Rage applying occurs when job seekers rapidly submit numerous applications out of frustration or desperation, often leading to lower success rates. Talent poaching refers to companies actively recruiting skilled employees from competitors to gain a strategic advantage and enhance workforce quality. Discover more insights on how these contrasting employment strategies impact hiring outcomes.
Why it is important
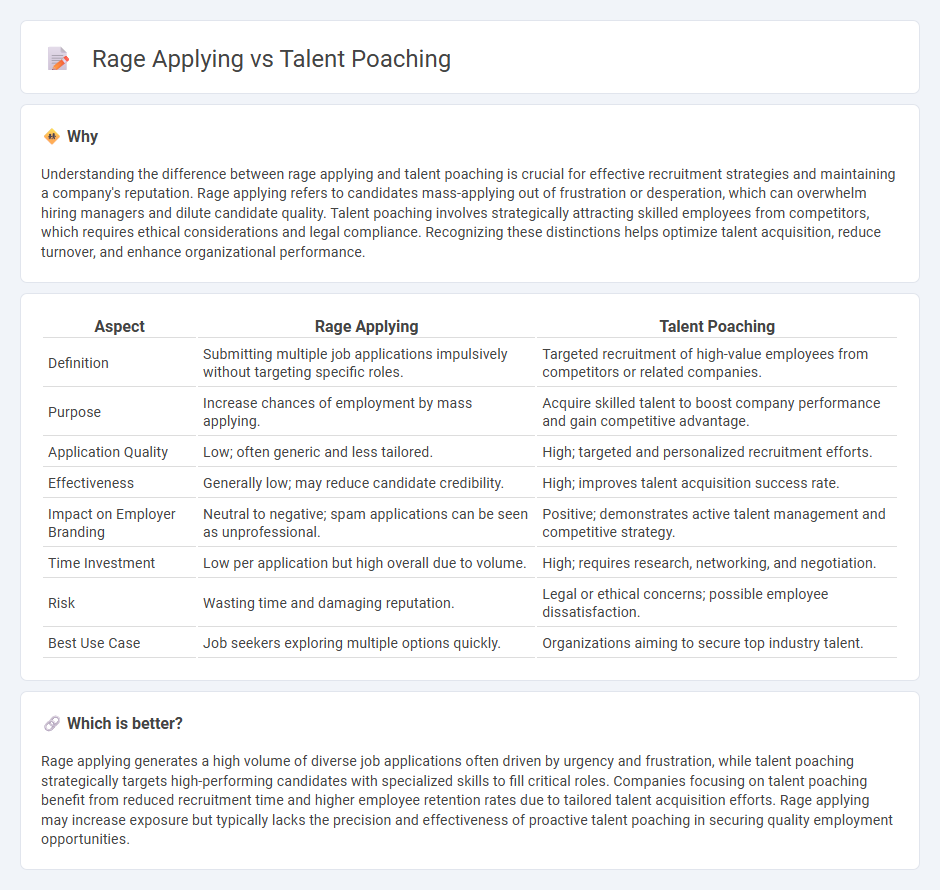
Understanding the difference between rage applying and talent poaching is crucial for effective recruitment strategies and maintaining a company's reputation. Rage applying refers to candidates mass-applying out of frustration or desperation, which can overwhelm hiring managers and dilute candidate quality. Talent poaching involves strategically attracting skilled employees from competitors, which requires ethical considerations and legal compliance. Recognizing these distinctions helps optimize talent acquisition, reduce turnover, and enhance organizational performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Rage Applying | Talent Poaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Submitting multiple job applications impulsively without targeting specific roles. | Targeted recruitment of high-value employees from competitors or related companies. |
| Purpose | Increase chances of employment by mass applying. | Acquire skilled talent to boost company performance and gain competitive advantage. |
| Application Quality | Low; often generic and less tailored. | High; targeted and personalized recruitment efforts. |
| Effectiveness | Generally low; may reduce candidate credibility. | High; improves talent acquisition success rate. |
| Impact on Employer Branding | Neutral to negative; spam applications can be seen as unprofessional. | Positive; demonstrates active talent management and competitive strategy. |
| Time Investment | Low per application but high overall due to volume. | High; requires research, networking, and negotiation. |
| Risk | Wasting time and damaging reputation. | Legal or ethical concerns; possible employee dissatisfaction. |
| Best Use Case | Job seekers exploring multiple options quickly. | Organizations aiming to secure top industry talent. |
Which is better?
Rage applying generates a high volume of diverse job applications often driven by urgency and frustration, while talent poaching strategically targets high-performing candidates with specialized skills to fill critical roles. Companies focusing on talent poaching benefit from reduced recruitment time and higher employee retention rates due to tailored talent acquisition efforts. Rage applying may increase exposure but typically lacks the precision and effectiveness of proactive talent poaching in securing quality employment opportunities.
Connection
Rage applying often triggers talent poaching as frustrated candidates aggressively submit applications, catching recruiters' attention through sheer volume and urgency. This increased activity signals high candidate availability, prompting employers to proactively scout for skilled individuals to strengthen their workforce. Consequently, intense rage applying indirectly drives talent poaching by highlighting active job seekers ripe for recruitment.
Key Terms
**Talent Poaching:**
Talent poaching involves strategically recruiting skilled professionals from competitors, focusing on their expertise and potential to enhance organizational performance. This approach targets high-value employees to gain a competitive edge, leveraging industry knowledge and experience. Explore effective talent poaching strategies to boost your company's workforce quality and innovation.
Head-hunting
Head-hunting specializes in targeted talent poaching, where recruiters actively seek out high-skilled professionals from competitors or related industries to fulfill specific organizational needs. Unlike rage applying, which involves mass unsolicited applications driven by frustration, head-hunting ensures precise alignment between candidate expertise and job requirements, enhancing recruitment efficiency. Explore comprehensive strategies and tools that optimize head-hunting success in competitive talent markets.
Non-compete agreement
Talent poaching involves actively recruiting employees from competitors, often breaching non-compete agreements designed to prevent such moves. Rage applying occurs when candidates flood potential employers with applications, disregarding non-compete clauses and risking legal repercussions. Explore how non-compete agreements influence both talent acquisition strategies and candidate behavior.
Source and External Links
What Is Employee Poaching? (Definition and Strategies To Prevent It) - Employee poaching is a legal practice where a company targets employees of competitors to attract them by offering higher pay or benefits, commonly used to acquire highly skilled talent in competitive industries.
Headhunting vs Talent Poaching | A-Z of HR Terms - Talent poaching involves enticing skilled employees from other organizations, often using incentives like better salaries or career growth, and differs from headhunting by focusing on actively recruiting employed individuals, raising ethical concerns in some cases.
The ethics and etiquette of employee poaching - Employee poaching intensifies competition for top talent but can lead to legal and ethical issues related to non-compete clauses and employee retention, prompting companies to improve compensation and career planning to prevent losing staff.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com