Fractional hiring allocates specific hours of work across multiple clients or projects, offering predictable income and flexibility, whereas zero-hour contracts provide no guaranteed hours, leading to variable earnings and uncertain job security. Employers benefit from fractional hiring through consistent workforce engagement and optimized resource allocation, while zero-hour contracts allow for maximum staffing flexibility but can impact employee loyalty. Explore deeper insights into how these employment models affect workforce management and labor dynamics.
Why it is important
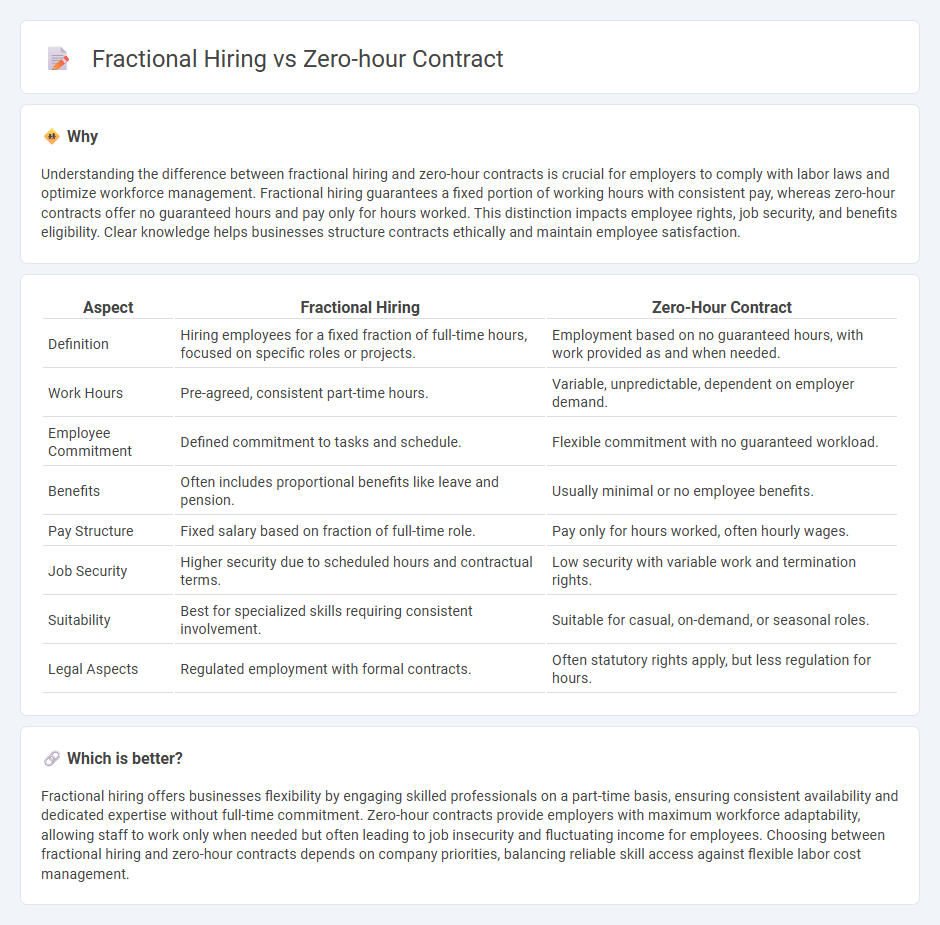
Understanding the difference between fractional hiring and zero-hour contracts is crucial for employers to comply with labor laws and optimize workforce management. Fractional hiring guarantees a fixed portion of working hours with consistent pay, whereas zero-hour contracts offer no guaranteed hours and pay only for hours worked. This distinction impacts employee rights, job security, and benefits eligibility. Clear knowledge helps businesses structure contracts ethically and maintain employee satisfaction.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Fractional Hiring | Zero-Hour Contract |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hiring employees for a fixed fraction of full-time hours, focused on specific roles or projects. | Employment based on no guaranteed hours, with work provided as and when needed. |
| Work Hours | Pre-agreed, consistent part-time hours. | Variable, unpredictable, dependent on employer demand. |
| Employee Commitment | Defined commitment to tasks and schedule. | Flexible commitment with no guaranteed workload. |
| Benefits | Often includes proportional benefits like leave and pension. | Usually minimal or no employee benefits. |
| Pay Structure | Fixed salary based on fraction of full-time role. | Pay only for hours worked, often hourly wages. |
| Job Security | Higher security due to scheduled hours and contractual terms. | Low security with variable work and termination rights. |
| Suitability | Best for specialized skills requiring consistent involvement. | Suitable for casual, on-demand, or seasonal roles. |
| Legal Aspects | Regulated employment with formal contracts. | Often statutory rights apply, but less regulation for hours. |
Which is better?
Fractional hiring offers businesses flexibility by engaging skilled professionals on a part-time basis, ensuring consistent availability and dedicated expertise without full-time commitment. Zero-hour contracts provide employers with maximum workforce adaptability, allowing staff to work only when needed but often leading to job insecurity and fluctuating income for employees. Choosing between fractional hiring and zero-hour contracts depends on company priorities, balancing reliable skill access against flexible labor cost management.
Connection
Fractional hiring allows companies to engage professionals on a part-time basis, providing flexibility similar to zero-hour contracts where workers have no guaranteed hours. Both employment models prioritize adaptable workforce management, enabling businesses to scale labor according to demand fluctuations. These approaches impact job security and income consistency, influencing labor market dynamics and worker rights debates.
Key Terms
Working hours flexibility
Zero-hour contracts offer maximum working hours flexibility by allowing employees to work on an as-needed basis without guaranteed hours, ideal for fluctuating demand. Fractional hiring involves part-time employees with fixed but reduced hours, providing predictable schedules tailored to workload needs. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which model suits your business's flexibility requirements best.
Job security
Zero-hour contracts offer minimal job security due to unpredictable hours and lack of guaranteed income, often leaving workers vulnerable to inconsistent work schedules. Fractional hiring provides greater job security by assigning professionals fixed portions of roles, ensuring stable income and scheduled work periods. Explore the benefits and risks of each employment model to determine the best option for job security.
Employment status
Zero-hour contracts classify workers as employees or workers with no guaranteed hours, leading to fluctuating income and limited employment rights under UK law. Fractional hiring offers fixed, pre-agreed part-time hours, providing clarity on employment status and entitlements like pensions and holiday pay. Explore the nuances of employment status for each model to determine the best fit for your workforce needs.
Source and External Links
Zero-hour contract - A type of employment contract primarily used in the United Kingdom where the employer does not guarantee any minimum working hours.
Hiring on-call employees with a zero-hours contract - A step-by-step guide on how to hire employees with zero-hours contracts, highlighting their rights and regulations in the Netherlands.
What Is a Zero-Hour Contract? - An explanation of the definition and benefits of zero-hour contracts, highlighting flexibility for both employers and employees.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com