Entrepreneurship in sustainable construction increasingly focuses on innovations like Passive Houses and Net Zero Buildings, both designed to minimize energy consumption and environmental impact. Passive Houses emphasize superior insulation and airtightness to reduce heating and cooling needs, while Net Zero Buildings generate as much energy as they consume through renewable sources. Discover how these energy-efficient building standards offer entrepreneurial opportunities in green technology and construction.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Passive House and Net Zero Building is crucial for entrepreneurs in sustainable construction, as Passive House focuses on energy efficiency through rigorous insulation and airtight design, while Net Zero Buildings aim to balance energy consumption with renewable energy production. This knowledge enables informed decision-making to meet regulatory standards, reduce operational costs, and attract eco-conscious clients. Entrepreneurs can optimize project designs to maximize environmental benefits and financial returns by leveraging the distinct principles of each building type. Recognizing these differences supports innovation and competitive advantage in the green building market.
Comparison Table
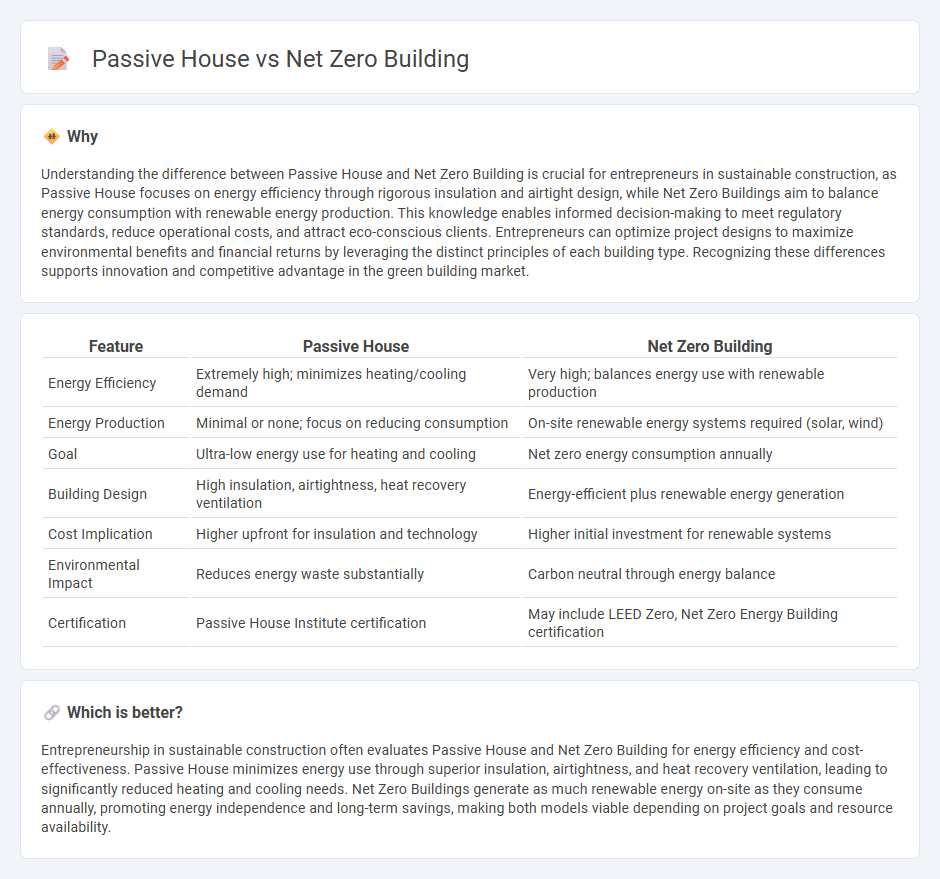
| Feature | Passive House | Net Zero Building |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Extremely high; minimizes heating/cooling demand | Very high; balances energy use with renewable production |
| Energy Production | Minimal or none; focus on reducing consumption | On-site renewable energy systems required (solar, wind) |
| Goal | Ultra-low energy use for heating and cooling | Net zero energy consumption annually |
| Building Design | High insulation, airtightness, heat recovery ventilation | Energy-efficient plus renewable energy generation |
| Cost Implication | Higher upfront for insulation and technology | Higher initial investment for renewable systems |
| Environmental Impact | Reduces energy waste substantially | Carbon neutral through energy balance |
| Certification | Passive House Institute certification | May include LEED Zero, Net Zero Energy Building certification |
Which is better?
Entrepreneurship in sustainable construction often evaluates Passive House and Net Zero Building for energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness. Passive House minimizes energy use through superior insulation, airtightness, and heat recovery ventilation, leading to significantly reduced heating and cooling needs. Net Zero Buildings generate as much renewable energy on-site as they consume annually, promoting energy independence and long-term savings, making both models viable depending on project goals and resource availability.
Connection
Passive House and Net Zero Building both focus on energy efficiency and sustainability by minimizing energy consumption through advanced insulation, airtight construction, and high-performance windows. Entrepreneurs in the green building sector leverage these concepts to create environmentally responsible buildings that reduce operational costs and carbon footprints. Integrating renewable energy systems into Passive House designs helps achieve Net Zero status, making such projects attractive for sustainable development ventures.
Key Terms
Energy Efficiency
Net Zero Buildings achieve energy efficiency by generating as much renewable energy on-site as they consume annually, minimizing reliance on external power sources. Passive Houses prioritize superior insulation, airtight construction, and ventilation systems to drastically reduce heating and cooling demands without active energy generation. Explore more to understand how these energy-efficient building standards compare and apply to your sustainable construction goals.
Carbon Emissions
Net Zero Buildings achieve carbon neutrality by balancing the energy consumed with renewable energy generated on-site, significantly reducing operational carbon emissions. Passive Houses prioritize energy efficiency through superior insulation, airtight construction, and heat recovery ventilation, minimizing the building's energy demand and associated emissions from heating and cooling. Explore more about how these sustainable building standards contribute to carbon emission reduction strategies.
Building Standards
Net Zero Buildings achieve energy balance by producing as much renewable energy on-site as they consume annually, adhering to standards like the International Living Future Institute's Zero Energy Certification. Passive House standards emphasize rigorous energy efficiency through superior insulation, airtightness, and heat recovery ventilation to minimize energy demand. Explore detailed comparisons and certifications to understand the best building standard for sustainable construction.
Source and External Links
Net Zero Energy Buildings - Net Zero Energy Buildings achieve a net energy consumption of zero annually by combining energy efficiency with renewable energy generation, typically relying on grid connection to balance use and surplus energy export, with federal goals targeting market-ready solutions by 2025.
Net Zero Buildings - Net Zero Buildings produce as much renewable energy on-site as they consume yearly, eliminating net emissions and reducing energy costs, representing a shift from conventional building practices.
Zero-energy building - A Net Zero Energy Building is highly energy-efficient and grid-connected, generating renewable energy to offset annual demand, enabling it to actively participate in the energy infrastructure by balancing energy flows.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com