Alt protein and insect protein represent innovative solutions to sustainable food production challenges, offering high nutritional value and lower environmental impact compared to traditional animal farming. Alt protein encompasses plant-based, cultured, and fermentation-derived sources, while insect protein capitalizes on efficient feed conversion and minimal resource use. Explore how entrepreneurship is driving these emerging markets to revolutionize the future of protein consumption.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between alt protein and insect protein is crucial for entrepreneurs targeting sustainable food markets, as alt protein typically includes plant-based and cultured options, while insect protein derives from entomophagy and has distinct production methods. This knowledge informs product development, marketing strategies, and regulatory compliance. Investors and consumers also prioritize transparency regarding health benefits and environmental impact. Accurate differentiation supports innovation and competitive advantage in the evolving alternative protein industry.
Comparison Table
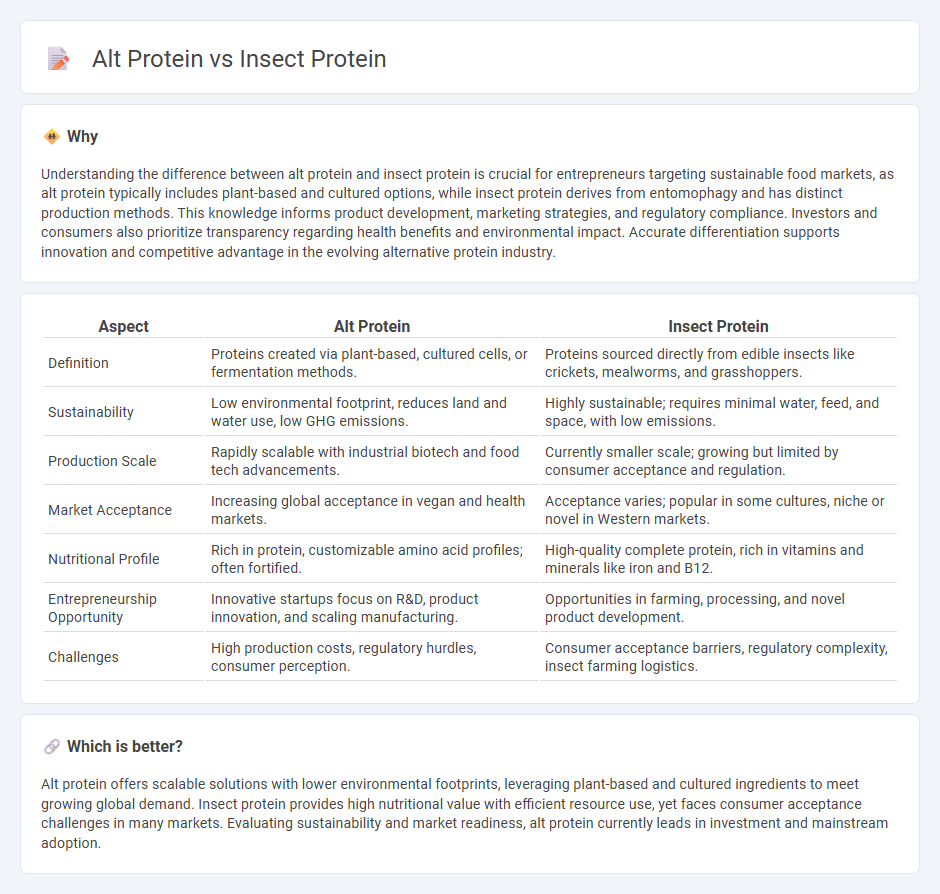
| Aspect | Alt Protein | Insect Protein |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Proteins created via plant-based, cultured cells, or fermentation methods. | Proteins sourced directly from edible insects like crickets, mealworms, and grasshoppers. |
| Sustainability | Low environmental footprint, reduces land and water use, low GHG emissions. | Highly sustainable; requires minimal water, feed, and space, with low emissions. |
| Production Scale | Rapidly scalable with industrial biotech and food tech advancements. | Currently smaller scale; growing but limited by consumer acceptance and regulation. |
| Market Acceptance | Increasing global acceptance in vegan and health markets. | Acceptance varies; popular in some cultures, niche or novel in Western markets. |
| Nutritional Profile | Rich in protein, customizable amino acid profiles; often fortified. | High-quality complete protein, rich in vitamins and minerals like iron and B12. |
| Entrepreneurship Opportunity | Innovative startups focus on R&D, product innovation, and scaling manufacturing. | Opportunities in farming, processing, and novel product development. |
| Challenges | High production costs, regulatory hurdles, consumer perception. | Consumer acceptance barriers, regulatory complexity, insect farming logistics. |
Which is better?
Alt protein offers scalable solutions with lower environmental footprints, leveraging plant-based and cultured ingredients to meet growing global demand. Insect protein provides high nutritional value with efficient resource use, yet faces consumer acceptance challenges in many markets. Evaluating sustainability and market readiness, alt protein currently leads in investment and mainstream adoption.
Connection
Alt protein and insect protein represent innovative sectors within entrepreneurship focusing on sustainable food solutions. Entrepreneurs leverage insect protein as a high-efficiency, eco-friendly source of alternative protein that addresses environmental concerns associated with traditional livestock farming. This connection drives investment in scalable production technologies, market expansion, and regulatory development to meet rising global protein demand.
Key Terms
Sustainability
Insect protein offers significant sustainability advantages over traditional alternative proteins due to its lower greenhouse gas emissions, reduced land and water usage, and efficient feed conversion ratios. Compared to plant-based and cultured meats, insects require less input to produce high-quality protein, making them a promising solution for reducing environmental impact in food production. Explore the environmental benefits of insect proteins to understand their potential role in sustainable nutrition.
Market Differentiation
Insect protein stands out in the alternative protein market due to its environmental sustainability, high feed conversion efficiency, and rich nutrient profile including essential amino acids and micronutrients. Unlike plant-based proteins, insect protein requires less land and water resources, making it a preferred choice for eco-conscious consumers and investors aiming to reduce the carbon footprint of food production. Explore the distinct advantages and market potential of insect protein to understand how it shapes the future of sustainable nutrition.
Regulatory Approval
Insect protein faces varying regulatory approval challenges globally, with the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) approving species like the yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) for human consumption, while the US FDA has recognized insect protein as Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) in specific cases. Alternative proteins, including plant-based and cultured meat, benefit from clearer regulatory frameworks and faster market entry due to broader acceptance and established safety data. Explore the evolving regulatory landscape shaping the future of innovative protein sources.
Source and External Links
Unlocking the Potential of Insect-Based Proteins - PubMed Central - Insect protein is highly efficient, sustainable, and rich in essential amino acids, with protein content variability influenced by diet, ecology, and processing; it offers a promising solution to nutrition and food security challenges worldwide.
Edible Insects as a Protein Source: A Review of Public Perception ... - Insect protein typically ranges from 35% to 60% dry weight and faces acceptance barriers in Western diets, but insect-based ingredients in familiar foods and improved safety standards could boost development of the insect protein industry.
Are Edible Insects the Future of Alternative Protein? - Edible insects are a sustainable, nutrient-rich alternative protein source requiring less land and water, but consumer reluctance remains a key challenge that may diminish over time with environmental concerns driving adoption.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com