Embedded finance integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, enabling seamless customer experiences and expanding business revenue streams. Core banking systems provide the foundational infrastructure that manages banking operations, transactions, and customer accounts through centralized software platforms. Explore how embedded finance transforms traditional banking by leveraging core systems for innovative entrepreneurship opportunities.
Why it is important
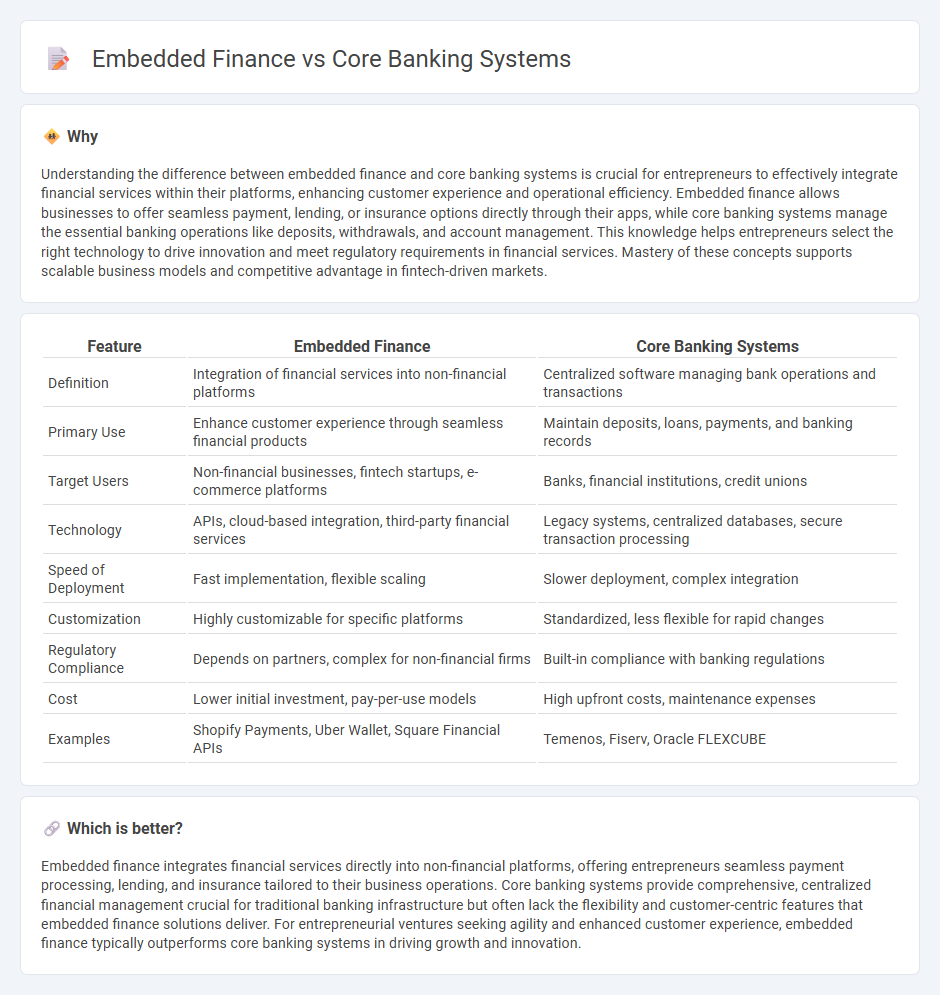
Understanding the difference between embedded finance and core banking systems is crucial for entrepreneurs to effectively integrate financial services within their platforms, enhancing customer experience and operational efficiency. Embedded finance allows businesses to offer seamless payment, lending, or insurance options directly through their apps, while core banking systems manage the essential banking operations like deposits, withdrawals, and account management. This knowledge helps entrepreneurs select the right technology to drive innovation and meet regulatory requirements in financial services. Mastery of these concepts supports scalable business models and competitive advantage in fintech-driven markets.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Embedded Finance | Core Banking Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of financial services into non-financial platforms | Centralized software managing bank operations and transactions |
| Primary Use | Enhance customer experience through seamless financial products | Maintain deposits, loans, payments, and banking records |
| Target Users | Non-financial businesses, fintech startups, e-commerce platforms | Banks, financial institutions, credit unions |
| Technology | APIs, cloud-based integration, third-party financial services | Legacy systems, centralized databases, secure transaction processing |
| Speed of Deployment | Fast implementation, flexible scaling | Slower deployment, complex integration |
| Customization | Highly customizable for specific platforms | Standardized, less flexible for rapid changes |
| Regulatory Compliance | Depends on partners, complex for non-financial firms | Built-in compliance with banking regulations |
| Cost | Lower initial investment, pay-per-use models | High upfront costs, maintenance expenses |
| Examples | Shopify Payments, Uber Wallet, Square Financial APIs | Temenos, Fiserv, Oracle FLEXCUBE |
Which is better?
Embedded finance integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, offering entrepreneurs seamless payment processing, lending, and insurance tailored to their business operations. Core banking systems provide comprehensive, centralized financial management crucial for traditional banking infrastructure but often lack the flexibility and customer-centric features that embedded finance solutions deliver. For entrepreneurial ventures seeking agility and enhanced customer experience, embedded finance typically outperforms core banking systems in driving growth and innovation.
Connection
Embedded finance integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, enabling seamless transactions and real-time credit access for entrepreneurial ventures. Core banking systems serve as the foundational infrastructure, processing and managing these financial operations with accuracy and compliance. The connection between embedded finance and core banking systems accelerates business growth by streamlining payments, lending, and account management within entrepreneurial ecosystems.
Key Terms
Integration
Core banking systems provide centralized control over financial transactions and customer accounts, enabling banks to manage deposits, loans, and payments seamlessly within their own infrastructure. Embedded finance integrates financial services directly into non-bank platforms such as e-commerce or SaaS applications, offering seamless access to payments, credit, and insurance through API-driven connectivity. Explore how these integration strategies transform customer experiences and drive innovation in fintech ecosystems.
API (Application Programming Interface)
Core banking systems rely on stable, secure APIs to enable seamless integration with financial services, ensuring real-time transaction processing and comprehensive account management. Embedded finance uses flexible, scalable APIs to integrate payment, lending, and insurance products directly into non-financial platforms, enhancing customer experience and expanding market reach. Explore the evolving role of APIs in transforming financial ecosystems and driving innovation.
Customer Experience
Core banking systems provide centralized, real-time processing of financial transactions, ensuring reliability and security across multiple banking services. Embedded finance integrates financial products directly into non-financial platforms, offering seamless and personalized experiences that enhance customer engagement and convenience. Discover how these technologies reshape customer experience in modern financial services.
Source and External Links
Core banking - Wikipedia - Core banking is a centralized banking service that allows customers to access accounts and perform transactions from any networked branch, supported by software that centralizes record keeping and enables real-time processing of deposits, loans, and payments across multiple channels.
Top Core Banking Software Companies List [2025] - SDK.finance - Core banking systems are centralized software solutions that manage all banking operations like account and transaction management, and leading providers include Temenos, Mambu, Oracle FLEXCUBE, and FIS, offering flexible, cloud or on-premises deployments to enhance operational efficiency and customer experience.
Core Banking Systems and Options for Modernization - Kansas City Fed - Core banking systems are critical IT infrastructures for processing daily banking transactions and account updates, many of which use legacy technology requiring modernization to support modern payment services like instant payments, involving coordination with core service providers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com