical models and real-time data to automate order executions, optimizing timing and pricing across multiple markets. Explore deeper insights into how these strategies transform modern financial trading dynamics.
Why it is important
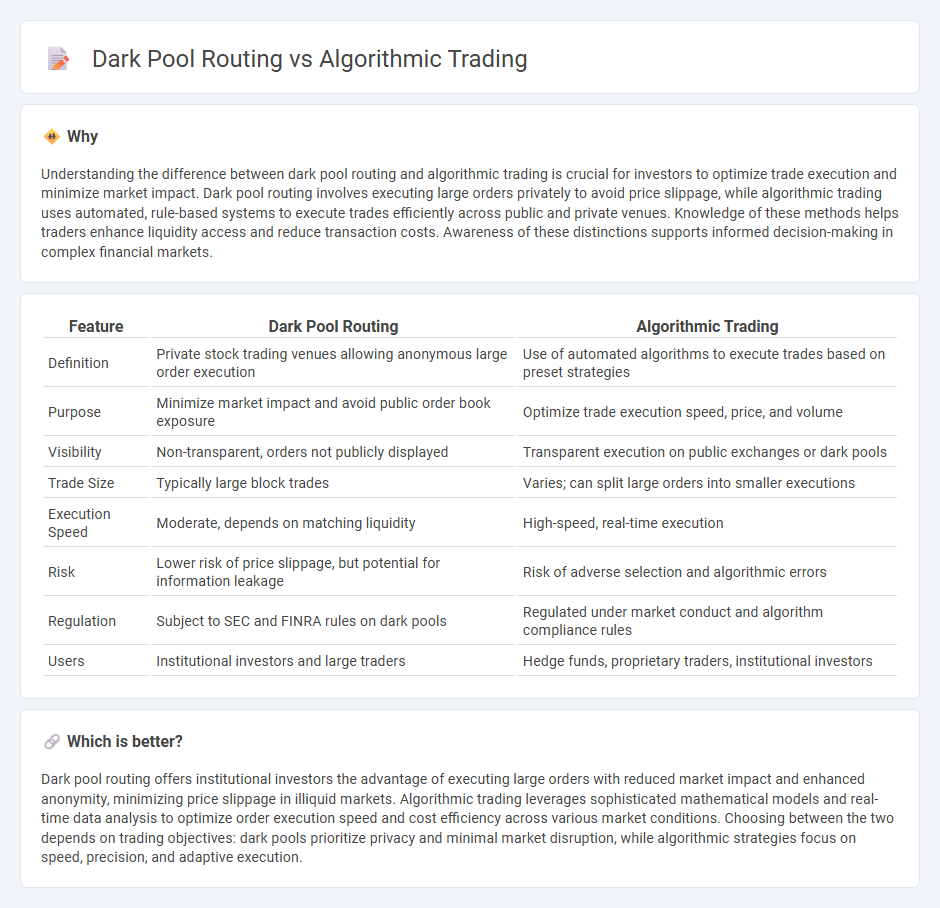
Understanding the difference between dark pool routing and algorithmic trading is crucial for investors to optimize trade execution and minimize market impact. Dark pool routing involves executing large orders privately to avoid price slippage, while algorithmic trading uses automated, rule-based systems to execute trades efficiently across public and private venues. Knowledge of these methods helps traders enhance liquidity access and reduce transaction costs. Awareness of these distinctions supports informed decision-making in complex financial markets.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Dark Pool Routing | Algorithmic Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Private stock trading venues allowing anonymous large order execution | Use of automated algorithms to execute trades based on preset strategies |
| Purpose | Minimize market impact and avoid public order book exposure | Optimize trade execution speed, price, and volume |
| Visibility | Non-transparent, orders not publicly displayed | Transparent execution on public exchanges or dark pools |
| Trade Size | Typically large block trades | Varies; can split large orders into smaller executions |
| Execution Speed | Moderate, depends on matching liquidity | High-speed, real-time execution |
| Risk | Lower risk of price slippage, but potential for information leakage | Risk of adverse selection and algorithmic errors |
| Regulation | Subject to SEC and FINRA rules on dark pools | Regulated under market conduct and algorithm compliance rules |
| Users | Institutional investors and large traders | Hedge funds, proprietary traders, institutional investors |
Which is better?
Dark pool routing offers institutional investors the advantage of executing large orders with reduced market impact and enhanced anonymity, minimizing price slippage in illiquid markets. Algorithmic trading leverages sophisticated mathematical models and real-time data analysis to optimize order execution speed and cost efficiency across various market conditions. Choosing between the two depends on trading objectives: dark pools prioritize privacy and minimal market disruption, while algorithmic strategies focus on speed, precision, and adaptive execution.
Connection
Dark pool routing leverages algorithmic trading strategies to execute large-volume orders anonymously, minimizing market impact and price slippage. Algorithmic trading systems analyze real-time market data to identify optimal dark pools, enhancing transaction efficiency and confidentiality. This synergy improves liquidity management and reduces adverse selection risks in electronic trading environments.
Key Terms
Execution Algorithms
Execution algorithms optimize order placement by breaking large trades into smaller, strategically timed orders to minimize market impact and achieve best execution prices. Dark pool routing directs orders to private, non-transparent trading venues to access liquidity without exposing trade intentions to the public market. Discover how these strategies can enhance trading efficiency and confidentiality in complex market environments.
Liquidity Access
Algorithmic trading leverages computer-coded strategies to efficiently execute large orders across multiple exchanges, optimizing liquidity access by minimizing market impact and achieving favorable pricing. Dark pool routing involves directing trade orders to private, non-transparent trading venues where large blocks of securities can be bought or sold with reduced market visibility, enhancing liquidity for institutional investors seeking anonymity. Explore how these methods transform liquidity access and trading strategies in modern financial markets.
Market Transparency
Algorithmic trading utilizes pre-programmed strategies executed by computers to optimize trade execution speed and efficiency, often increasing overall market transparency by publicly displaying orders on regulated exchanges. Dark pool routing involves executing large trades in private forums to minimize market impact and information leakage, which can limit transparency and obscure true market demand. Explore the dynamics between these trading methods and their implications on market transparency for a deeper understanding.
Source and External Links
What is Algorithmic Trading and How Do You Get Started? - IG - Algorithmic trading uses computer codes to open and close trades based on preset rules like price movement, with main strategies including price action, technical analysis, or a combination, often used by scalpers in high-frequency trading.
Algorithmic Trading - Definition, Example, Pros, Cons - Algorithmic trading involves executing trades automatically via programmed rules, such as moving average strategies, to efficiently manage trades and reduce market impact through incremental order execution.
Algorithmic trading - Wikipedia - Algorithmic trading consists of pre-programmed trading instructions that account for variables like time and price, with advanced methods incorporating machine learning, like deep reinforcement learning and directional change algorithms, to adapt dynamically to market conditions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com