Digital nomad visas enable remote professionals to legally work from foreign countries without traditional employment contracts, offering flexibility and access to new markets. Student work visas grant international students permission to engage in part-time or full-time employment while pursuing their studies, helping to offset living costs and gain local job experience. Explore the distinct benefits and requirements of both visa types to determine which aligns best with your career and lifestyle goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between digital nomad visas and student work visas is crucial for ensuring legal employment status and compliance with immigration laws. Digital nomad visas typically allow remote work for foreign employers without local labor market integration, while student work visas permit limited on-campus or part-time employment tied to educational programs. Misusing either visa can lead to visa revocation, legal penalties, or deportation, affecting long-term residency opportunities. Clarity on eligibility, work rights, and duration ensures smooth employment experiences and proper tax obligations.
Comparison Table
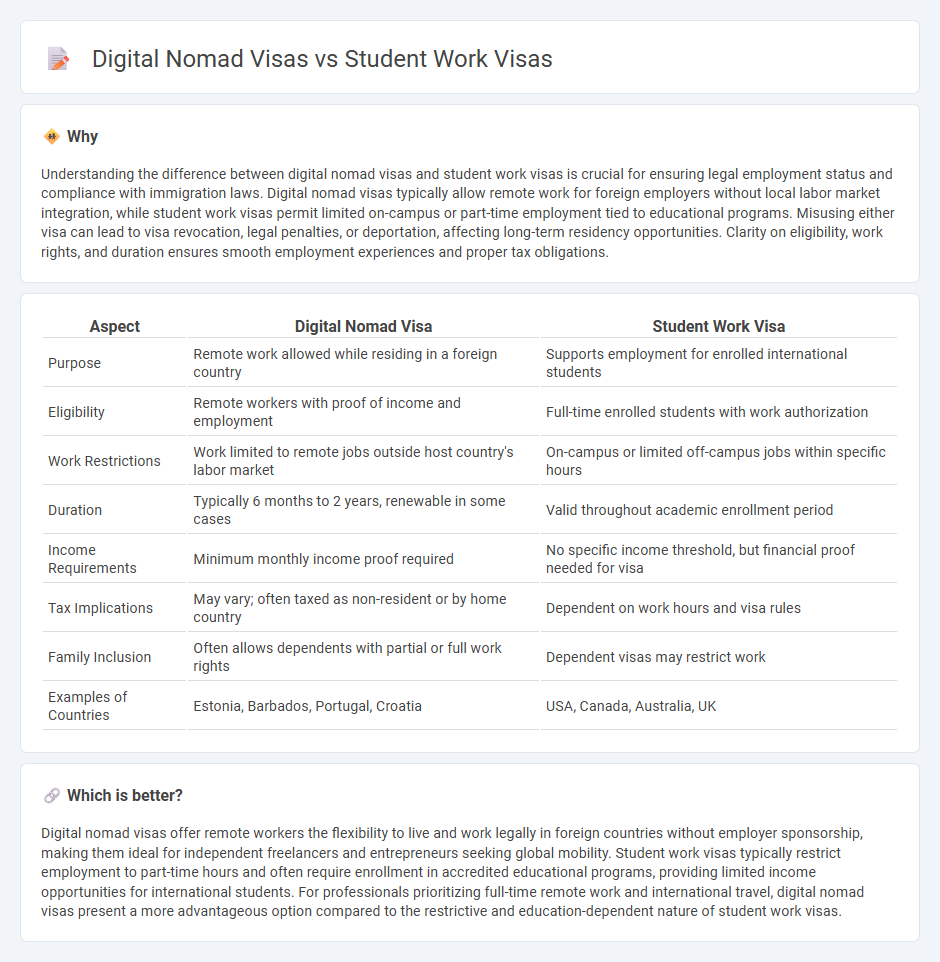
| Aspect | Digital Nomad Visa | Student Work Visa |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Remote work allowed while residing in a foreign country | Supports employment for enrolled international students |
| Eligibility | Remote workers with proof of income and employment | Full-time enrolled students with work authorization |
| Work Restrictions | Work limited to remote jobs outside host country's labor market | On-campus or limited off-campus jobs within specific hours |
| Duration | Typically 6 months to 2 years, renewable in some cases | Valid throughout academic enrollment period |
| Income Requirements | Minimum monthly income proof required | No specific income threshold, but financial proof needed for visa |
| Tax Implications | May vary; often taxed as non-resident or by home country | Dependent on work hours and visa rules |
| Family Inclusion | Often allows dependents with partial or full work rights | Dependent visas may restrict work |
| Examples of Countries | Estonia, Barbados, Portugal, Croatia | USA, Canada, Australia, UK |
Which is better?
Digital nomad visas offer remote workers the flexibility to live and work legally in foreign countries without employer sponsorship, making them ideal for independent freelancers and entrepreneurs seeking global mobility. Student work visas typically restrict employment to part-time hours and often require enrollment in accredited educational programs, providing limited income opportunities for international students. For professionals prioritizing full-time remote work and international travel, digital nomad visas present a more advantageous option compared to the restrictive and education-dependent nature of student work visas.
Connection
Digital nomad visas and student work visas both facilitate international employment by allowing individuals to legally work while residing temporarily in a foreign country. These visas support the global workforce mobility trend, enabling remote workers and students to earn income without traditional local work permits. Employers benefit from this increased talent pool, while workers gain opportunities to combine travel, education, and professional development.
Key Terms
Sponsorship
Student work visas typically require sponsorship from an educational institution, which acts as the primary sponsor throughout the duration of the studies and any authorized employment. Digital nomad visas, on the other hand, rarely involve sponsorship; instead, applicants generally demonstrate proof of remote employment or financial stability without needing a local sponsor. Explore the specific sponsorship requirements for each visa type to find the best option for your work and travel plans.
Remote work eligibility
Student work visas typically restrict employment to on-campus jobs or specific part-time roles related to the field of study, limiting remote work options. Digital nomad visas explicitly cater to remote workers, allowing individuals to live and work legally in a foreign country while performing jobs online. Explore the key differences in eligibility and benefits to determine the best visa for your remote work lifestyle.
Residency requirements
Student work visas typically mandate enrollment in an accredited educational institution and may require proof of full-time student status to maintain residency. Digital nomad visas often demand proof of remote employment or freelance work with an income threshold, allowing residency without traditional work or study commitments. Explore more details to determine which visa suits your residency needs best.
Source and External Links
Students and Employment - USCIS - International students on F-1 visas may work on-campus during their first academic year and can engage in off-campus employment such as Curricular Practical Training (CPT), Optional Practical Training (OPT), and STEM OPT extensions after the first year, while M-1 visa holders can work only after completing their studies, with all off-campus employment requiring prior authorization from the school official and USCIS.
Working in the United States - Study in the States - Homeland Security - F-1 students can apply for on-campus employment up to 30 days before classes start, limited to 20 hours per week during school sessions, and may request off-campus employment only after completing a full academic year due to economic hardship, requiring USCIS approval and an Employment Authorization Document (EAD).
Student Visa - Travel - To study in the U.S., international students need either an F visa (for academic programs) or an M visa (for vocational or recognized nonacademic programs); they cannot study on visitor (B) visas, and their visa type depends on the educational institution and program attended.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com