No-collar work refers to roles that typically involve creative, tech-driven, or non-traditional job functions without standard office attire or strict hierarchical structures. Grey-collar workers bridge blue-collar and white-collar sectors, often performing technical, skilled trades or supervisory responsibilities that blend manual labor with administrative tasks. Explore the distinctions and evolving trends in no-collar and grey-collar employment to understand their impact on the modern workforce.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between no-collar work and grey-collar work helps employers tailor recruitment and training strategies effectively. No-collar work typically involves creative or technology-driven roles that prioritize innovation, whereas grey-collar jobs blend manual labor with technical skills, often bridging blue-collar and white-collar responsibilities. Recognizing these distinctions enhances workforce planning and addresses specific skill gaps in evolving industries. This knowledge supports optimized human resource allocation and improved employee engagement in diverse economic sectors.
Comparison Table
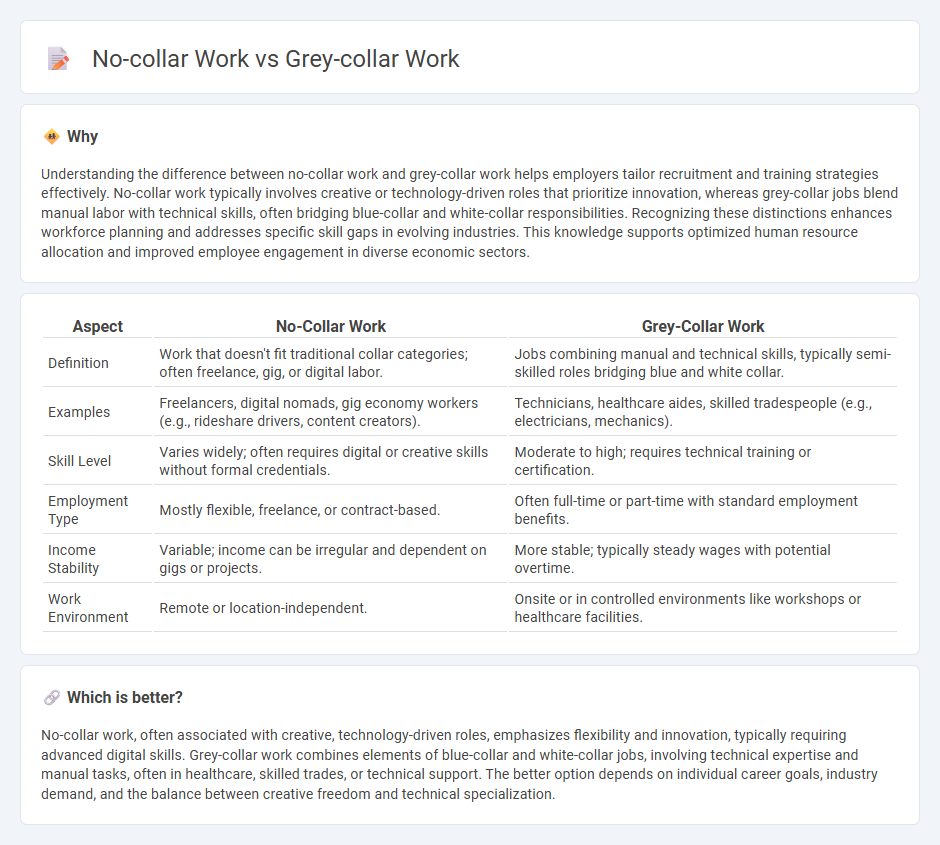
| Aspect | No-Collar Work | Grey-Collar Work |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Work that doesn't fit traditional collar categories; often freelance, gig, or digital labor. | Jobs combining manual and technical skills, typically semi-skilled roles bridging blue and white collar. |
| Examples | Freelancers, digital nomads, gig economy workers (e.g., rideshare drivers, content creators). | Technicians, healthcare aides, skilled tradespeople (e.g., electricians, mechanics). |
| Skill Level | Varies widely; often requires digital or creative skills without formal credentials. | Moderate to high; requires technical training or certification. |
| Employment Type | Mostly flexible, freelance, or contract-based. | Often full-time or part-time with standard employment benefits. |
| Income Stability | Variable; income can be irregular and dependent on gigs or projects. | More stable; typically steady wages with potential overtime. |
| Work Environment | Remote or location-independent. | Onsite or in controlled environments like workshops or healthcare facilities. |
Which is better?
No-collar work, often associated with creative, technology-driven roles, emphasizes flexibility and innovation, typically requiring advanced digital skills. Grey-collar work combines elements of blue-collar and white-collar jobs, involving technical expertise and manual tasks, often in healthcare, skilled trades, or technical support. The better option depends on individual career goals, industry demand, and the balance between creative freedom and technical specialization.
Connection
No-collar work, characterized by creative roles in emerging industries like technology and entertainment, intersects with grey-collar jobs that combine manual labor and skilled expertise often found in healthcare and technical fields. Both categories emphasize adaptability and interdisciplinary skills, bridging traditional blue- and white-collar distinctions. This connection reflects evolving labor market demands where innovation and specialized knowledge drive employment trends.
Key Terms
Skilled labor
Grey-collar work involves skilled labor that blends manual and technical tasks, typically in trades such as electricians, technicians, and maintenance workers. No-collar work, often associated with creative or tech industries, emphasizes knowledge and innovation without a strict hierarchical or uniform structure. Explore the distinctions and career opportunities within grey-collar and no-collar skilled labor roles to enhance your understanding of modern workforce trends.
Knowledge work
Grey-collar work typically involves roles that require specialized technical skills combined with manual tasks, such as healthcare technicians or IT support specialists, bridging blue-collar and white-collar categories. No-collar work, often linked to creative industries and knowledge work, emphasizes innovation, intellectual engagement, and flexibility without strict adherence to traditional job classifications, seen in freelancers or tech entrepreneurs. Explore deeper insights into how knowledge work shapes evolving employment landscapes and impacts grey-collar and no-collar distinctions.
Automation
Grey-collar work involves jobs that blend manual labor with technical skills, often impacted by automation through the integration of robotics and AI to enhance productivity. No-collar work typically refers to creative or knowledge-based roles less susceptible to automation but increasingly reliant on digital tools and AI for innovation and efficiency. Explore the evolving landscape of grey-collar and no-collar jobs shaped by automation to understand future workforce trends.
Source and External Links
Grey-collar - Wikipedia - Grey-collar refers to jobs that blend blue-collar and white-collar elements, involving both physical and intellectual labor, requiring a mix of training, licensure, and education that does not fit strictly into either category.
Grey Collar Jobs - TCWGlobal - Grey-collar jobs combine manual labor with technical skills, often requiring specialized training, and include roles like healthcare technicians, IT support, electricians, and plumbers.
Gray-collar jobs will rise in the US between 2022 and 2032 - Gray-collar jobs, falling between blue- and white-collar roles, are increasing in the US, driven especially by sectors like technology and healthcare that require both physical labor and professional knowledge.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com