Entrepreneurship in the tiny houses business involves hands-on construction, customization, and meeting local housing regulations, often requiring significant upfront investment and long-term customer relationships. Dropshipping entrepreneurship, by contrast, emphasizes leveraging e-commerce platforms, managing supplier relationships, and minimizing inventory risk with a focus on digital marketing and fast product turnover. Explore the unique challenges and opportunities each business model presents to determine the best entrepreneurial path for your goals.
Why it is important
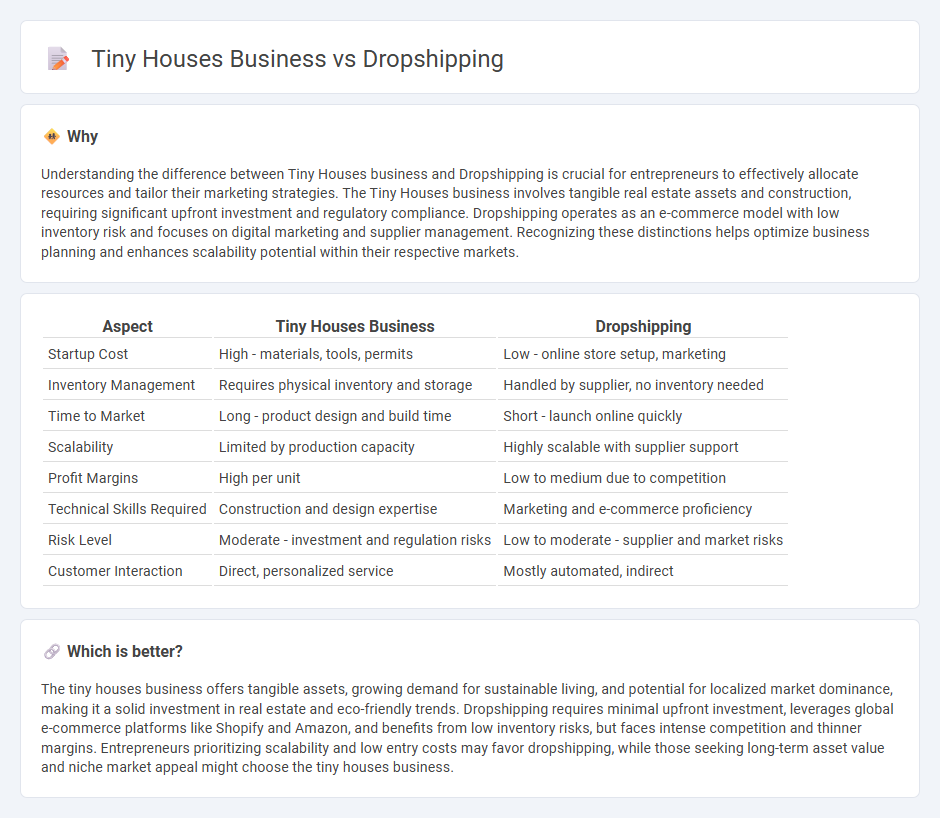
Understanding the difference between Tiny Houses business and Dropshipping is crucial for entrepreneurs to effectively allocate resources and tailor their marketing strategies. The Tiny Houses business involves tangible real estate assets and construction, requiring significant upfront investment and regulatory compliance. Dropshipping operates as an e-commerce model with low inventory risk and focuses on digital marketing and supplier management. Recognizing these distinctions helps optimize business planning and enhances scalability potential within their respective markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tiny Houses Business | Dropshipping |
|---|---|---|
| Startup Cost | High - materials, tools, permits | Low - online store setup, marketing |
| Inventory Management | Requires physical inventory and storage | Handled by supplier, no inventory needed |
| Time to Market | Long - product design and build time | Short - launch online quickly |
| Scalability | Limited by production capacity | Highly scalable with supplier support |
| Profit Margins | High per unit | Low to medium due to competition |
| Technical Skills Required | Construction and design expertise | Marketing and e-commerce proficiency |
| Risk Level | Moderate - investment and regulation risks | Low to moderate - supplier and market risks |
| Customer Interaction | Direct, personalized service | Mostly automated, indirect |
Which is better?
The tiny houses business offers tangible assets, growing demand for sustainable living, and potential for localized market dominance, making it a solid investment in real estate and eco-friendly trends. Dropshipping requires minimal upfront investment, leverages global e-commerce platforms like Shopify and Amazon, and benefits from low inventory risks, but faces intense competition and thinner margins. Entrepreneurs prioritizing scalability and low entry costs may favor dropshipping, while those seeking long-term asset value and niche market appeal might choose the tiny houses business.
Connection
The Tiny Houses business and Dropshipping model intersect through their shared emphasis on low overhead and scalable operations, allowing entrepreneurs to test markets without heavy inventory investments. Both sectors leverage e-commerce platforms to reach niche audiences seeking sustainable living solutions or curated products, optimizing customer acquisition and fulfillment processes. This synergy enables flexible business strategies that adapt to evolving consumer preferences while minimizing financial risk.
Key Terms
Supply Chain Management
Dropshipping relies heavily on efficient supply chain management through direct partnerships with suppliers, minimizing inventory overhead and enabling rapid order fulfillment across global markets. In contrast, the tiny houses business demands robust supply chain coordination involving raw materials sourcing, manufacturing timelines, and logistics for large, bulky items, often within localized regions. Explore more about optimizing supply chain strategies in these distinct business models.
Overhead Costs
Dropshipping businesses generally incur lower overhead costs since there is no need for inventory storage, warehousing, or physical storefronts, relying on supplier partnerships to fulfill orders directly to customers. In contrast, tiny houses enterprises face higher overhead expenses due to materials, labor, permits, and specialized tools required for construction or customization. Explore detailed financial comparisons and strategic insights to optimize your overhead management in these niche markets.
Scalability
Dropshipping offers unparalleled scalability due to low upfront costs, global supplier networks, and automation tools that enable rapid expansion without inventory constraints. In contrast, tiny houses require significant capital investment, physical space, and regulatory compliance, limiting quick scalability but offering niche market stability and customization potential. Explore deeper insights on how each business model aligns with your growth strategy.
Source and External Links
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? - Dropshipping is a retail fulfillment model where sellers list and market products without stocking inventory, and suppliers handle storage and shipping directly to customers.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? (2025) - In dropshipping, online stores sell products supplied by third parties who manage inventory and ship orders directly to buyers, while the store focuses on marketing and customer service.
What is Dropshipping: A Comprehensive Guide for Entrepreneurs - Dropshipping allows businesses to sell products online without maintaining inventory, as suppliers process and ship orders directly, reducing upfront costs and storage needs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com