Talent arbitrage leverages global skill disparities to optimize workforce costs by strategically sourcing professionals from regions with competitive salaries and high expertise. Labor brokering involves outsourcing recruitment and staffing processes to third-party agencies that manage temporary or contract workers on behalf of companies. Explore how these distinct employment strategies impact talent acquisition and organizational efficiency.
Why it is important
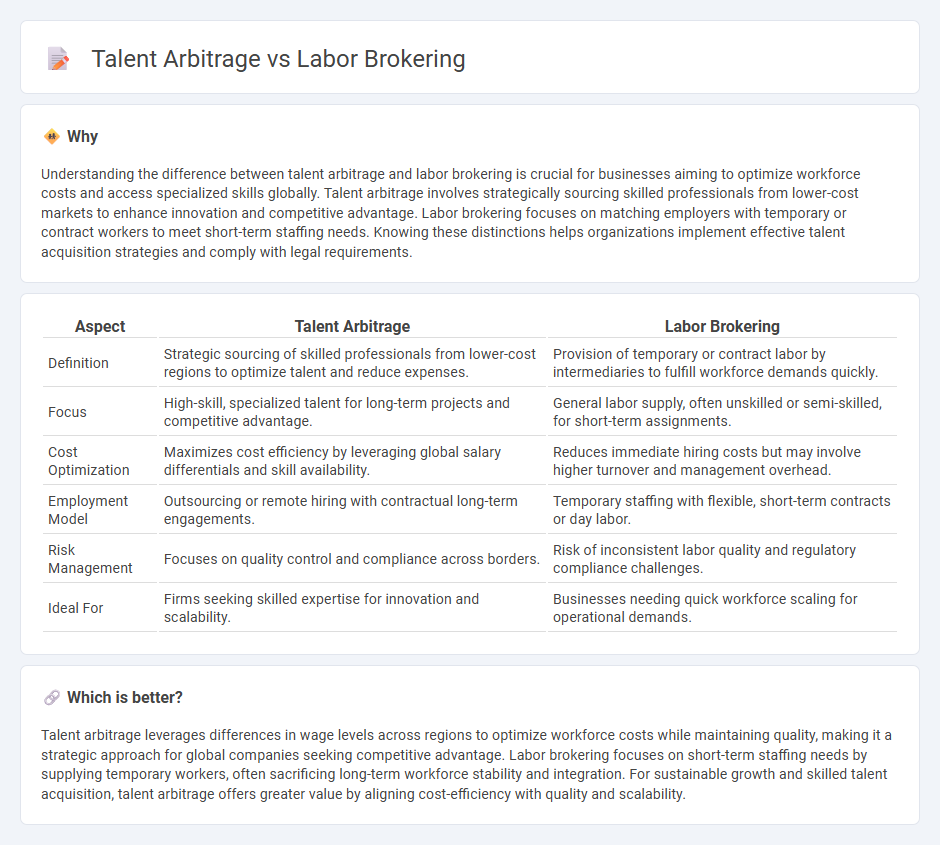
Understanding the difference between talent arbitrage and labor brokering is crucial for businesses aiming to optimize workforce costs and access specialized skills globally. Talent arbitrage involves strategically sourcing skilled professionals from lower-cost markets to enhance innovation and competitive advantage. Labor brokering focuses on matching employers with temporary or contract workers to meet short-term staffing needs. Knowing these distinctions helps organizations implement effective talent acquisition strategies and comply with legal requirements.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Talent Arbitrage | Labor Brokering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategic sourcing of skilled professionals from lower-cost regions to optimize talent and reduce expenses. | Provision of temporary or contract labor by intermediaries to fulfill workforce demands quickly. |
| Focus | High-skill, specialized talent for long-term projects and competitive advantage. | General labor supply, often unskilled or semi-skilled, for short-term assignments. |
| Cost Optimization | Maximizes cost efficiency by leveraging global salary differentials and skill availability. | Reduces immediate hiring costs but may involve higher turnover and management overhead. |
| Employment Model | Outsourcing or remote hiring with contractual long-term engagements. | Temporary staffing with flexible, short-term contracts or day labor. |
| Risk Management | Focuses on quality control and compliance across borders. | Risk of inconsistent labor quality and regulatory compliance challenges. |
| Ideal For | Firms seeking skilled expertise for innovation and scalability. | Businesses needing quick workforce scaling for operational demands. |
Which is better?
Talent arbitrage leverages differences in wage levels across regions to optimize workforce costs while maintaining quality, making it a strategic approach for global companies seeking competitive advantage. Labor brokering focuses on short-term staffing needs by supplying temporary workers, often sacrificing long-term workforce stability and integration. For sustainable growth and skilled talent acquisition, talent arbitrage offers greater value by aligning cost-efficiency with quality and scalability.
Connection
Talent arbitrage involves sourcing skilled labor from regions with lower wage expectations to reduce employment costs, while labor brokering acts as the intermediary facilitating this process by matching employers with these outsourced workers. Both practices optimize workforce allocation by leveraging geographic wage disparities, ultimately enhancing operational efficiencies for multinational companies. The integration of talent arbitrage and labor brokering drives cost-effective talent acquisition strategies across global employment markets.
Key Terms
Third-party Mediation
Labor brokering involves third-party mediation by connecting employers with temporary or contract workers, facilitating workforce flexibility without direct hiring. Talent arbitrage exploits global wage differences by sourcing skilled professionals from lower-cost regions through intermediaries, optimizing cost-efficiency for businesses. Explore the practical benefits and challenges of third-party mediation in labor brokering and talent arbitrage for a deeper understanding.
Workforce Flexibility
Labor brokering involves outsourcing temporary staffing needs to third-party agencies, providing businesses with on-demand workforce flexibility to manage fluctuating labor demands efficiently. Talent arbitrage leverages geographic and economic disparities by sourcing skilled labor from lower-cost regions, optimizing cost-effectiveness while maintaining access to specialized expertise. Explore how these strategies can enhance your workforce flexibility and operational agility by learning more about their applications.
Cost Optimization
Labor brokering involves hiring temporary or contract workers through intermediaries to reduce immediate staffing costs, while talent arbitrage leverages differences in global wage rates by outsourcing skilled labor to lower-cost regions to optimize long-term expenses. Cost optimization in labor brokering centers on flexibility and minimizing overhead associated with full-time employees, whereas talent arbitrage emphasizes strategic sourcing of specialized talent at competitive global rates. Discover more about how these strategies can transform your workforce cost efficiency.
Source and External Links
8 Concerns with Labor Brokers - Labor brokering involves hiring laborers and assigning them to employers, creating a three-way employment relationship that can lead to various risks and challenges.
Understanding the Role of Labor Brokers in Human Trafficking - This document explores how labor brokers can increase the risk of debt bondage and forced labor through deceptive recruitment practices and excessive fees.
Is Your Subcontractor Actually a 'Labor Broker'? - The article discusses how a subcontractor might be considered a labor broker if they primarily supply workers rather than providing services or goods directly.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com