Labor hoarding involves companies retaining more employees than needed during economic downturns to preserve talent and avoid future hiring costs. Job sharing distributes available work hours among multiple employees to reduce layoffs and maintain workforce morale. Explore further to understand how these strategies impact employment stability and organizational resilience.
Why it is important
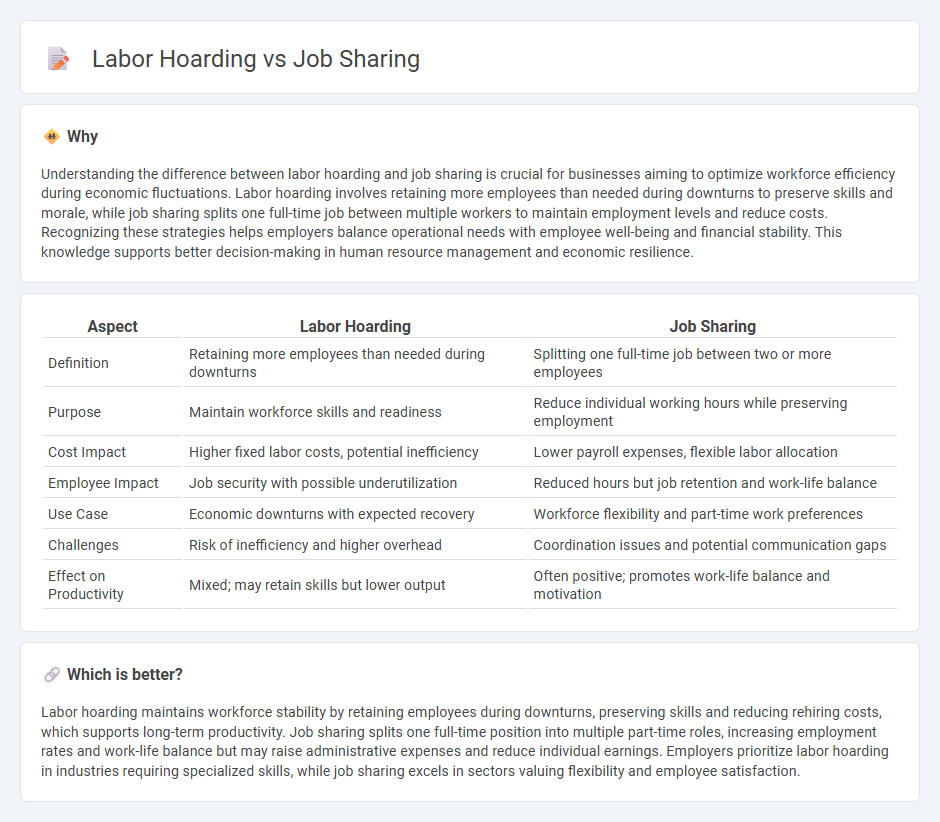
Understanding the difference between labor hoarding and job sharing is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize workforce efficiency during economic fluctuations. Labor hoarding involves retaining more employees than needed during downturns to preserve skills and morale, while job sharing splits one full-time job between multiple workers to maintain employment levels and reduce costs. Recognizing these strategies helps employers balance operational needs with employee well-being and financial stability. This knowledge supports better decision-making in human resource management and economic resilience.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Labor Hoarding | Job Sharing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Retaining more employees than needed during downturns | Splitting one full-time job between two or more employees |
| Purpose | Maintain workforce skills and readiness | Reduce individual working hours while preserving employment |
| Cost Impact | Higher fixed labor costs, potential inefficiency | Lower payroll expenses, flexible labor allocation |
| Employee Impact | Job security with possible underutilization | Reduced hours but job retention and work-life balance |
| Use Case | Economic downturns with expected recovery | Workforce flexibility and part-time work preferences |
| Challenges | Risk of inefficiency and higher overhead | Coordination issues and potential communication gaps |
| Effect on Productivity | Mixed; may retain skills but lower output | Often positive; promotes work-life balance and motivation |
Which is better?
Labor hoarding maintains workforce stability by retaining employees during downturns, preserving skills and reducing rehiring costs, which supports long-term productivity. Job sharing splits one full-time position into multiple part-time roles, increasing employment rates and work-life balance but may raise administrative expenses and reduce individual earnings. Employers prioritize labor hoarding in industries requiring specialized skills, while job sharing excels in sectors valuing flexibility and employee satisfaction.
Connection
Labor hoarding occurs when employers retain more workers than needed during economic downturns to preserve skills and avoid rehiring costs, while job sharing distributes existing work hours among employees to reduce individual workload without layoffs. Both strategies aim to maintain employment stability and reduce unemployment risks by adjusting labor input rather than cutting jobs abruptly. Implementing labor hoarding and job sharing together helps businesses manage costs and protect workforce morale during fluctuating market conditions.
Key Terms
Work Schedule Flexibility
Job sharing offers enhanced work schedule flexibility by allowing two employees to split one full-time position, enabling part-time work without reducing overall coverage. Labor hoarding involves retaining more employees than necessary, often leading to underutilized labor but maintaining workforce stability during economic uncertainty. Explore more about how these strategies impact organizational agility and employee satisfaction.
Workforce Retention
Job sharing enhances workforce retention by allowing employees to split full-time roles, reducing burnout and increasing job satisfaction. Labor hoarding retains employees by maintaining staffing levels during economic downturns, preserving skills and company loyalty despite reduced workload. Explore further strategies to optimize workforce retention through balancing job sharing and labor hoarding.
Productivity
Job sharing enhances productivity by distributing work among employees, reducing burnout, and maintaining high engagement levels. Labor hoarding, while preserving jobs during downturns, can lead to underutilized workforce capacity and decreased efficiency. Explore how optimizing these strategies can boost your organization's productivity.
Source and External Links
The Benefits of Job Sharing for Employers and Employees - Job sharing allows two or more employees to split the responsibilities and duties of one full-time role, providing flexibility and maintaining job functions with shared work hours and tasks.
What is job sharing? - Job sharing is a flexible working arrangement where two employees share one full-time job's duties, pay, and benefits on a pro-rata basis, often coordinated to suit schedules and maximize workflow efficiency.
Job sharing - Job sharing is an employment setup in which two or more individuals perform a job normally done by one full-time person, splitting pay, holidays, and responsibilities proportionally while working as a team.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com