Solopreneurs manage all aspects of their business independently, maintaining full control and reaping all profits, while partnerships involve shared responsibilities, resources, and decision-making among two or more individuals. Each structure offers distinct advantages; solopreneurs benefit from agility and autonomy, whereas partnerships enable collaboration and combined expertise. Explore deeper insights to determine which entrepreneurial path suits your goals.
Why it is important
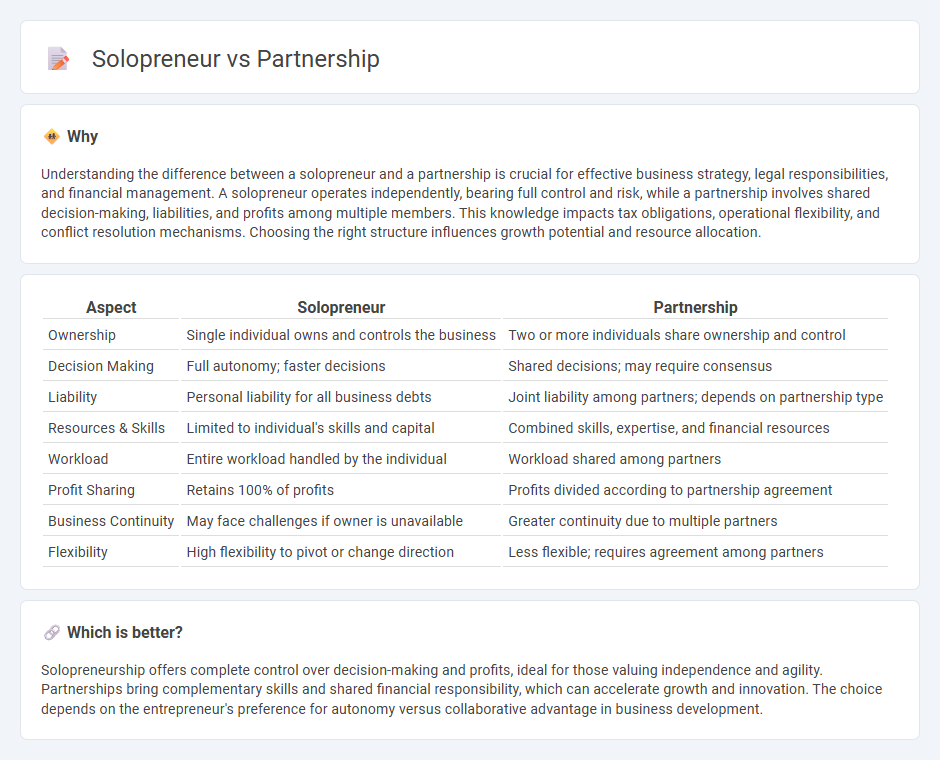
Understanding the difference between a solopreneur and a partnership is crucial for effective business strategy, legal responsibilities, and financial management. A solopreneur operates independently, bearing full control and risk, while a partnership involves shared decision-making, liabilities, and profits among multiple members. This knowledge impacts tax obligations, operational flexibility, and conflict resolution mechanisms. Choosing the right structure influences growth potential and resource allocation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Solopreneur | Partnership |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Single individual owns and controls the business | Two or more individuals share ownership and control |
| Decision Making | Full autonomy; faster decisions | Shared decisions; may require consensus |
| Liability | Personal liability for all business debts | Joint liability among partners; depends on partnership type |
| Resources & Skills | Limited to individual's skills and capital | Combined skills, expertise, and financial resources |
| Workload | Entire workload handled by the individual | Workload shared among partners |
| Profit Sharing | Retains 100% of profits | Profits divided according to partnership agreement |
| Business Continuity | May face challenges if owner is unavailable | Greater continuity due to multiple partners |
| Flexibility | High flexibility to pivot or change direction | Less flexible; requires agreement among partners |
Which is better?
Solopreneurship offers complete control over decision-making and profits, ideal for those valuing independence and agility. Partnerships bring complementary skills and shared financial responsibility, which can accelerate growth and innovation. The choice depends on the entrepreneur's preference for autonomy versus collaborative advantage in business development.
Connection
Solopreneurs and partnerships both embody entrepreneurial ventures that drive innovation and business growth, with solopreneurs managing solo operations while partnerships leverage shared skills and resources. Collaboration in partnerships can enhance strategic decision-making and risk distribution, complementing the independent, agile approach typical of solopreneurs. Understanding the dynamic between these models enables entrepreneurs to choose structures that best align with their business goals and scalability potential.
Key Terms
Liability
In a partnership, liability is shared among partners, making each individually responsible for the business's debts and obligations, which can increase personal financial risk. Solopreneurs, however, assume full liability for their business, bearing all financial and legal responsibilities alone, potentially limiting external liability exposure if structured properly. Explore the nuances of liability to decide the best structure for your entrepreneurial goals.
Decision-making
Decision-making in a partnership involves collaborative input from multiple stakeholders, enhancing diverse perspectives and shared responsibilities, which can lead to balanced and well-rounded choices. In contrast, solopreneurs have full autonomy, allowing for swift decisions but bearing sole accountability and potential biases. Explore deeper insights into how these decision-making dynamics impact business success.
Resource sharing
Partnerships enable efficient resource sharing by combining financial capital, skills, and networks, leading to greater scalability and reduced individual risk for business growth. Solopreneurs, managing limited resources independently, face challenges in scaling quickly but maintain full control and agility in decision-making. Explore how strategic resource allocation can maximize success in both partnership and solopreneurship models.
Source and External Links
Partnership - Wikipedia - A partnership is an agreement where parties cooperate to advance their mutual interests, often involving a partnership agreement covering roles, responsibilities, and profit sharing, and can involve individuals or businesses cooperating legally to achieve common goals.
Definition of Partnership: How They Work, Taxation and Types - A partnership is a legally binding agreement between two or more people who share ownership, responsibilities, and management of a business, combining resources and skills to grow or manage a company.
partnership | Wex | US Law | LII / Legal Information Institute - Legally, a partnership is a voluntary, contractual association between two or more parties acting as co-owners to carry out business for profit, formed by association rather than necessarily by express agreement.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com