Labor hoarding involves retaining more employees than necessary during economic downturns to preserve organizational knowledge and reduce future hiring costs. Job rotation systematically moves employees between different roles to enhance skills, increase job satisfaction, and improve workplace flexibility. Explore these employment strategies further to understand their impact on workforce management and business resilience.
Why it is important
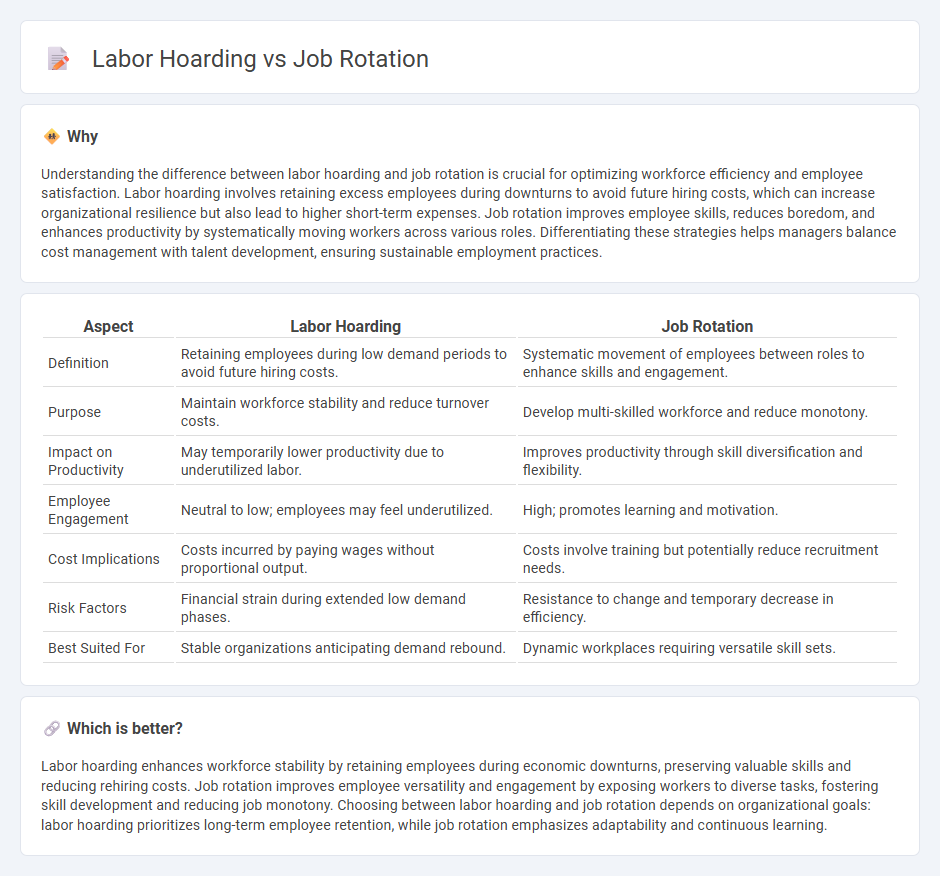
Understanding the difference between labor hoarding and job rotation is crucial for optimizing workforce efficiency and employee satisfaction. Labor hoarding involves retaining excess employees during downturns to avoid future hiring costs, which can increase organizational resilience but also lead to higher short-term expenses. Job rotation improves employee skills, reduces boredom, and enhances productivity by systematically moving workers across various roles. Differentiating these strategies helps managers balance cost management with talent development, ensuring sustainable employment practices.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Labor Hoarding | Job Rotation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Retaining employees during low demand periods to avoid future hiring costs. | Systematic movement of employees between roles to enhance skills and engagement. |
| Purpose | Maintain workforce stability and reduce turnover costs. | Develop multi-skilled workforce and reduce monotony. |
| Impact on Productivity | May temporarily lower productivity due to underutilized labor. | Improves productivity through skill diversification and flexibility. |
| Employee Engagement | Neutral to low; employees may feel underutilized. | High; promotes learning and motivation. |
| Cost Implications | Costs incurred by paying wages without proportional output. | Costs involve training but potentially reduce recruitment needs. |
| Risk Factors | Financial strain during extended low demand phases. | Resistance to change and temporary decrease in efficiency. |
| Best Suited For | Stable organizations anticipating demand rebound. | Dynamic workplaces requiring versatile skill sets. |
Which is better?
Labor hoarding enhances workforce stability by retaining employees during economic downturns, preserving valuable skills and reducing rehiring costs. Job rotation improves employee versatility and engagement by exposing workers to diverse tasks, fostering skill development and reducing job monotony. Choosing between labor hoarding and job rotation depends on organizational goals: labor hoarding prioritizes long-term employee retention, while job rotation emphasizes adaptability and continuous learning.
Connection
Labor hoarding occurs when firms retain more employees than needed during economic downturns to avoid future hiring costs, promoting job security. Job rotation complements this by reallocating employees across various roles, enhancing skills and maintaining engagement while minimizing layoffs. Together, these strategies optimize workforce flexibility and sustain organizational knowledge, reducing turnover and increasing productivity.
Key Terms
Skill diversification
Job rotation promotes skill diversification by systematically moving employees across different roles, enhancing their adaptability and expertise in multiple job functions. Labor hoarding, on the other hand, prioritizes retaining employees during downturns, which may limit opportunities for skill expansion due to repetitive tasks. Explore how companies balance job rotation and labor hoarding to maximize workforce versatility and resilience.
Workforce flexibility
Job rotation enhances workforce flexibility by exposing employees to various roles, increasing skill diversity and adaptability within the organization. Labor hoarding, however, maintains excess staff to buffer against demand fluctuations, potentially limiting agile redeployment but preserving institutional knowledge. Explore how balancing these strategies can optimize workforce resilience and operational efficiency.
Employee retention
Job rotation enhances employee retention by offering skill diversification and increased job satisfaction, reducing monotony and burnout. Labor hoarding preserves workforce stability during economic downturns but may limit opportunities for employee growth and motivation. Explore how balancing these strategies can optimize talent retention in your organization.
Source and External Links
Job rotation - Wikipedia - Job rotation is the lateral transfer of employees between jobs in an organization without a change in their rank or salary, used for motivation, skill development, and career growth, differing from promotion and specialization principles.
Job rotation | EBSCO Research Starters - Job rotation is an HR strategy that moves employees through different tasks or departments to develop skills, reduce monotony, improve motivation, and boost workforce flexibility benefiting both employees and employers.
Job Rotation: A Full Guide with 5 Examples - AIHR - Job rotation involves temporarily moving employees between roles, exemplified by programs like The Slumber Yard's quarterly rotations and Heineken's Technologist traineeship, aiming to reduce turnover and build a multiskilled workforce.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com