Algorithmic management employs data-driven algorithms to optimize workforce productivity by automating task assignments, performance monitoring, and decision-making processes, often enhancing efficiency and scalability. Democratic management, in contrast, prioritizes employee participation and collective decision-making, fostering workplace transparency, collaboration, and job satisfaction. Explore the impacts of these management styles on employee engagement and organizational performance to understand which approach suits your business model best.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between algorithmic management and democratic management is crucial for employment as it directly impacts worker autonomy, job satisfaction, and productivity. Algorithmic management relies on automated decision-making tools that optimize tasks and monitor performance efficiently but may reduce employee input. Democratic management fosters inclusive decision-making by encouraging employee participation, which can enhance engagement and trust. Recognizing these differences helps organizations balance efficiency with employee well-being and adapt management styles to diverse work environments.
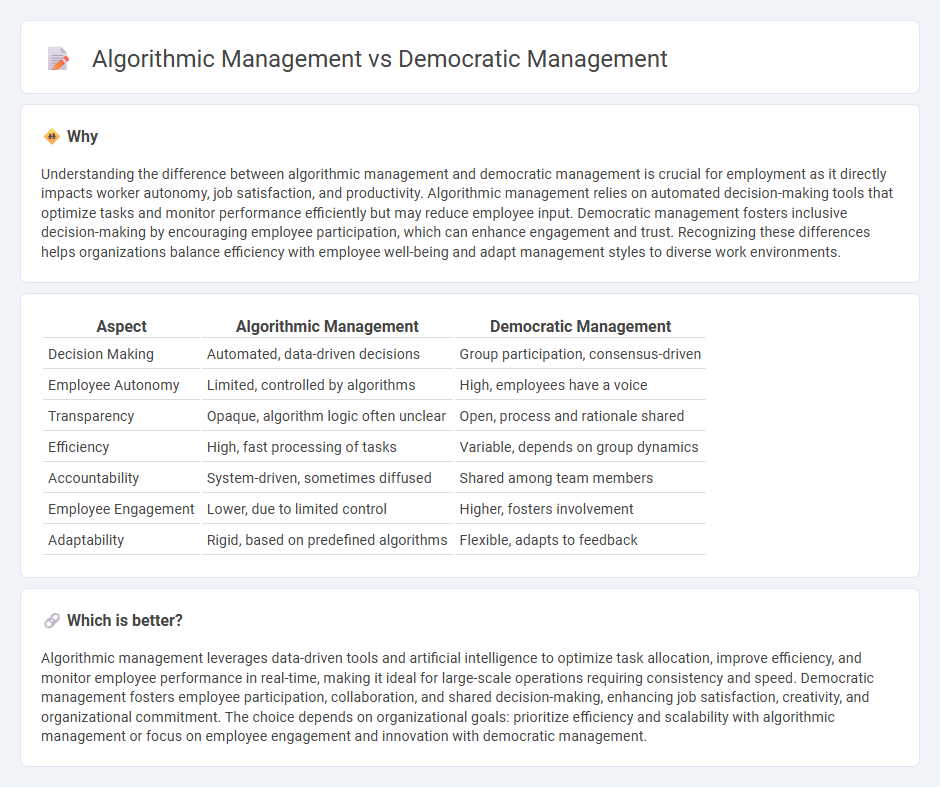
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Algorithmic Management | Democratic Management |
|---|---|---|
| Decision Making | Automated, data-driven decisions | Group participation, consensus-driven |
| Employee Autonomy | Limited, controlled by algorithms | High, employees have a voice |
| Transparency | Opaque, algorithm logic often unclear | Open, process and rationale shared |
| Efficiency | High, fast processing of tasks | Variable, depends on group dynamics |
| Accountability | System-driven, sometimes diffused | Shared among team members |
| Employee Engagement | Lower, due to limited control | Higher, fosters involvement |
| Adaptability | Rigid, based on predefined algorithms | Flexible, adapts to feedback |
Which is better?
Algorithmic management leverages data-driven tools and artificial intelligence to optimize task allocation, improve efficiency, and monitor employee performance in real-time, making it ideal for large-scale operations requiring consistency and speed. Democratic management fosters employee participation, collaboration, and shared decision-making, enhancing job satisfaction, creativity, and organizational commitment. The choice depends on organizational goals: prioritize efficiency and scalability with algorithmic management or focus on employee engagement and innovation with democratic management.
Connection
Algorithmic management leverages data-driven algorithms to optimize workforce productivity and monitor employee performance, while democratic management emphasizes participatory decision-making and employee empowerment. Integrating democratic principles within algorithmic management can enhance transparency, fairness, and worker autonomy, reducing resistance to automated oversight. This synergy fosters a balanced organizational environment where technology supports both efficiency and inclusive employee engagement.
Key Terms
Decision-making authority
Democratic management emphasizes shared decision-making authority, involving team members in defining goals and strategies to enhance collaboration and ownership. Algorithmic management centralizes decision-making power within automated systems using data-driven algorithms to optimize efficiency and monitor employee performance. Explore the distinct impacts of democratic versus algorithmic decision-making models on organizational culture and productivity.
Transparency
Democratic management prioritizes transparency by involving employees in decision-making processes, fostering trust and collaboration through open communication and shared responsibilities. Algorithmic management relies on data-driven algorithms to make decisions, often lacking transparency as workers may not fully understand how or why certain outcomes are determined by opaque systems. Explore the impact of transparency on workplace efficiency and employee satisfaction in democratic versus algorithmic management models to learn more.
Worker autonomy
Democratic management empowers workers with significant autonomy, encouraging participative decision-making and collaborative problem-solving, which enhances job satisfaction and innovation. Algorithmic management, in contrast, relies on data-driven systems to direct tasks and monitor performance, often limiting worker autonomy by automating control and reducing human discretion. Explore how these contrasting approaches impact workplace dynamics and employee empowerment.
Source and External Links
Democratic Management | Results for America - Democratic management is defined as a leadership style that balances meeting business needs with maintaining accountability and shared power among managers, boards, and employees in a democratic workplace, supported by tools like skills assessments for professional development.
Democratic Management: A Practical Guide for Managers and Others - This practical guide offers tools, activities, and frameworks for managers in democratic organizations, particularly worker cooperatives, to implement and sustain democratic workplace practices involving power, information, people, and money.
Democratic leadership in the workplace | Achievers - Democratic leadership is a collaborative style where team members actively participate in decision-making, fostering transparency, engagement, and trust, with leaders guiding but incorporating input, thus creating empowered and motivated teams.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com