Digital nomadism offers professionals location-independent employment, leveraging technology to work remotely from anywhere in the world, while the gig economy emphasizes short-term, flexible jobs often facilitated through online platforms. Both trends reflect shifting employment paradigms driven by digital transformation, prioritizing autonomy and diverse income streams over traditional, full-time roles. Explore how these evolving work models reshape the future of employment and workforce dynamics.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between digital nomadism and the gig economy is crucial for employment strategies because digital nomads prioritize location-independent, often long-term remote work, while gig economy workers engage in short-term, task-based jobs with flexible schedules. This distinction impacts job stability, income predictability, and access to employee benefits. Employers and employees can tailor contracts, work policies, and career development accordingly. Clear differentiation helps optimize workforce management in the evolving digital labor market.
Comparison Table
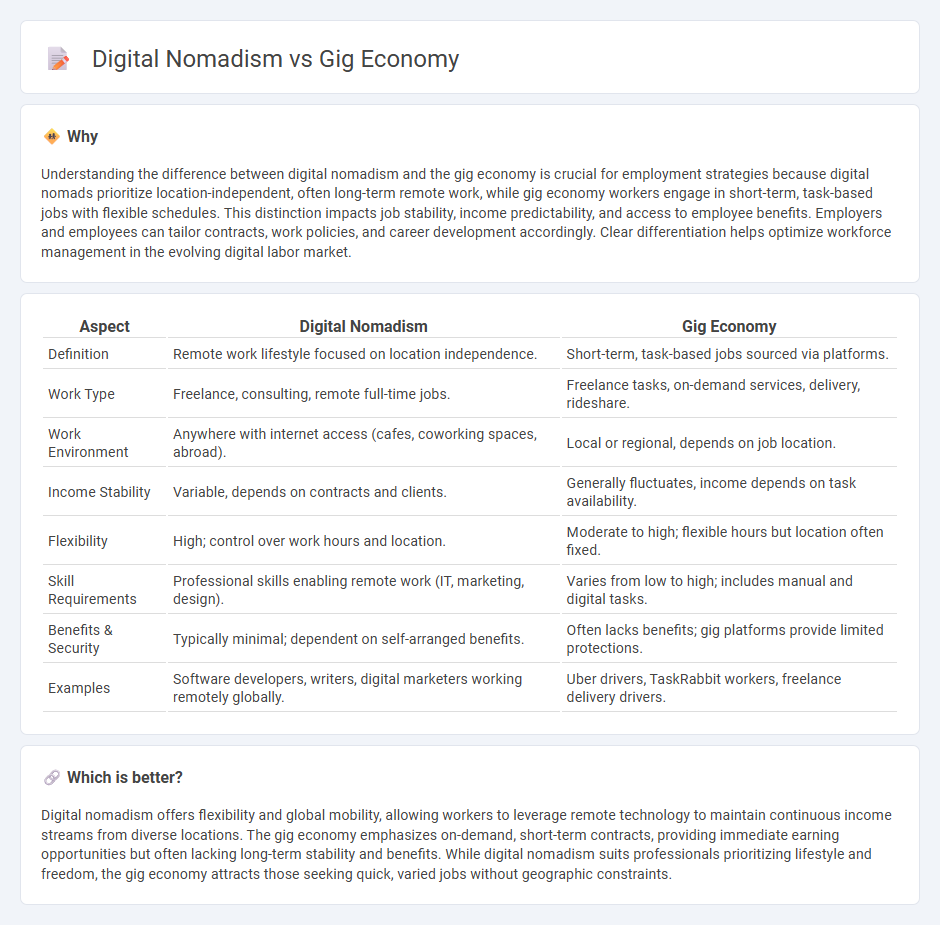
| Aspect | Digital Nomadism | Gig Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Remote work lifestyle focused on location independence. | Short-term, task-based jobs sourced via platforms. |
| Work Type | Freelance, consulting, remote full-time jobs. | Freelance tasks, on-demand services, delivery, rideshare. |
| Work Environment | Anywhere with internet access (cafes, coworking spaces, abroad). | Local or regional, depends on job location. |
| Income Stability | Variable, depends on contracts and clients. | Generally fluctuates, income depends on task availability. |
| Flexibility | High; control over work hours and location. | Moderate to high; flexible hours but location often fixed. |
| Skill Requirements | Professional skills enabling remote work (IT, marketing, design). | Varies from low to high; includes manual and digital tasks. |
| Benefits & Security | Typically minimal; dependent on self-arranged benefits. | Often lacks benefits; gig platforms provide limited protections. |
| Examples | Software developers, writers, digital marketers working remotely globally. | Uber drivers, TaskRabbit workers, freelance delivery drivers. |
Which is better?
Digital nomadism offers flexibility and global mobility, allowing workers to leverage remote technology to maintain continuous income streams from diverse locations. The gig economy emphasizes on-demand, short-term contracts, providing immediate earning opportunities but often lacking long-term stability and benefits. While digital nomadism suits professionals prioritizing lifestyle and freedom, the gig economy attracts those seeking quick, varied jobs without geographic constraints.
Connection
Digital nomadism and the gig economy are interconnected through flexible, location-independent work arrangements enabled by digital platforms. Both rely heavily on technology to connect workers with short-term projects or freelance opportunities, promoting autonomy and diverse income streams. This synergy supports a dynamic labor market that challenges traditional 9-to-5 employment models.
Key Terms
Freelancing
Freelancing lies at the intersection of the gig economy and digital nomadism, offering flexible work opportunities across various digital platforms like Upwork and Fiverr. While gig economy freelancers often engage in short-term tasks or projects, digital nomads leverage freelancing to sustain a location-independent lifestyle that blends travel and work. Explore how freelancing transforms work paradigms by visiting our detailed guide on maximizing the benefits of both models.
Remote work
Remote work has radically transformed modern employment by enabling gig economy workers to perform flexible, short-term tasks via digital platforms such as Uber, Upwork, and Fiverr. Digital nomadism, characterized by professionals leveraging remote work to travel while maintaining productivity, emphasizes location-independent careers often centered on tech, marketing, and creative services. Explore more to understand how remote work bridges gig economy dynamics and the freedom of digital nomad lifestyles.
Independent contractor
Independent contractors dominate the gig economy by offering flexible, project-based services across platforms like Uber, Fiverr, and Upwork, leveraging digital tools for client acquisition and task execution. Digital nomads, often independent contractors themselves, blend remote work with travel, utilizing co-working spaces and reliable internet to maintain productivity worldwide. Explore how independent contractors optimize their roles amidst these evolving work trends.
Source and External Links
Gig Economy - Overview, Advantages, Disadvantages - A gig economy operates flexibly, matching buyers and sellers of labor through digital platforms like Uber and Airbnb, allowing organizations to hire independent contractors for temporary, on-demand work.
The Pros and Cons of the Gig Economy - The gig economy enables individuals to work on short-term projects or "gigs" rather than full-time roles, driven by digital platforms that connect workers to diverse opportunities for flexible income streams.
What is the Gig Economy?| Definition from TechTarget - The gig economy is a free market system where temporary positions are common and organizations hire independent workers for short-term commitments, often facilitated by gig apps and remote work technologies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com