Grey market imports refer to the legal purchase and resale of genuine goods through unauthorized channels, often bypassing official distribution networks to offer lower prices. Smuggling involves the illegal import or export of goods without paying taxes or following regulatory protocols, posing significant risks to national economies and law enforcement. Explore the differences and impacts of these practices on the economy for a deeper understanding.
Why it is important
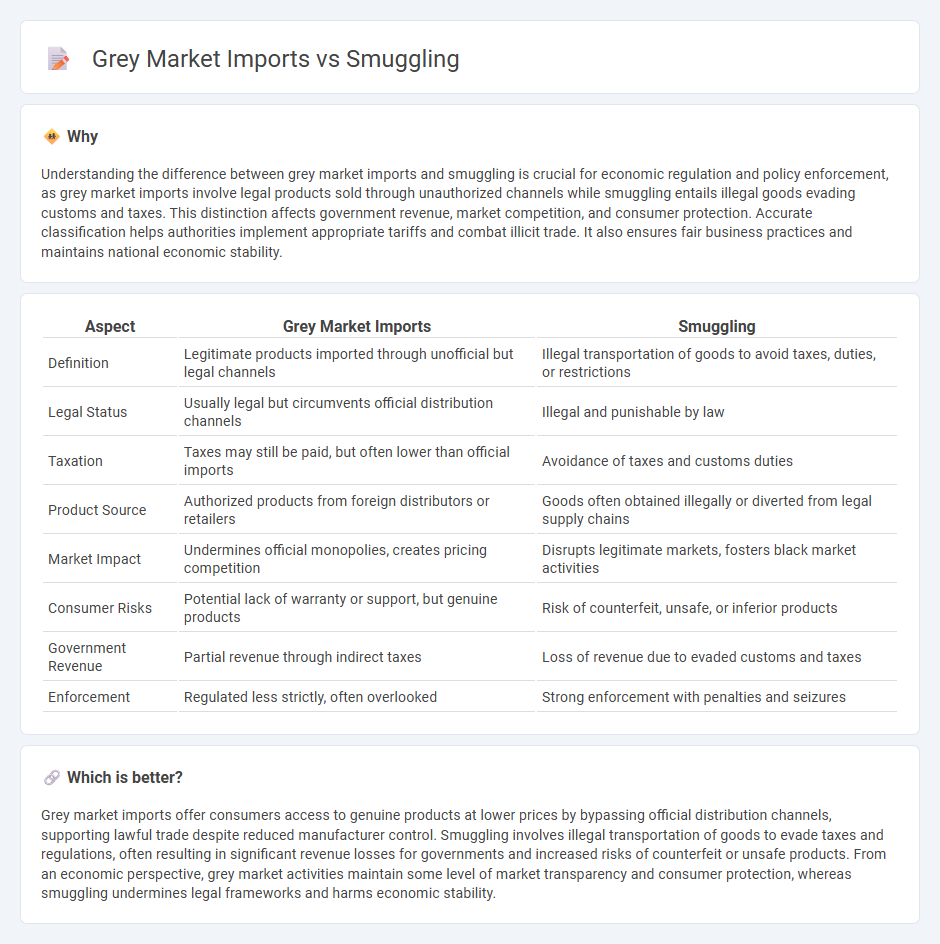
Understanding the difference between grey market imports and smuggling is crucial for economic regulation and policy enforcement, as grey market imports involve legal products sold through unauthorized channels while smuggling entails illegal goods evading customs and taxes. This distinction affects government revenue, market competition, and consumer protection. Accurate classification helps authorities implement appropriate tariffs and combat illicit trade. It also ensures fair business practices and maintains national economic stability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Grey Market Imports | Smuggling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legitimate products imported through unofficial but legal channels | Illegal transportation of goods to avoid taxes, duties, or restrictions |
| Legal Status | Usually legal but circumvents official distribution channels | Illegal and punishable by law |
| Taxation | Taxes may still be paid, but often lower than official imports | Avoidance of taxes and customs duties |
| Product Source | Authorized products from foreign distributors or retailers | Goods often obtained illegally or diverted from legal supply chains |
| Market Impact | Undermines official monopolies, creates pricing competition | Disrupts legitimate markets, fosters black market activities |
| Consumer Risks | Potential lack of warranty or support, but genuine products | Risk of counterfeit, unsafe, or inferior products |
| Government Revenue | Partial revenue through indirect taxes | Loss of revenue due to evaded customs and taxes |
| Enforcement | Regulated less strictly, often overlooked | Strong enforcement with penalties and seizures |
Which is better?
Grey market imports offer consumers access to genuine products at lower prices by bypassing official distribution channels, supporting lawful trade despite reduced manufacturer control. Smuggling involves illegal transportation of goods to evade taxes and regulations, often resulting in significant revenue losses for governments and increased risks of counterfeit or unsafe products. From an economic perspective, grey market activities maintain some level of market transparency and consumer protection, whereas smuggling undermines legal frameworks and harms economic stability.
Connection
Grey market imports and smuggling are interconnected through their common involvement in circumventing official trade regulations and customs duties. Both practices undermine government revenue by introducing goods into the market without proper authorization or tax payment, often flooding local markets with cheaper alternatives. This illicit trade distorts legitimate economic activities, affects pricing, and challenges regulatory enforcement.
Key Terms
Legality
Smuggling involves the illegal importation of goods that bypass customs regulations, taxes, and controls, making it a criminal offense under international and national laws. Grey market imports, while often unauthorized or unofficial, do not always violate laws but operate outside the manufacturer's authorized distribution channels, creating legal ambiguities. Explore the detailed distinctions and legal implications of smuggling versus grey market imports to understand their impact on commerce and law enforcement.
Tariffs
Smuggling involves illegal importation of goods evading all tariff payments and customs regulations, resulting in substantial revenue loss for governments and unfair competition for legitimate businesses. Grey market imports, while legal in terms of not violating intellectual property rights, bypass authorized distribution channels and often exploit tariff differentials to offer lower prices without paying appropriate customs duties. Explore more about the economic impact and policy measures addressing smuggling and grey market imports related to tariffs.
Supply chain
Smuggling bypasses legal supply chains entirely, causing disruptions by introducing untaxed and possibly unsafe goods, while grey market imports operate through unauthorized but legal channels, often exploiting supply chain loopholes to redistribute products without manufacturer approval. The impact on supply chains includes revenue loss, inventory mismanagement, and potential damage to brand integrity due to inconsistent product standards. Explore further to understand effective strategies for mitigating risks in both smuggling and grey market supply chain challenges.
Source and External Links
HUMAN TRAFFICKING & MIGRANT SMUGGLING - This document discusses migrant smuggling, which involves voluntarily entering into an agreement with a smuggler for illegal entry into a foreign country.
5 facts you need to know about migrant smuggling - Migrant smuggling is a lucrative crime driven by demand for crossing borders irregularly and affects many countries worldwide.
Smuggling - Smuggling refers to the illegal transportation of objects or people across international borders, violating applicable laws or regulations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com