Tiny acquisitions focus on purchasing very small businesses, often owner-operated with revenues under $1 million, allowing entrepreneurs to enter the market with minimal capital and management complexity. Micro private equity involves investing in slightly larger companies, typically generating $1 million to $10 million in revenue, targeting scalable growth and operational improvements. Explore further to understand which approach aligns best with your entrepreneurial goals.
Why it is important
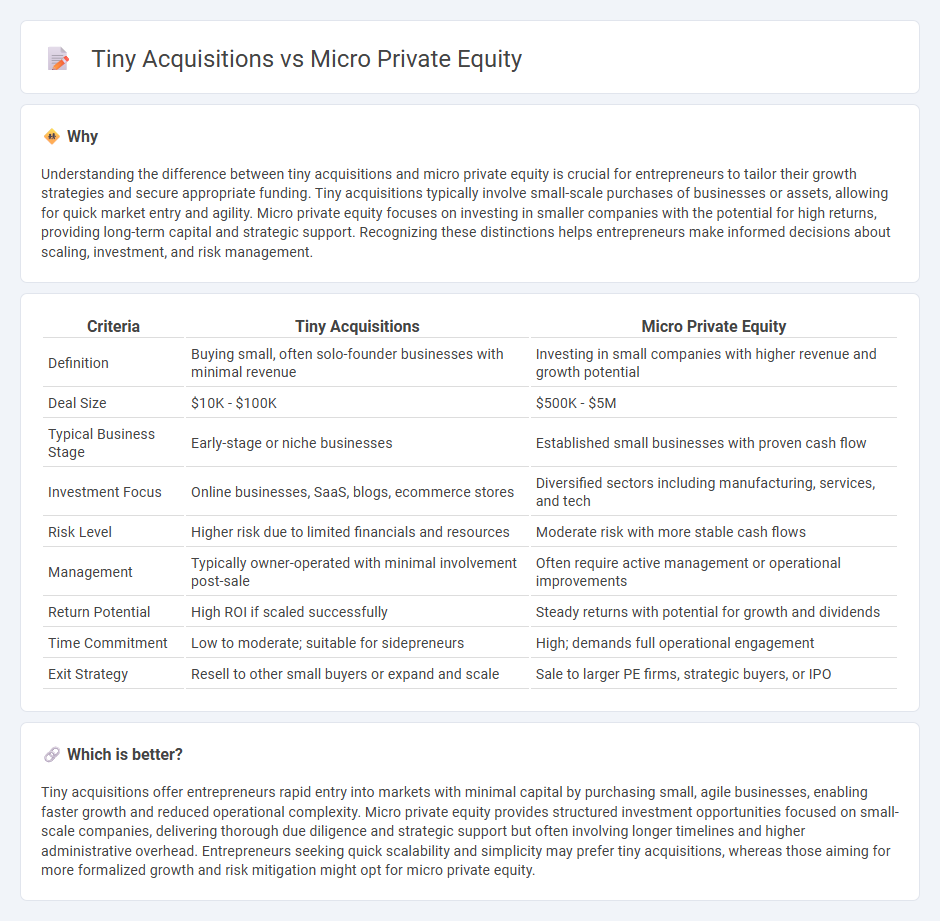
Understanding the difference between tiny acquisitions and micro private equity is crucial for entrepreneurs to tailor their growth strategies and secure appropriate funding. Tiny acquisitions typically involve small-scale purchases of businesses or assets, allowing for quick market entry and agility. Micro private equity focuses on investing in smaller companies with the potential for high returns, providing long-term capital and strategic support. Recognizing these distinctions helps entrepreneurs make informed decisions about scaling, investment, and risk management.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Tiny Acquisitions | Micro Private Equity |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Buying small, often solo-founder businesses with minimal revenue | Investing in small companies with higher revenue and growth potential |
| Deal Size | $10K - $100K | $500K - $5M |
| Typical Business Stage | Early-stage or niche businesses | Established small businesses with proven cash flow |
| Investment Focus | Online businesses, SaaS, blogs, ecommerce stores | Diversified sectors including manufacturing, services, and tech |
| Risk Level | Higher risk due to limited financials and resources | Moderate risk with more stable cash flows |
| Management | Typically owner-operated with minimal involvement post-sale | Often require active management or operational improvements |
| Return Potential | High ROI if scaled successfully | Steady returns with potential for growth and dividends |
| Time Commitment | Low to moderate; suitable for sidepreneurs | High; demands full operational engagement |
| Exit Strategy | Resell to other small buyers or expand and scale | Sale to larger PE firms, strategic buyers, or IPO |
Which is better?
Tiny acquisitions offer entrepreneurs rapid entry into markets with minimal capital by purchasing small, agile businesses, enabling faster growth and reduced operational complexity. Micro private equity provides structured investment opportunities focused on small-scale companies, delivering thorough due diligence and strategic support but often involving longer timelines and higher administrative overhead. Entrepreneurs seeking quick scalability and simplicity may prefer tiny acquisitions, whereas those aiming for more formalized growth and risk mitigation might opt for micro private equity.
Connection
Tiny acquisitions serve as strategic investments within micro private equity, targeting small-scale businesses to drive portfolio diversification and growth. Micro private equity firms focus on acquiring companies with revenues typically under $10 million, optimizing operational efficiencies and scaling potential. These acquisitions enable rapid value creation by leveraging niche markets and specialized management expertise.
Key Terms
Deal Size
Micro private equity typically involves investments ranging from $1 million to $10 million, targeting small to lower-middle-market companies with growth potential. Tiny acquisitions, often under $1 million, focus on acquiring very small businesses or niche assets that require minimal capital but offer quick ownership transition. Explore detailed comparisons to understand the strategic implications of deal size on investment outcomes.
Acquisition Strategy
Micro private equity emphasizes acquiring smaller companies typically valued between $5 million and $50 million, targeting niche markets with high growth potential and operational improvements. Tiny acquisitions usually involve transactions under $5 million, often focusing on quick integrations and minimal operational changes to rapidly expand product lines or geographic reach. Explore in-depth strategies and tactical advantages of both approaches to optimize your acquisition portfolio.
Operational Involvement
Micro private equity investments typically involve acquiring companies with enterprise values ranging from $5 million to $50 million, emphasizing active operational involvement to drive growth and improve efficiencies. Tiny acquisitions, usually under $5 million, often focus on niche markets or individual business units where hands-on management is essential for integration and value creation. Discover more about how tailored operational strategies differentiate these investment approaches.
Source and External Links
The Rise of Micro Private Equity - Micro private equity (Micro PE) focuses on acquiring small, already-profitable businesses--often valued under $5 million--such as SaaS tools, eCommerce stores, or B2B platforms, differing from traditional PE or VC by targeting stable, cash-flow-positive companies rather than high-growth startups or large corporations.
The Rise of Micro Private Equity - Micro PE funds specialize in buying small businesses, typically under $5 million in value, with a primary goal of acquiring and later selling these companies (often internet-based like SaaS firms), though some investors hold them indefinitely, and the sector is growing due to retiring business owners and the rise of bootstrapped, profitable small companies.
What is Micro PE? Where to Find Opportunities & Why It... - Micro private equity involves acquiring stakes in small, privately-held companies (usually with revenues up to $5 million), pooling investor capital to build a diversified portfolio across sectors, and offering accredited investors access to growth-oriented small businesses that benefit from strategic guidance and capital infusion.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com