Entrepreneurship in the passion economy centers on creators monetizing unique skills and interests through personalized, value-driven offerings. In contrast, the platform economy emphasizes scalable marketplaces where intermediaries connect producers with large audiences via technology. Discover how these economic models shape the future of entrepreneurial opportunities and business growth.
Why it is important
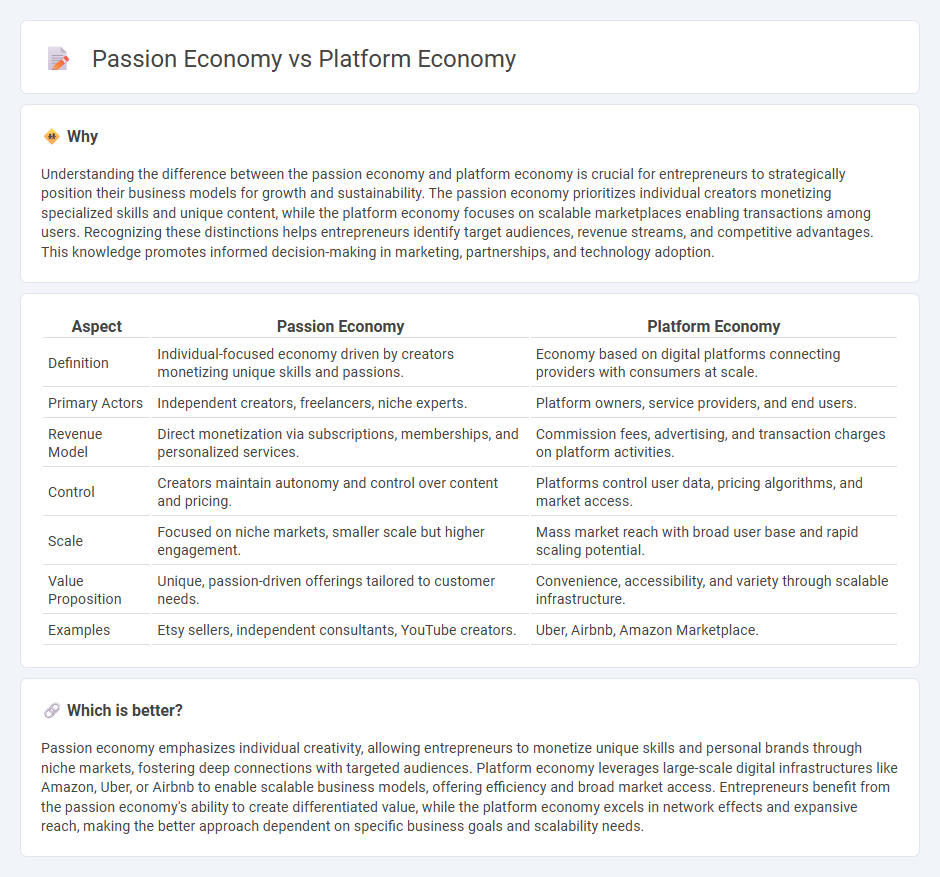
Understanding the difference between the passion economy and platform economy is crucial for entrepreneurs to strategically position their business models for growth and sustainability. The passion economy prioritizes individual creators monetizing specialized skills and unique content, while the platform economy focuses on scalable marketplaces enabling transactions among users. Recognizing these distinctions helps entrepreneurs identify target audiences, revenue streams, and competitive advantages. This knowledge promotes informed decision-making in marketing, partnerships, and technology adoption.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Passion Economy | Platform Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individual-focused economy driven by creators monetizing unique skills and passions. | Economy based on digital platforms connecting providers with consumers at scale. |
| Primary Actors | Independent creators, freelancers, niche experts. | Platform owners, service providers, and end users. |
| Revenue Model | Direct monetization via subscriptions, memberships, and personalized services. | Commission fees, advertising, and transaction charges on platform activities. |
| Control | Creators maintain autonomy and control over content and pricing. | Platforms control user data, pricing algorithms, and market access. |
| Scale | Focused on niche markets, smaller scale but higher engagement. | Mass market reach with broad user base and rapid scaling potential. |
| Value Proposition | Unique, passion-driven offerings tailored to customer needs. | Convenience, accessibility, and variety through scalable infrastructure. |
| Examples | Etsy sellers, independent consultants, YouTube creators. | Uber, Airbnb, Amazon Marketplace. |
Which is better?
Passion economy emphasizes individual creativity, allowing entrepreneurs to monetize unique skills and personal brands through niche markets, fostering deep connections with targeted audiences. Platform economy leverages large-scale digital infrastructures like Amazon, Uber, or Airbnb to enable scalable business models, offering efficiency and broad market access. Entrepreneurs benefit from the passion economy's ability to create differentiated value, while the platform economy excels in network effects and expansive reach, making the better approach dependent on specific business goals and scalability needs.
Connection
The passion economy drives entrepreneurship by enabling individuals to monetize specialized skills and unique content through digital platforms. Platform economy provides the infrastructure and audience necessary for passionate creators to scale their offerings globally and generate sustainable income. This synergy fosters innovative business models where personal creativity meets scalable technology, fueling new entrepreneurial opportunities.
Key Terms
Multi-sided Marketplace
The platform economy thrives on multi-sided marketplaces by connecting buyers, sellers, and service providers through centralized digital platforms that facilitate transactions and scale network effects efficiently. In contrast, the passion economy emphasizes individualized creators leveraging niche audiences and personalized content within or alongside multi-sided marketplaces, driving direct, meaningful engagement and monetization. Explore the intricate dynamics and opportunities of these economies in multi-sided marketplaces to understand their evolving impact on digital commerce.
Creator Monetization
The platform economy enables creators to monetize their work by leveraging large-scale digital marketplaces like YouTube and Instagram, which connect users with vast audiences through algorithm-driven content distribution. In contrast, the passion economy emphasizes direct relationships between creators and niche audiences, allowing personalized monetization through subscriptions, exclusive content, and service offerings on platforms like Patreon and Substack. Explore how these contrasting economic models shape the future of creator monetization and individual empowerment.
Network Effects
The platform economy leverages network effects by connecting millions of users to create value through scale and data-driven interactions, driving growth primarily via user accumulation and engagement. In contrast, the passion economy emphasizes individual creators who build deep, niche communities around personal brands, monetizing unique skills and expertise without relying heavily on large network sizes. Explore how network effects shape these economies and influence digital market dynamics.
Source and External Links
Platform economy - The platform economy involves economic and social activities enabled by digital platforms like Amazon, Uber, and Airbnb that act as intermediaries facilitating interactions and transactions, rapidly scaling through network effects but also raising challenges around labor, market concentration, and regulation.
Platform economy | EBSCO Research Starters - The platform economy refers to economic activities on digital marketplaces that connect suppliers and consumers using advanced technologies, transforming traditional business models and driving innovation in global commerce.
The Rise of the Platform Economy - The platform economy is emerging through the use of big data, cloud computing, and new algorithms to create digital infrastructures that fundamentally transform work, economic value creation, and global market dynamics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com