Resale involves purchasing products at retail prices and selling them for profit, often targeting individual consumers through online platforms or local markets. Wholesaling focuses on buying goods in bulk directly from manufacturers or distributors to sell at lower prices to retailers or other businesses. Explore the key differences between resale and wholesaling strategies to determine which suits your entrepreneurial goals.
Why it is important
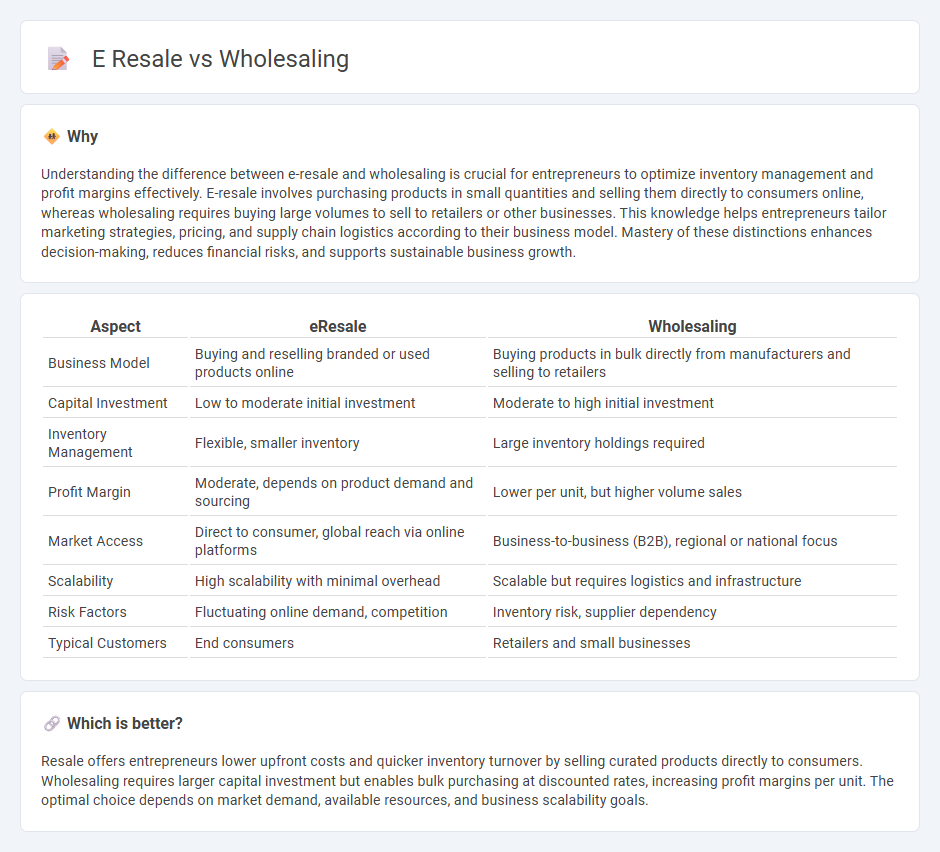
Understanding the difference between e-resale and wholesaling is crucial for entrepreneurs to optimize inventory management and profit margins effectively. E-resale involves purchasing products in small quantities and selling them directly to consumers online, whereas wholesaling requires buying large volumes to sell to retailers or other businesses. This knowledge helps entrepreneurs tailor marketing strategies, pricing, and supply chain logistics according to their business model. Mastery of these distinctions enhances decision-making, reduces financial risks, and supports sustainable business growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | eResale | Wholesaling |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Buying and reselling branded or used products online | Buying products in bulk directly from manufacturers and selling to retailers |
| Capital Investment | Low to moderate initial investment | Moderate to high initial investment |
| Inventory Management | Flexible, smaller inventory | Large inventory holdings required |
| Profit Margin | Moderate, depends on product demand and sourcing | Lower per unit, but higher volume sales |
| Market Access | Direct to consumer, global reach via online platforms | Business-to-business (B2B), regional or national focus |
| Scalability | High scalability with minimal overhead | Scalable but requires logistics and infrastructure |
| Risk Factors | Fluctuating online demand, competition | Inventory risk, supplier dependency |
| Typical Customers | End consumers | Retailers and small businesses |
Which is better?
Resale offers entrepreneurs lower upfront costs and quicker inventory turnover by selling curated products directly to consumers. Wholesaling requires larger capital investment but enables bulk purchasing at discounted rates, increasing profit margins per unit. The optimal choice depends on market demand, available resources, and business scalability goals.
Connection
Resale and wholesaling are connected through the supply chain dynamics of entrepreneurship, where wholesalers purchase goods in bulk from manufacturers and resellers acquire smaller quantities to sell directly to consumers. This relationship allows entrepreneurs to optimize inventory management and capitalize on market demand by leveraging bulk pricing and distribution networks. Understanding this connection enhances strategic sourcing decisions, driving profitability and scalability in entrepreneurial ventures.
Key Terms
Supply Chain Management
Wholesaling involves bulk purchasing and distributing goods to retailers or other businesses, emphasizing efficient inventory turnover and supplier relationships within the supply chain. E resale focuses on purchasing products from wholesalers or manufacturers and selling them directly to consumers online, requiring robust logistics, warehousing, and order fulfillment strategies to manage demand fluctuations. Explore how optimizing supply chain management can enhance profitability and customer satisfaction in both wholesaling and e resale models.
Inventory Ownership
Inventory ownership distinguishes wholesaling from resale; wholesalers purchase goods in bulk directly from manufacturers, maintaining ownership until sold to retailers. Resellers acquire products from wholesalers or manufacturers to sell to the end consumer, holding inventory temporarily before final sale. Discover how inventory management strategies impact profitability in both wholesaling and resale sectors.
Profit Margins
Wholesaling typically offers thinner profit margins due to bulk sales at lower prices, while e-resale provides higher margins by selling individual items at retail prices. Understanding market demand and product sourcing critically impacts profitability in both models. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which approach maximizes your revenue potential.
Source and External Links
Wholesaling - Wikipedia - Wholesaling is the sale of goods in bulk, usually purchased directly from the manufacturer at a discount, which are then sold to retailers or other businesses rather than end consumers.
Wholesaling: How to Start a Wholesale Business in 2025 - Shopify - Starting a wholesale business involves buying products in large quantities from manufacturers and selling them to retailers at discounted rates, serving as an intermediary in the supply chain.
Wholesale real estate: A beginner's guide | Rocket Mortgage - In real estate, wholesaling refers to contracting properties under market value and selling the purchase contract to an investor, often without actually owning the property.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com