Ghost kitchens operate exclusively for delivery services without a customer-facing storefront, reducing overhead costs and increasing operational efficiency. Shared kitchens provide multiple food businesses with access to fully equipped commercial kitchen spaces, fostering collaboration and cost-sharing. Explore the distinct business models and benefits of ghost kitchens versus shared kitchens to determine the best fit for your entrepreneurial goals.
Why it is important
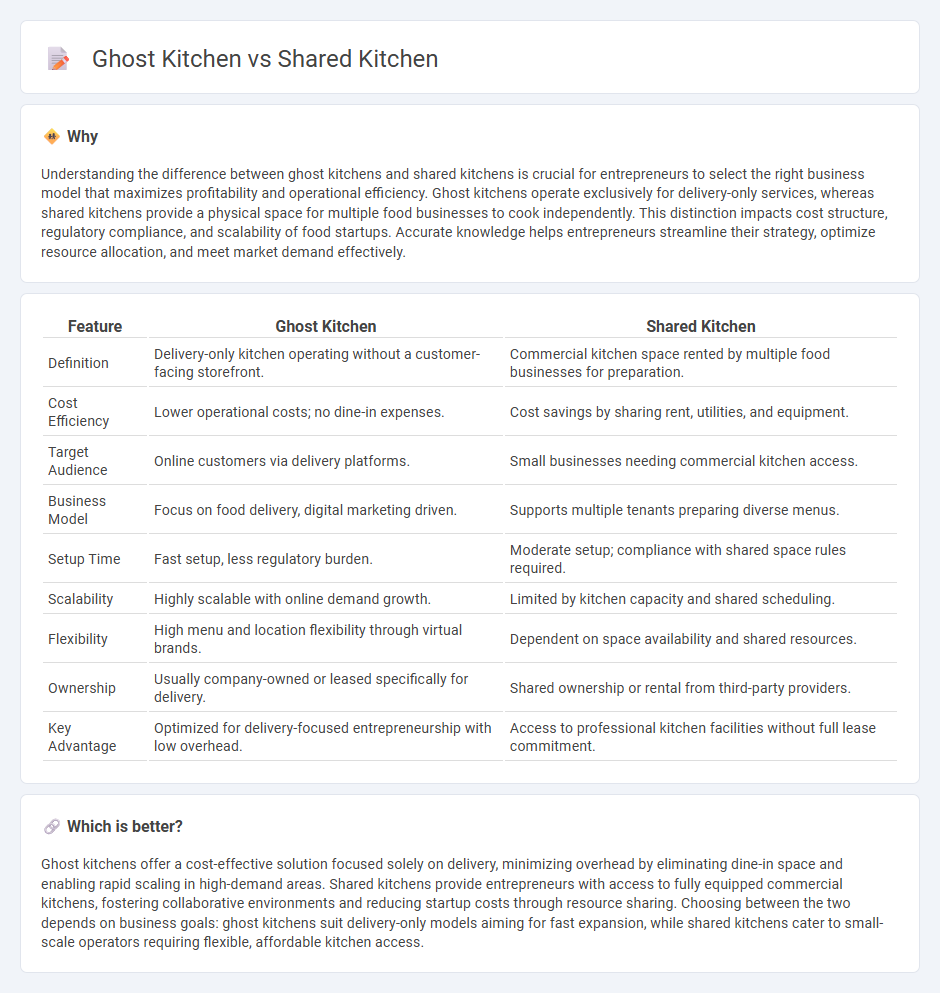
Understanding the difference between ghost kitchens and shared kitchens is crucial for entrepreneurs to select the right business model that maximizes profitability and operational efficiency. Ghost kitchens operate exclusively for delivery-only services, whereas shared kitchens provide a physical space for multiple food businesses to cook independently. This distinction impacts cost structure, regulatory compliance, and scalability of food startups. Accurate knowledge helps entrepreneurs streamline their strategy, optimize resource allocation, and meet market demand effectively.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Ghost Kitchen | Shared Kitchen |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Delivery-only kitchen operating without a customer-facing storefront. | Commercial kitchen space rented by multiple food businesses for preparation. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs; no dine-in expenses. | Cost savings by sharing rent, utilities, and equipment. |
| Target Audience | Online customers via delivery platforms. | Small businesses needing commercial kitchen access. |
| Business Model | Focus on food delivery, digital marketing driven. | Supports multiple tenants preparing diverse menus. |
| Setup Time | Fast setup, less regulatory burden. | Moderate setup; compliance with shared space rules required. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with online demand growth. | Limited by kitchen capacity and shared scheduling. |
| Flexibility | High menu and location flexibility through virtual brands. | Dependent on space availability and shared resources. |
| Ownership | Usually company-owned or leased specifically for delivery. | Shared ownership or rental from third-party providers. |
| Key Advantage | Optimized for delivery-focused entrepreneurship with low overhead. | Access to professional kitchen facilities without full lease commitment. |
Which is better?
Ghost kitchens offer a cost-effective solution focused solely on delivery, minimizing overhead by eliminating dine-in space and enabling rapid scaling in high-demand areas. Shared kitchens provide entrepreneurs with access to fully equipped commercial kitchens, fostering collaborative environments and reducing startup costs through resource sharing. Choosing between the two depends on business goals: ghost kitchens suit delivery-only models aiming for fast expansion, while shared kitchens cater to small-scale operators requiring flexible, affordable kitchen access.
Connection
Ghost kitchens and shared kitchens are interconnected concepts in the entrepreneurial food industry, providing low-cost infrastructure for food startups to operate without traditional restaurant setups. Ghost kitchens utilize shared kitchen spaces to create multiple virtual restaurant brands, maximizing resource efficiency and reducing overhead expenses. This synergy accelerates market entry, enabling entrepreneurs to focus on delivery-driven business models with flexible scalability.
Key Terms
Facility Usage
Shared kitchens maximize facility usage by allowing multiple food businesses to operate within a single commercial space, reducing overhead costs through shared equipment and utilities. Ghost kitchens solely focus on delivery, often operating in optimized facilities designed to enhance efficiency and minimize downtime by catering exclusively to online orders. Explore the differences further to understand which kitchen model suits your business needs.
Branding
A shared kitchen provides multiple food brands with a communal cooking space, allowing each to maintain distinct brand identities while minimizing overhead costs. Ghost kitchens operate solely for delivery services, emphasizing rapid scalability and brand experimentation without a physical storefront, enhancing digital presence and market reach. Explore the nuances of branding strategies in shared kitchens and ghost kitchens to maximize your culinary business potential.
Customer Interaction
Shared kitchens provide physical spaces where multiple food businesses prepare meals, enabling direct customer interaction through dine-in or takeout options, fostering brand loyalty and real-time feedback. Ghost kitchens operate exclusively through online orders without storefronts, limiting direct contact but optimizing delivery efficiency and broadening market reach via digital platforms. Explore detailed insights to understand how each kitchen model impacts customer experience and business growth.
Source and External Links
Shared Kitchens | City of New York - NYC.gov: Business - Shared kitchens are commercial food preparation facilities that allow food entrepreneurs to rent kitchen space and access professional equipment to grow their businesses without the high startup costs of operating their own commercial kitchen, requiring operators to hold permits and entrepreneurs to obtain food service permits if selling food publicly.
Shared-use Kitchens: The Definitive Guide - Optix - Shared commercial kitchens, also called commissary kitchens, are professional-grade facilities that provide affordable, licensed cooking space with specialized equipment on flexible schedules, fostering a collaborative environment for food entrepreneurs to start and expand their culinary businesses.
Guidance for Shared Use Kitchens - New York State Agriculture & Markets - Shared use kitchens are food preparation facilities that lease or rent commercial kitchen space and equipment to multiple operators, with defined responsibilities for owners and operators to ensure food safety and compliance with sanitary standards under state licensing and regulations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com