Career cushioning focuses on proactively developing skills and networking to stay adaptable in changing job markets, while job security emphasizes maintaining long-term stability within a single position or company. Embracing career cushioning increases resilience against layoffs and technological disruption, enhancing overall employability. Explore the differences between career cushioning and job security to optimize your employment strategy.
Why it is important
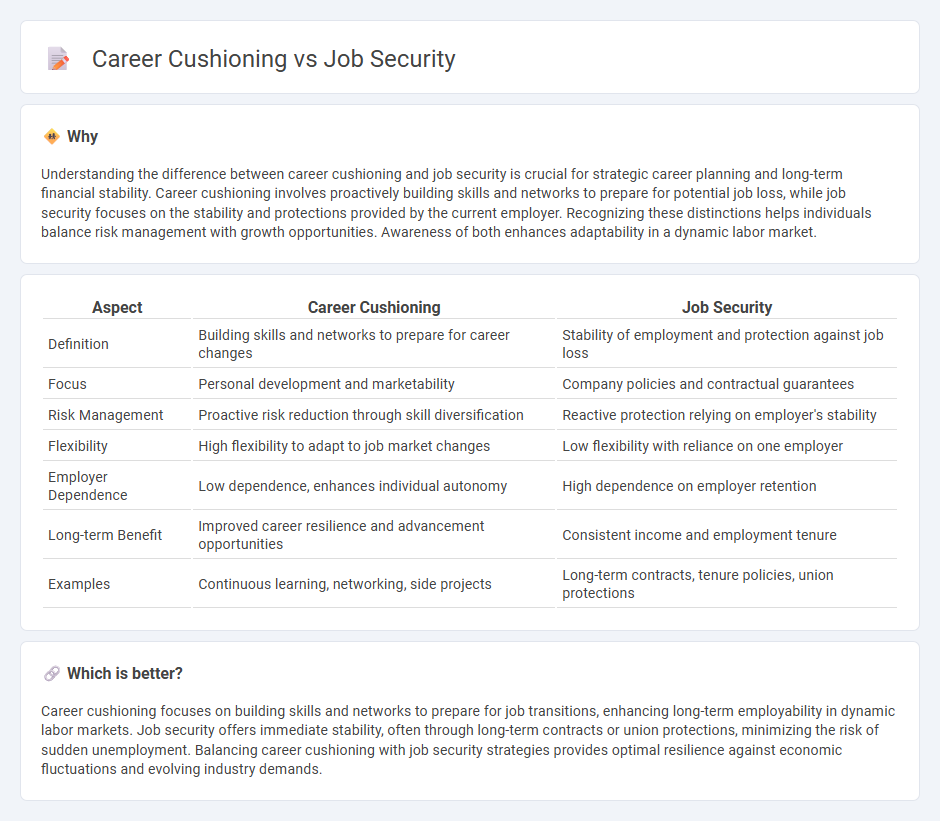
Understanding the difference between career cushioning and job security is crucial for strategic career planning and long-term financial stability. Career cushioning involves proactively building skills and networks to prepare for potential job loss, while job security focuses on the stability and protections provided by the current employer. Recognizing these distinctions helps individuals balance risk management with growth opportunities. Awareness of both enhances adaptability in a dynamic labor market.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Career Cushioning | Job Security |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Building skills and networks to prepare for career changes | Stability of employment and protection against job loss |
| Focus | Personal development and marketability | Company policies and contractual guarantees |
| Risk Management | Proactive risk reduction through skill diversification | Reactive protection relying on employer's stability |
| Flexibility | High flexibility to adapt to job market changes | Low flexibility with reliance on one employer |
| Employer Dependence | Low dependence, enhances individual autonomy | High dependence on employer retention |
| Long-term Benefit | Improved career resilience and advancement opportunities | Consistent income and employment tenure |
| Examples | Continuous learning, networking, side projects | Long-term contracts, tenure policies, union protections |
Which is better?
Career cushioning focuses on building skills and networks to prepare for job transitions, enhancing long-term employability in dynamic labor markets. Job security offers immediate stability, often through long-term contracts or union protections, minimizing the risk of sudden unemployment. Balancing career cushioning with job security strategies provides optimal resilience against economic fluctuations and evolving industry demands.
Connection
Career cushioning involves building skills and professional networks to mitigate job loss risks, directly enhancing job security by preparing individuals for unforeseen employment changes. By proactively expanding expertise and maintaining multiple income streams or opportunities, workers reduce dependence on a single employer, strengthening their position in the labor market. This strategy is essential in volatile industries, where job security is increasingly linked to adaptability and continuous personal development.
Key Terms
Stability
Job security offers employees a sense of stability through long-term employment guarantees, often linked to established companies or union contracts. Career cushioning involves proactively developing skills and networks to reduce risks of sudden job loss and enhance future employment opportunities. Explore strategies to balance stability with adaptability for sustained career success.
Adaptability
Prioritizing adaptability enhances job security by enabling employees to navigate evolving industry demands and technological advancements effectively. Emphasizing continuous learning and skill diversification supports career cushioning, providing a safety net through flexible career options. Explore strategies to boost adaptability and safeguard your professional future.
Risk Management
Job security offers stability through long-term employment contracts and benefits, but it may limit flexibility in adapting to market changes. Career cushioning involves proactive skill development, networking, and side projects to mitigate risks associated with job loss or industry shifts. Explore strategies to balance job security with career cushioning for effective risk management.
Source and External Links
Job security - Wikipedia - Job security is the probability that an individual will keep their job and can be affected by factors like globalization, outsourcing, downsizing, recession, and technology; governments and unions influence job security through laws and collective bargaining, while individuals can increase it by improving skills and adaptability.
What is Job Security? - Growthspace - Job security includes actual job security, such as tenure or vital company roles, and psychological job security, with protections sometimes ensured by government regulations and unions that prevent layoffs.
The Importance of Job Security in the Workplace (With Tips) - Indeed - Job security matters for both employers and employees by attracting and retaining talent, maintaining productivity, encouraging loyalty, and fostering positive employee morale.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com