Rage applying, the impulsive submission of multiple job applications without tailored customization, often leads to low response rates and missed opportunities. In contrast, upskilling enhances relevant competencies and boosts employability by aligning skills with market demands. Explore effective strategies to transition from frustration to career growth through targeted skill development.
Why it is important
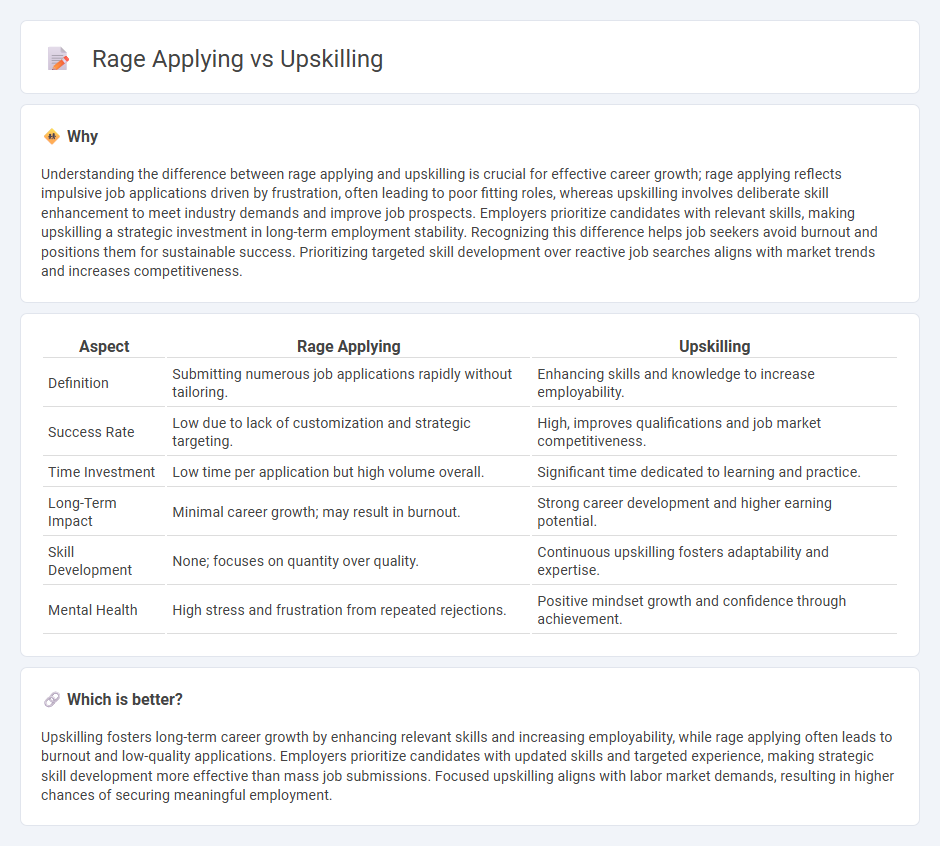
Understanding the difference between rage applying and upskilling is crucial for effective career growth; rage applying reflects impulsive job applications driven by frustration, often leading to poor fitting roles, whereas upskilling involves deliberate skill enhancement to meet industry demands and improve job prospects. Employers prioritize candidates with relevant skills, making upskilling a strategic investment in long-term employment stability. Recognizing this difference helps job seekers avoid burnout and positions them for sustainable success. Prioritizing targeted skill development over reactive job searches aligns with market trends and increases competitiveness.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Rage Applying | Upskilling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Submitting numerous job applications rapidly without tailoring. | Enhancing skills and knowledge to increase employability. |
| Success Rate | Low due to lack of customization and strategic targeting. | High, improves qualifications and job market competitiveness. |
| Time Investment | Low time per application but high volume overall. | Significant time dedicated to learning and practice. |
| Long-Term Impact | Minimal career growth; may result in burnout. | Strong career development and higher earning potential. |
| Skill Development | None; focuses on quantity over quality. | Continuous upskilling fosters adaptability and expertise. |
| Mental Health | High stress and frustration from repeated rejections. | Positive mindset growth and confidence through achievement. |
Which is better?
Upskilling fosters long-term career growth by enhancing relevant skills and increasing employability, while rage applying often leads to burnout and low-quality applications. Employers prioritize candidates with updated skills and targeted experience, making strategic skill development more effective than mass job submissions. Focused upskilling aligns with labor market demands, resulting in higher chances of securing meaningful employment.
Connection
Rage applying often stems from frustration in job searches, prompting individuals to rapidly submit numerous applications without targeted efforts. Upskilling enhances relevant competencies, making applications more strategic and increasing the likelihood of securing employment. Combining focused skill development with deliberate application processes mitigates the negative effects of rage applying and improves career outcomes.
Key Terms
Skill Development
Upskilling involves intentionally enhancing specific competencies through training and practice to improve job performance and career growth. Rage applying, in contrast, entails submitting numerous job applications hastily without targeted skill development, often leading to lower success rates. Explore how strategic skill development can transform your job search and career prospects.
Job Satisfaction
Upskilling enhances job satisfaction by equipping individuals with advanced skills that increase competence and career growth potential, leading to more fulfilling work experiences. Rage applying, characterized by impulsive job applications without strategic focus, often stems from job dissatisfaction and may result in poor job matches and ongoing frustration. Explore effective strategies to balance skill development with purposeful job searching for sustained career fulfillment.
Employee Retention
Upskilling enhances employee retention by equipping staff with new competencies that increase job satisfaction and career growth potential, reducing turnover rates. Rage applying, often triggered by job dissatisfaction or burnout, leads to impulsive job searches that can destabilize workplace dynamics and negatively impact team cohesion. Explore strategies to effectively incorporate upskilling and address rage applying for better employee retention outcomes.
Source and External Links
The Importance of Upskilling for Future Professional Growth - Upskilling is the process of learning new skills or enhancing existing ones to stay ahead in a rapidly changing workplace, supporting both personal growth and organizational agility.
Upskilling: What It Means and How It Can Help Your Career - Upskilling means intentionally building new or advanced skills relevant to your current role, often through courses, certifications, or mentorship, to advance your career and take on more challenging projects.
How to Upskill Employees: Best Practices, Methods - Organizations can upskill employees by identifying skill gaps, offering targeted training, and encouraging self-directed learning to ensure the workforce remains proficient and adaptable in a digital era.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com