Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) leverage blockchain technology to enable transparent, automated decision-making without centralized control, fostering innovation and democratized ownership. Partnerships rely on legally binding agreements between individuals or entities, emphasizing shared responsibility, trust, and direct collaboration for business management. Explore the distinct advantages and challenges of DAOs versus partnerships to determine the best entrepreneurial structure for your venture.
Why it is important
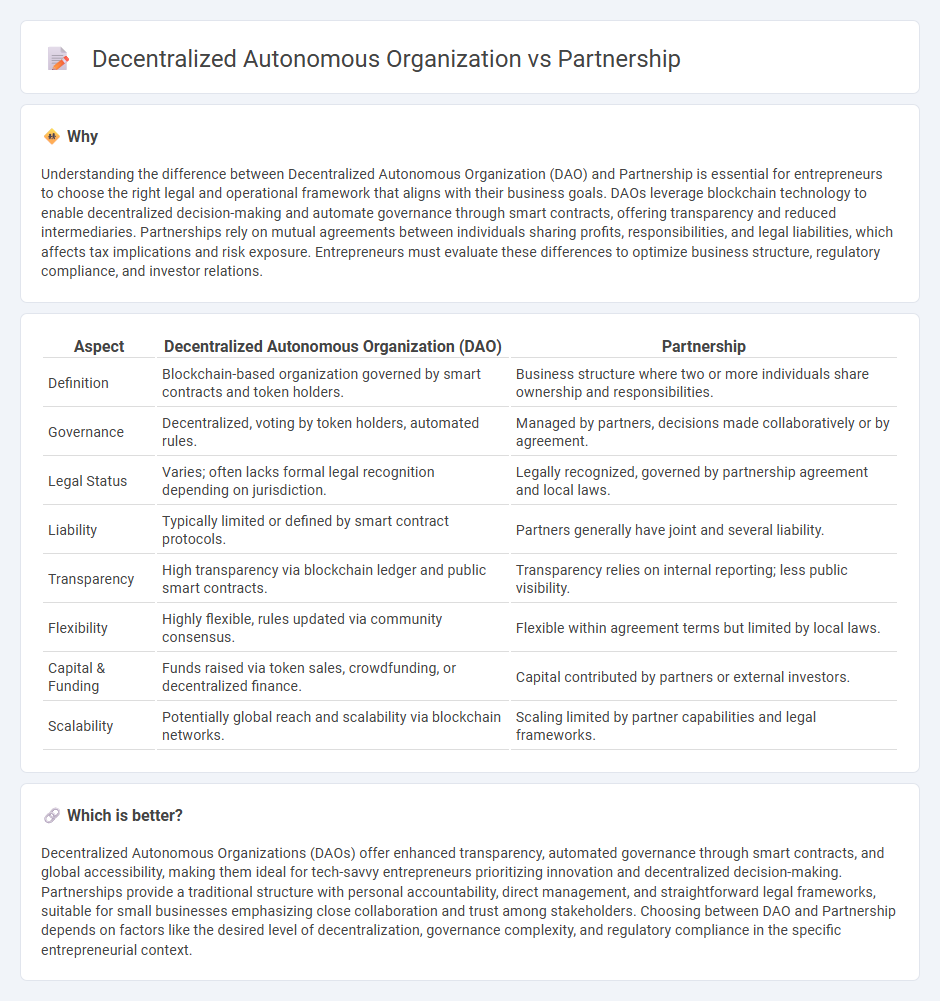
Understanding the difference between Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) and Partnership is essential for entrepreneurs to choose the right legal and operational framework that aligns with their business goals. DAOs leverage blockchain technology to enable decentralized decision-making and automate governance through smart contracts, offering transparency and reduced intermediaries. Partnerships rely on mutual agreements between individuals sharing profits, responsibilities, and legal liabilities, which affects tax implications and risk exposure. Entrepreneurs must evaluate these differences to optimize business structure, regulatory compliance, and investor relations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) | Partnership |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Blockchain-based organization governed by smart contracts and token holders. | Business structure where two or more individuals share ownership and responsibilities. |
| Governance | Decentralized, voting by token holders, automated rules. | Managed by partners, decisions made collaboratively or by agreement. |
| Legal Status | Varies; often lacks formal legal recognition depending on jurisdiction. | Legally recognized, governed by partnership agreement and local laws. |
| Liability | Typically limited or defined by smart contract protocols. | Partners generally have joint and several liability. |
| Transparency | High transparency via blockchain ledger and public smart contracts. | Transparency relies on internal reporting; less public visibility. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, rules updated via community consensus. | Flexible within agreement terms but limited by local laws. |
| Capital & Funding | Funds raised via token sales, crowdfunding, or decentralized finance. | Capital contributed by partners or external investors. |
| Scalability | Potentially global reach and scalability via blockchain networks. | Scaling limited by partner capabilities and legal frameworks. |
Which is better?
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) offer enhanced transparency, automated governance through smart contracts, and global accessibility, making them ideal for tech-savvy entrepreneurs prioritizing innovation and decentralized decision-making. Partnerships provide a traditional structure with personal accountability, direct management, and straightforward legal frameworks, suitable for small businesses emphasizing close collaboration and trust among stakeholders. Choosing between DAO and Partnership depends on factors like the desired level of decentralization, governance complexity, and regulatory compliance in the specific entrepreneurial context.
Connection
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) and partnerships share a foundational goal of collaborative decision-making and resource pooling to achieve business objectives. DAOs leverage blockchain technology to automate governance, ensuring transparent and trustless interactions among partners, which enhances traditional partnership models by eliminating intermediaries. This integration fosters innovative entrepreneurial ecosystems where stakeholders jointly manage ventures with increased efficiency and reduced conflict.
Key Terms
Shared Ownership
Partnerships involve shared ownership where profits, losses, and decision-making responsibilities are divided among a limited group of partners based on contribution agreements. Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) distribute ownership through token holdings, enabling broader participation in governance and profit-sharing via blockchain technology. Explore the intricate differences between these models to understand which shared ownership structure aligns with your goals.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts automate and enforce agreements within decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs), eliminating intermediaries common in traditional partnerships. While partnerships rely on legal frameworks and human oversight, DAOs leverage blockchain technology to ensure transparency, immutability, and self-execution of contract terms. Explore how smart contracts revolutionize organizational management by learning more about their applications in DAOs and partnerships.
Governance Structure
A partnership features a governance structure where decision-making power is typically concentrated among partners who share responsibilities and liabilities based on their stakes and agreements, often formalized in a partnership agreement. In contrast, a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) employs blockchain technology to enable a distributed governance model where token holders propose and vote on decisions, ensuring transparency and democratic control without centralized authority. Explore the unique governance mechanisms of DAOs and partnerships to understand their impact on organizational efficiency and control.
Source and External Links
Partnership - Wikipedia - A partnership is an agreement where two or more parties agree to cooperate to advance mutual interests, often sharing profits or losses from a business carried on by them collectively or individually acting for all.
Definition of Partnership: How They Work, Taxation and Types - A partnership is a legally binding agreement between two or more people who share responsibilities, ownership, and management of a business, combining resources and expertise to achieve shared business objectives.
Partnership - Overview, Types of Partners, Types of Partnerships - An unincorporated business structure co-owned by two or more parties, where partners may have unlimited or limited liability and share profits; types include general partnerships, limited partnerships, and limited liability partnerships.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com