Ghost jobs, positions advertised but never intended to be filled, distort the labor market by creating false demand and misleading job seekers. Talent hoarding occurs when companies retain more employees than necessary, restricting workforce mobility and stifling career growth opportunities. Explore the impact of these practices on employment dynamics and job market efficiency.
Why it is important
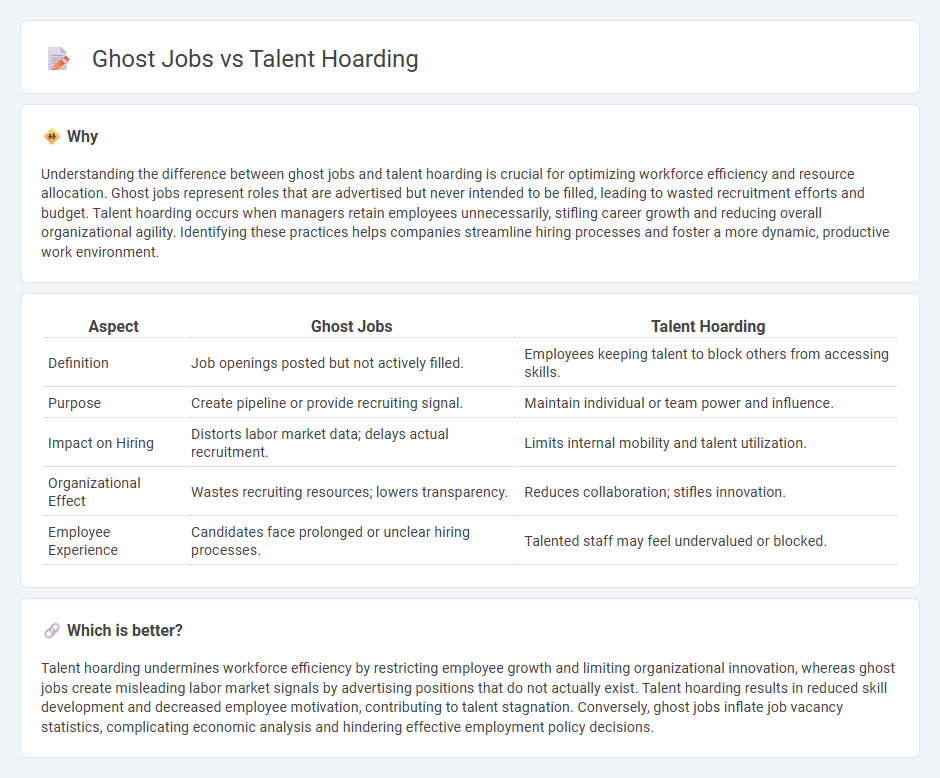
Understanding the difference between ghost jobs and talent hoarding is crucial for optimizing workforce efficiency and resource allocation. Ghost jobs represent roles that are advertised but never intended to be filled, leading to wasted recruitment efforts and budget. Talent hoarding occurs when managers retain employees unnecessarily, stifling career growth and reducing overall organizational agility. Identifying these practices helps companies streamline hiring processes and foster a more dynamic, productive work environment.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Jobs | Talent Hoarding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Job openings posted but not actively filled. | Employees keeping talent to block others from accessing skills. |
| Purpose | Create pipeline or provide recruiting signal. | Maintain individual or team power and influence. |
| Impact on Hiring | Distorts labor market data; delays actual recruitment. | Limits internal mobility and talent utilization. |
| Organizational Effect | Wastes recruiting resources; lowers transparency. | Reduces collaboration; stifles innovation. |
| Employee Experience | Candidates face prolonged or unclear hiring processes. | Talented staff may feel undervalued or blocked. |
Which is better?
Talent hoarding undermines workforce efficiency by restricting employee growth and limiting organizational innovation, whereas ghost jobs create misleading labor market signals by advertising positions that do not actually exist. Talent hoarding results in reduced skill development and decreased employee motivation, contributing to talent stagnation. Conversely, ghost jobs inflate job vacancy statistics, complicating economic analysis and hindering effective employment policy decisions.
Connection
Ghost jobs inflate labor market demand by listing positions that are never intended to be filled, creating misleading employment opportunities. Talent hoarding occurs when companies retain skilled employees longer than necessary, limiting internal mobility and reducing new job openings. Together, these practices distort job availability, hinder workforce fluidity, and challenge accurate labor market analysis.
Key Terms
Internal Mobility
Talent hoarding occurs when companies retain top performers in current roles, limiting opportunities for internal mobility and growth, while ghost jobs represent positions advertised internally or externally without real intent to fill them, often hindering genuine career advancement. Internal mobility thrives when organizations promote transparent job postings and actively encourage employee development, reducing talent stagnation and enhancing workforce agility. Explore strategies to optimize internal mobility and overcome challenges like talent hoarding and ghost jobs for improved organizational performance.
Job Vacancy Transparency
Talent hoarding occurs when companies keep job vacancies unadvertised or internal, limiting candidate access and market competition, while ghost jobs refer to positions listed without real intent to hire, often inflating organizational size or talent demand metrics. Transparent job vacancy practices improve labor market efficiency by providing accurate information, enhancing candidate experience, and promoting fair hiring processes. Explore how promoting job vacancy transparency transforms recruitment strategies and strengthens workforce development.
Talent Acquisition
Talent hoarding in talent acquisition occurs when companies retain more candidates than necessary, often to block competitors or appear talent-rich, which hinders market mobility and inflates recruitment costs. Ghost jobs refer to unadvertised or fictitious vacancies used to build passive candidate pools without genuine intent to hire, causing confusion and inefficiency in the hiring process. Explore more about balancing transparency and strategy in talent acquisition to optimize recruiting outcomes.
Source and External Links
Talent Hoarding in Organizations: Two Researched-Based Studies - This article shares scientific studies on how talent hoarding negatively impacts internal mobility within organizations by restricting employee promotions and transfers.
Talent Hoarding in Organizations - AWS - This empirical research shows that managers hoard talent to maintain team productivity, preventing workers from seeking promotions, which causes misallocation of talent and perpetuates gender inequality in pay and representation.
How to Manage the Problem of Talent Hoarding - Wowledge - Talent hoarding is described as managers restricting employees' movement and visibility within an organization to retain high performers, limiting workers' career growth and access to developmental opportunities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com