Digital nomad visas and freelance visas both cater to professionals seeking remote work flexibility, yet they differ in eligibility criteria and permitted activities. Digital nomad visas often require proof of salaried employment with a foreign company, whereas freelance visas typically target self-employed individuals offering services independently. Explore the specific requirements and benefits of each visa type to determine the best fit for your remote work lifestyle.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between digital nomad visas and freelance visas is crucial for compliance with immigration laws and securing appropriate work authorization. Digital nomad visas typically cater to remote workers employed by companies abroad, allowing them to reside temporarily in a foreign country without engaging in local employment. Freelance visas, on the other hand, permit individuals to independently offer services or run businesses within the host country's jurisdiction. Selecting the correct visa ensures legal work status, optimizes tax obligations, and minimizes risks of visa violations or penalties.
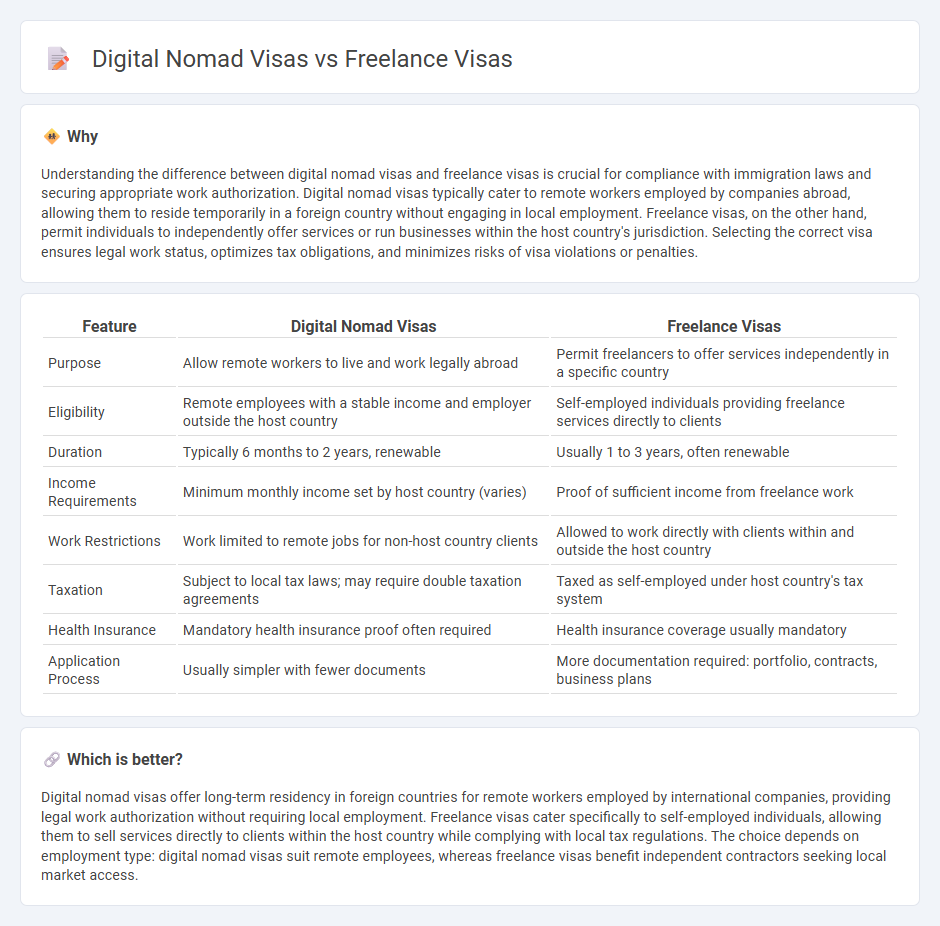
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Nomad Visas | Freelance Visas |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Allow remote workers to live and work legally abroad | Permit freelancers to offer services independently in a specific country |
| Eligibility | Remote employees with a stable income and employer outside the host country | Self-employed individuals providing freelance services directly to clients |
| Duration | Typically 6 months to 2 years, renewable | Usually 1 to 3 years, often renewable |
| Income Requirements | Minimum monthly income set by host country (varies) | Proof of sufficient income from freelance work |
| Work Restrictions | Work limited to remote jobs for non-host country clients | Allowed to work directly with clients within and outside the host country |
| Taxation | Subject to local tax laws; may require double taxation agreements | Taxed as self-employed under host country's tax system |
| Health Insurance | Mandatory health insurance proof often required | Health insurance coverage usually mandatory |
| Application Process | Usually simpler with fewer documents | More documentation required: portfolio, contracts, business plans |
Which is better?
Digital nomad visas offer long-term residency in foreign countries for remote workers employed by international companies, providing legal work authorization without requiring local employment. Freelance visas cater specifically to self-employed individuals, allowing them to sell services directly to clients within the host country while complying with local tax regulations. The choice depends on employment type: digital nomad visas suit remote employees, whereas freelance visas benefit independent contractors seeking local market access.
Connection
Digital nomad visas and freelance visas both cater to remote workers seeking legal employment options abroad, allowing individuals to live and work in foreign countries without traditional work permits. These visas facilitate employment flexibility by granting freelancers and remote employees the right to earn income independently of local employers, supporting the growing gig economy and global digital workforce. Countries offering these visas target economic growth by attracting skilled professionals whose remote employment generates revenue without competing for local jobs.
Key Terms
Work Authorization
Freelance visas typically provide specific work authorization limited to freelancing activities within the host country, requiring applicants to prove income sources and local tax compliance. Digital nomad visas often allow remote workers to legally stay and work for foreign employers without local work permits, facilitating greater flexibility and reduced bureaucratic barriers. Explore detailed differences and application processes to determine which visa best suits your work authorization needs.
Residency Requirement
Freelance visas generally require applicants to establish a legal residence and demonstrate a stable income source within the host country, often mandating physical presence for a specified duration. Digital nomad visas offer more flexible residency requirements, allowing remote workers to maintain temporary stays without strict mandates on continuous residence or local employment. Explore detailed country-specific residency rules to determine which visa aligns best with your lifestyle and professional goals.
Tax Implications
Freelance visas often require individuals to register as self-employed and adhere to local tax laws, which may include paying income tax and social security contributions in the host country. Digital nomad visas typically offer tax benefits by allowing remote workers to maintain tax residency in their home country while legally residing abroad, reducing complex tax liabilities. Explore detailed tax implications and compliance requirements to determine the best visa option for your international work lifestyle.
Source and External Links
How to Get a Freelance Visa in 2025 - SolidGigs - For 2025, countries like Germany and Portugal offer prominent freelance visas, with Germany requiring around EUR3,000 monthly income and a business plan, and Portugal's D7 visa requiring a minimum monthly income of EUR705 with proof of accommodation and health insurance.
Ultimate List of Freelance & Digital Nomad Visas (2025) - Czechia offers a freelance visa that includes requirements like proof of funds (~$5700), accommodation, health insurance, and a background check, with an initial visa period of 8 months that can be extended on meeting income thresholds.
German Freelance "Freiberufler" Visa - Germany Visa - Germany's freelance visa allows independent work with a visa valid up to 3 years and costs EUR75; eligibility depends on freelancing in certain professions and proof of financial means, health insurance, and work evidence is needed.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com